Edward Daniel Howard was an American prelate of the Roman Catholic Church. He served as the Auxiliary Bishop of Davenport from 1924 to 1926 and the Archbishop of Portland from 1926 to 1966. At the time of his death in 1983 he was the oldest Catholic bishop in the world.
The Franciscan Sisters of Christian Charity are a Congregation of Roman Catholic apostolic religious women. The congregation was founded in 1869 in Manitowoc, Wisconsin in the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Milwaukee, later part of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Green Bay. The sisters have active apostolates in education, health care, spiritual direction, and other community ministries. As of 2021, there are 188 sisters in the community. The FSCC is a member of the Council of Major Superiors of Women Religious, an organization which represents women religious in the United States.

The Archdiocese of Portland in Oregon is a Latin Church archdiocese of the Catholic Church in western Oregon in the United States.

The Sisters of St. Joseph, also known as the Congregation of the Sisters of St. Joseph, abbreviated CSJ or SSJ, is a Catholic religious congregation of women founded in Le Puy-en-Velay, France, in 1650. This congregation, named for Saint Joseph, has approximately 14,000 members worldwide: about 7,000 in the United States; 2,000 in France; and are active in 50 other countries.

The Congregation of the Religious of the Virgin Mary (Spanish: Religiosas de la Beata Virgen María, abbreviated RVM, is a Catholic centralized religious institute of consecrated life of Pontifical Right for women founded in Manila in 1684 by the Filipina Venerable Mother Ignacia del Espíritu Santo.
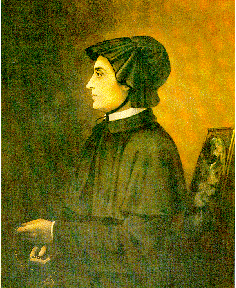
The Sisters of Charity of Saint Vincent de Paul of New York, most often known as the Sisters of Charity of New York, is a religious congregation of sisters in the Catholic Church whose primary missions are education and nursing and who are dedicated in particular to the service of the poor. The motherhouse is located at Mt. St. Vincent in the Riverdale section of the Bronx. They were founded by Elizabeth Ann Seton in 1809.
The Sisters of the Immaculate Heart of Mary (IHM), founded as the Daughters of the Most Holy and Immaculate Heart of the Blessed Virgin Mary, is a Catholic religious teaching institute for women. The institute was founded in the Catalan city of Olot, (Spain) in 1848 by Father Joaquim Masmitjà i de Puig as a means of rebuilding society through the education of young women. A daughter house of the community was founded in Los Angeles, California, United States, in 1871, and in 1924 formally separated from the Spanish congregation and was established as a distinct institute.
The Franciscan Sisters of Mary is a Roman Catholic religious congregation of religious sisters based in St. Louis, Missouri, noted for its operation of SSM Health Care, a group of some 20 hospitals throughout the Midwestern United States. It was formed in 1987 from the merger of two related congregations that founded many of the hospitals.
The Third Order of Saint Francis is a third order in the Franciscan tradition of Christianity, founded by the medieval Italian Catholic friar Francis of Assisi.

The Oblate Sisters of Providence (OSP) is a Catholic women's religious institute founded by Mother Mary Elizabeth Lange, and Father James Nicholas Joubert in 1829 in Baltimore, Maryland for the education of girls of African descent. It was the first permanent community of Black Catholic sisters in the United States.

The Sisters of the Blessed Sacrament (SBS) are a Catholic order of religious sisters in the United States. They were founded in 1891 by Katharine Drexel as the Sisters of the Blessed Sacrament for Indians and Colored People.
The Benedictine Sisters of St. Walburg Monastery is a Roman Catholic congregation of women. whose motherhouse, St. Walburg Monastery, is located at Villa Madonna, in Villa Hills, Kentucky. It was founded in 1859 by three sisters of the Benedictine congregation of Mount St. Benedict Monastery in Erie, Pennsylvania, who came to Covington to teach the German-speaking children of St. Joseph's parish. They became an independent congregation in 1867. Villa Madonna Academy, a private, Roman Catholic K-12 school is part of the sisters' ministry in Kentucky. Besides operating the Academy, the sisters taught in parish schools and staffed St. John's Orphanage.

William Hickley Gross, C.Ss.R., was an American prelate of the Roman Catholic Church who was a member of the Congregation of the Most Holy Redeemer. He served as Bishop of Savannah (1873–1885) and Archbishop of Oregon City (1885–1898).

Joseph Gregory Dwenger, C.P.P.S was an American prelate of the Catholic Church. He served as Bishop of Fort Wayne from 1872 to 1893.
The Dominican Sisters of Blauvelt are a religious congregation within the Dominican Order of religious sisters founded in 1890. They are based in the town of Blauvelt, New York, a northern suburb of New York City. Their traditional service has been childcare, both through teaching and caring for orphans.

The Sisters of Charity of Our Lady Mother of Mercy (SCMM) are a Catholic religious congregation founded in the Netherlands in 1832 by Fr Johannes Zwijsen, aided by Mary M. Leijsen, for the instruction of children and the betterment of people deprived of spiritual aid. The motherhouse is in Tilburg.
The Sisters of the Precious Blood is a Roman Catholic female religious order founded in 1845 in Steinerberg, Switzerland by Magdalene Weber and a number of young women from Baden.

The Sisters of the Precious Blood is a Catholic religious order for women founded in Grisons, Switzerland, in 1834 by Mother Maria Anna Brunner. Precious Blood Sisters form an active apostolic congregation with sisters currently serving in the United States, Chile, and Guatemala.
Mother Mary Joseph Lynch was the founder of the Native American boarding school that became the University of Minnesota Morris. She was a member of the Catholic order the Sisters of Mercy.











