Beijing Jiaotong University, previously Northern Jiaotong University, is a public university in Beijing, China. It is affiliated with the Ministry of Education, and co-sponsored by the Ministry of Education, the Ministry of Transport, the Beijing Municipal People's Government, and China State Railway Group Company Limited. The university is part of the Double First-Class Construction and Project 211.
The German Research Foundation is a German research funding organization, which functions as a self-governing institution for the promotion of science and research in the Federal Republic of Germany. In 2019, the DFG had a funding budget of €3.3 billion.

The University of Bremen is a public university in Bremen, Germany, with approximately 23,500 people from 115 countries. It is one of 11 institutions which were successful in the category "Institutional Strategies" of the Excellence Initiative launched by the Federal Government and the Federal States in 2012. The university was also successful in the categories "Graduate Schools" and "Clusters of Excellence" of the initiative.

Qinghai University is a provincial public university in Xining, Qinghai, China. It is affiliated with the Province of Qinghai, and co-sponsored by the Qinghai Provincial People's Government and the Ministry of Education of China. The university is part of Project 211 and the Double First-Class Construction.

The University of Konstanz is a university in the city of Konstanz in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Its main campus was opened on the Gießberg in 1972 after being founded in 1966. The university is Germany's southernmost university and is situated on the shore of Lake Constance just four kilometres from the Swiss border. It has been successful in all three funding lines of the Excellence Initiative, and is therefore one of Germany's elite "Universities of Excellence", a group of prestigious universities often considered the German Ivy League. The university is ranked in top 100 worldwide in the field of social policy and administration in the 2020 QS World University Rankings, and ranked 51 in Political Science according to the 2020 ShanghaiRanking. The U.S. Department of Energy also refers to the University of Konstanz as a "small Harvard".

Ulm University is a public university in Ulm, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The University was founded in 1967 and focuses on natural sciences, medicine, engineering sciences, mathematics, economics and computer science. With 9,891 students, it is one of the youngest public universities in Germany. The campus of the university is located north of the city on a hill called Oberer Eselsberg, while the university hospital has additional sites across the city.

The Ministry of Science and Technology is the executive department of the Central Science and Technology Commission, which coordinates science and technology activities in the country. The office is located in Xicheng District, Beijing.

People's Republic of China has an embassy in Athens. The Hellenic Republic has an embassy in Beijing and three general consulates in Guangzhou, Hong-Kong and since 2005 in Shanghai. The Port of Piraeus is important from a geostrategic view for China, as it helps China's transactions with the whole of Europe. Thousands of Chinese people are living in Greece in the Overseas Chinese context and approximately 1000 Greek citizens are living in China. Modern diplomatic relations between the two countries were established in 1972. Today, Greece and China enjoy a very good relationship based on a solid foundation, which continues to be growing steadily.
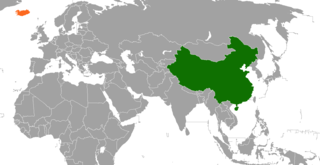
China–Iceland relations formally began on 8 December 1971, when Iceland recognised Beijing. Prior to the signing of a Free Trade Agreement between the two countries in 2013, diplomatic activities between them were relatively few in number. However, since this event, political cooperation has increased. There is growing number of economic and cultural ties, as their political partnership has expanded.

The National Library of Economics is the world's largest research infrastructure for economic literature, online as well as offline. The ZBW is a member of the Leibniz Association and has been a foundation under public law since 2007. Several times the ZBW received the international LIBER Award for its innovative work in librarianship. The ZBW allows for access of millions of documents and research on economics, partnering with over 40 research institutions to create a connective Open Access portal and social web of research. Through its EconStor and EconBiz, researchers and students have accessed millions of datasets and thousands of articles. The ZBW also edits two journals: Wirtschaftsdienst and Intereconomics.

The CBS International Business School (CBS) is a state-recognised, private business school which emerged in 2020 from the individual brands Cologne Business School (CBS) and European Management School (EMS). At its locations in Cologne, Mainz, Potsdam, Aachen, Brühl, Neuss and Solingen, it offers approximately 3,000 students its predominantly English-language business management study courses with the academic degrees Bachelor of Arts, Bachelor of Science, Master of Arts, Master of Science and MBA. The CBS Cologne Business School GmbH is the responsible body of the university.

People's Republic of China–Ethiopia relations were established in 1970. Ethiopia has an embassy in Beijing and the People's Republic of China has an embassy in Addis Ababa.
Aurore is a Sino-French community portal for science and university cooperation. It was created in 2009 by the Offices for Science and University of the Consulate-general of France in Shanghai, in partnership with the French Academy of Sciences. The Portal was inaugurated on May 21, 2010 at the French pavilion of the Shanghai Expo 2010.

The German National Library of Science and Technology, abbreviated TIB, is the national library of the Federal Republic of Germany for all fields of engineering, technology, and the natural sciences. It is jointly funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and the 16 German states. Founded in 1959, the library operates in conjunction with the Leibniz Universität Hannover. In addition to acquiring scientific literature, it conducts applied research in such areas as the archiving of non-textual materials, data visualization and the future Internet. The library is also involved in a number of open access initiatives. With a collection of over 9 million items in 2017, the TIB is the largest science and technology library in the world.
“International Years of Science” has been hosted by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) every year. Since 2007, in collaboration with a strategically important partner country in order to enhance Germany's visibility as an attractive country for international collaboration in education, research, and innovation. The event promotes university association, research and development projects, and support for vocational education and training.

The ASEAN European Academic University Network (ASEA-UNINET) is a network of universities, consisting of European and south-east Asian universities. It was founded in 1994 by universities from Austria, Indonesia, Thailand and Vietnam with the goal of promoting the continuous internationalisation of education and research. Today ASEA-UNINET consists of 83 universities from 17 different countries.
The Czech Science Foundation (GACR) was established in 1993 as an independent public organisation supporting basic research in the Czech Republic. On the basis of calls for proposals and a public competition, the Czech Science Foundation provides financial support for both experienced and young and early-stage researchers. It also funds international projects on a bilateral basis in cooperation with several partner agencies as well as projects carried out within international research programmes. It is one of two major government-supported research funding agencies in the Czech Republic, the other being the Technology Agency of the Czech Republic (TAČR).
The European Union's scientific collaboration beyond the bloc describes the European Union's frameworks for bilateral cooperation and specific projects in science and technology, with countries and regional blocs situated beyond the European Union.

Russian Foundation for Basic Research (RFBR) is a national science funding body of the Russian government created on 27 April 1992 by a decree of the President of Russia.

The Joint Working Group (JWG) was the first official bilateral administrative mechanism formed post the 1962 boundary war by India and China to discuss the boundary question with the aim of finding a solution. It was officially announced in a joint press communique in Beijing on 23 December 1988. A total of fifteen meetings of the JWG were held between 1989 and 2005. The last meeting was held on 30–31 March 2005.