
The Sisters of Mercy is a religious institute for women in the Roman Catholic Church. It was founded in 1831 in Dublin, Ireland, by Catherine McAuley. As of 2019, the institute has about 6200 sisters worldwide, organized into a number of independent congregations. They also started many education and health care facilities around the world.

Elizabeth Ann Bayley Seton was a Catholic religious sister in the United States and an educator, known as a founder of the country's parochial school system. Born in New York and reared as an Episcopalian, she married and had five children with her husband William Seton. Two years after his death, she converted to Catholicism in 1805.

Many religious communities have the term Sisters of Charity in their name. Some Sisters of Charity communities refer to the Vincentian tradition alone, or in America to the tradition of Saint Elizabeth Ann Seton, but others are unrelated. The rule of Vincent de Paul for the Daughters of Charity has been adopted and adapted by at least sixty founders of religious institutes for sisters around the world.

The Diocese of Fort Wayne–South Bend is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory, or diocese, of the Catholic Church in north-central and northeastern Indiana in the United States.

James Roosevelt Bayley was an American prelate of the Catholic Church. He served as the first Bishop of Newark (1853–1872) and the eighth Archbishop of Baltimore (1872–1877).

The Diocese of Paterson is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory, or diocese, of the Catholic Church in northern New Jersey. It is a suffragan diocese in the ecclesiastical province of the metropolitan Archdiocese of Newark.

The Archdiocese of Newark is a Latin Church ecclesiastical jurisdiction, or archdiocese, of the Catholic Church in northeastern New Jersey in the United States.
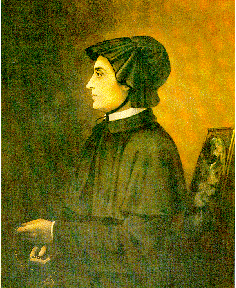
The Sisters of Charity of Saint Vincent de Paul of New York, most often known as the Sisters of Charity of New York, is a religious congregation of sisters in the Catholic Church whose primary missions are education and nursing and who are dedicated in particular to the service of the poor. The motherhouse is located at Mt. St. Vincent in the Riverdale section of the Bronx. They were founded by Elizabeth Ann Seton in 1809.

The Sisters of Charity Federation in the Vincentian-Setonian Tradition is an organization of fourteen congregations of religious women in the Catholic Church who trace their lineage to Saint Elizabeth Seton, Saint Vincent de Paul, and Saint Louise de Marillac.

Miriam Teresa Demjanovich, SC was an American Ruthenian Greek Catholic Sister of Charity who was beatified by the Catholic Church in 2014. The beatification ceremony was the first to take place in the United States, being held in Newark, New Jersey.
The Sisters of Charity of Seton Hill were founded by Sister Aloysia Lowe. In 1870, she and sisters Blanche O'Keefe, Maria Theresa O'Donnell, Maria Kavanaugh and two novices were sent to western Pennsylvania from the Sisters of Charity of Cincinnati and began their work, founding and staffing schools. The sisters later expanded their work to include healthcare.
The Sisters of Charity of Cincinnati were founded in 1852 by Mother Margaret Farrell George, by the separation of the community from the Sisters of Charity in Emmitsburg, Maryland. the motherhouse of the community is at Mount Saint Joseph, Ohio.

The Sisters of Charity of Saint Vincent de Paul were founded on May 11, 1849, when the four founding Sisters of Charity arrived in Halifax, Nova Scotia, from New York City; this has been designated a National Historic Event.

Robert Seton was a descendant of the New York "aristocratic" Seton and Bayley families, Seton was also a monsignor in the Roman Catholic Church and titular archbishop of Heliopolis.

Mary Xavier Mehegan, S.C. was a Roman Catholic sister who founded the Sisters of Charity of Saint Elizabeth and opened New Jersey's first four-year college for women.
Thomas Aloysius Boland was an American prelate of the Roman Catholic Church. He served as archbishop of the Archdiocese of Newark in New Jersey from 1952 to 1974. He previously served as an auxiliary bishop of the same diocese from 1940 to 1947 and bishop of the Diocese of Paterson in New Jersey from 1947 to 1952.
The Sisters of Charity of Our Lady of Mercy is a Roman Catholic religious institute founded by Bishop John England of the Diocese of Charleston in South Carolina, in 1829 as the Sisters of Our Lady of Mercy. In 1949 the word "Charity" was added to the congregation's name, in order to identify it more explicitly with others that follow the Rule of Life of St. Vincent de Paul. They came to serve throughout the Eastern United States. The members of the congregation use the postnominal initials of O.L.M.

Richard Bayley was a prominent New York City physician and the first chief health officer of the city. An expert in yellow fever, he helped discover its epidemiology, improved city sanitation, and authored the federal Quarantine Act of 1799. The 1788 Doctors' Riot was sparked by fears that his students were secretly removing corpses from graves in order to dissect them.
William Aloysius Griffin was an American prelate of the Roman Catholic Church. He served as bishop of the Diocese of Trenton in New Jersey from 1940 until his death in 1950. He previously served as an auxiliary bishop of the Archdiocese of Newark in New Jersey from 1938 to 1940.















