The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North and Central European Plain.
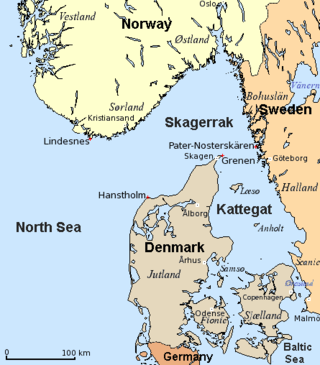
The Kattegat is a 30,000 km2 (12,000 sq mi) sea area bounded by the Jutlandic peninsula in the west, the Danish Straits islands of Denmark and the Baltic Sea to the south and the provinces of Bohuslän, Västergötland, Halland and Skåne in Sweden in the east. The Baltic Sea drains into the Kattegat through the Danish Straits. The sea area is a continuation of the Skagerrak and may be seen as a bay of the North Sea, but in traditional Scandinavian usage, this is not the case.

Vänern is the largest lake in Sweden, the largest lake in the European Union and the third-largest lake in Europe after Ladoga and Onega in Russia. It is located in the provinces of Västergötland, Dalsland, and Värmland in the southwest of the country. With its surface located at 44 metres (144 ft) with a maximum depth of 106 metres (348 ft), the lowest point of the Vänern basin is at 62 metres (203 ft) below sea level. The average depth is at a more modest 28 metres (92 ft), which means that the average point of the lake floor remains above sea level.

Øresund or Öresund, commonly known in English as the Sound, is a strait which forms the Danish–Swedish border, separating Zealand (Denmark) from Scania (Sweden). The strait has a length of 118 kilometres (73 mi); its width varies from 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) to 28 kilometres (17 mi). It is 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) wide at its narrowest point between Helsingør in Denmark and Helsingborg in Sweden.

Læsø is the largest island in the North Sea bay of Kattegat, and is located 19 kilometres (12 mi) off the northeast coast of the Jutland Peninsula, the Danish mainland. Læsø is also the name of the municipality on that island. The island is a location mentioned in several instances in Old Norse sources detailing Norse mythology.

Long Point is a sand spit and medium-sized hamlet on the north shore of Lake Erie, part of Norfolk County in the province of Ontario, Canada.

Delaware Bay is the estuary outlet of the Delaware River on the northeast seaboard of the United States, lying between the states of Delaware and New Jersey. It is approximately 782 square miles (2,030 km2) in area, the bay's freshwater mixes for many miles with the saltwater of the Atlantic Ocean.

The Firth of Thames is a large bay located in the north of the North Island of New Zealand. It is the firth of the rivers Waihou and Piako, the former of which was formerly named the Thames River, and the town of Thames lies on its southeastern coast.

Carlingford Lough is a glacial fjord or sea inlet in northeastern Ireland, forming part of the border between Northern Ireland to the north and the Republic of Ireland to the south. On its northern shore is County Down, the Mourne Mountains, and the town of Warrenpoint; on its southern shore is County Louth, the Cooley Mountains and the village of Carlingford. The Newry River flows into the loch from the northwest.

Djursland is a 44 km × 33 km hilly lowland peninsula in Denmark at the entrance to the Baltic Sea, between Denmark and Sweden in Northern Europe. Djursland protrudes into the Kattegat sea, as part of the larger peninsula of Jutland, which itself extends from the Central European continent. Djursland comprises the two municipalities of Norddjurs and Syddjurs.

The Cape May National Wildlife Refuge is a protected area on the Cape May Peninsula in Cape May County, New Jersey. It is part of the National Wildlife Refuge System and managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. Established in January 1989 with 90 acres (0.36 km2) acquired from the Nature Conservancy, it has since grown to more than 11,000 acres (45 km2) in size, and plans call for its further expansion to more than 21,200 acres (86 km2). It comprises three distinct and non-contiguous units: the Delaware Bay Division, the Great Cedar Swamp Division and the Two Mile Beach Unit. Located in the Middle Atlantic coastal forests ecoregion, the cape provides habitat for large numbers of migratory birds.

The Swan Bay is a shallow, 30-square-kilometre (12 sq mi) marine embayment at the eastern end of the Bellarine Peninsula in Port Phillip, Victoria, Australia. The township of Queenscliff lies at its southern end, and St Leonards at its northern. It is partly separated from Port Phillip by Swan Island, Duck Island and Edwards Point. Most of the area is included in the Port Phillip Heads Marine National Park as well as being listed as a wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention as part of the Port Phillip Bay and Bellarine Peninsula Ramsar Site. The bay is part of the Swan Bay and Port Phillip Bay Islands Important Bird Area, identified as such by BirdLife International because of its importance for orange-bellied parrots, waders and seabirds.
The Port Phillip Bay and Bellarine Peninsula Ramsar Site is one of the Australian sites listed under the Ramsar Convention as a wetland of international importance. It was designated on 15 December 1982, and is listed as Ramsar Site No.266. Much of the site is also part of either the Swan Bay and Port Phillip Bay Islands Important Bird Area or the Werribee and Avalon Important Bird Area, identified as such by BirdLife International because of their importance for wetland and waterbirds as well as for orange-bellied parrots. It comprises some six disjunct, largely coastal, areas of land, totalling 229 km2, along the western shore of Port Phillip and on the Bellarine Peninsula, in the state of Victoria. Wetland types protected include shallow marine waters, estuaries, freshwater lakes, seasonal swamps, intertidal mudflats and seagrass beds.

Getterön Nature Reserve is a nature reserve at Getterön in Varberg Municipality, Sweden. It consists of parts of the peninsula Getterön and an area to the north. It has an area of 350 hectares, of which 235 are land. The reserve was established in 1970.

Kandalaksha Nature Reserve is a Russian 'zapovednik' on the south shore of Kandalaksha Bay in the Murmansk and Karelia regions on the opening to the White Sea. The reserve also includes two small sectors on the northern coast of the Kola peninsula on the Barents Sea; notably, the warm Atlantic current causes the northern sectors on the Barents Sea to be warmer than the more southerly White Sea sectors. Over 550 islands are covered in the boundaries of the reserve. It is one of the oldest nature reserves in Russia, created in 1932 to protect the marine habitats and waterfowl of the region, particularly the eider. The reserve is situated in the Kandalakshsky District, Kolsky District, and Lovozersky District of Murmansk Oblast. The nearest city, Kandalaksha, is at the northwest entrance to the Kandalaksha Gulf, about 5 km from the nearest point in the reserve. Since 1976, the reserve has been part of the Ramsar wetland site of international importance "Kandalaksha Bay". It covers an area of 70,530 ha (272.3 sq mi).

The coastline of Djursland in Denmark is 260 kilometers long as measured from the ferry berth in Voer in the middle of Randers Fjord ending at Avlsgård in Aarhus Bay to the south. There are 18 sandy beaches for swimming along the coastline according to the folder, Kystkort Djursland published by the peninsula's two municipalities, Norddjurs and Syddjurs. These beaches cover 15 – 20%. of the total coastline. The remaining 200 plus kilometres are mostly unspoiled coastal nature.

Agger Tange is a peninsula located between the Limfjord and the North Sea. Agger Tange protrudes from the North Jutlandic Island, immediately south of the village Agger in Thy.

Laholm Bay is a bay of the Kattegat, between Tylösand in the north and Hovs Hallar in the south. The Bjäre Peninsula, which forms its southern edge, separates it from Skälder Bay.

The Étang d'Urbino is a coastal lagoon beside the Tyrrhenian Sea in the Haute-Corse department on the French island of Corsica.