Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:

The Baltic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively or as a second language by a population of about 6.5–7.0 million people mainly in areas extending east and southeast of the Baltic Sea in Europe. Together with the Slavic languages, they form the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European family.

The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the Early Middle Ages, which in turn is thought to have descended from the earlier Proto-Balto-Slavic language, linking the Slavic languages to the Baltic languages in a Balto-Slavic group within the Indo-European family.

Cyril and Methodius (815–885) were brothers, Byzantine Christian theologians and missionaries. For their work evangelizing the Slavs, they are known as the "Apostles to the Slavs".
The Slavs or Slavic peoples are a group of peoples who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, and Southeastern Europe, though there is a large Slavic minority scattered across the Baltic states, Northern Asia, and Central Asia, and a substantial Slavic diaspora in the Americas, Western Europe, and Northern Europe.

Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic is the first Slavic literary language.

The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which they claim as their cultural ancestor. Today Belarusians, Russians and Ukrainians are the existent East Slavic nations. Rusyns can also be considered as a separate nation, although they are often considered a subgroup of the Ukrainian people.

Slavic mythology or Slavic paganism is the religious beliefs, myths, and ritual practices of the Slavs before Christianisation, which occurred at various stages between the 8th and the 13th century.

Old East Slavic was a language used by the East Slavs from the 7th or 8th century to the 13th or 14th century, until it diverged into the Russian and Ruthenian languages. Ruthenian eventually evolved into the Belarusian, Rusyn, and Ukrainian languages.

The Balto-Slavic languages form a branch of the Indo-European family of languages, traditionally comprising the Baltic and Slavic languages. Baltic and Slavic languages share several linguistic traits not found in any other Indo-European branch, which points to a period of common development and origin.
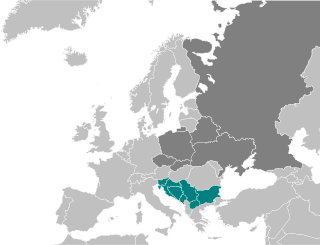
South Slavs are Slavic people who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hungary, Romania, and the Black Sea, the South Slavs today include Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes.
The term North Slavic languages is used in three main senses:

The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic languages diversified into their historically attested forms over the 10th to 14th centuries.
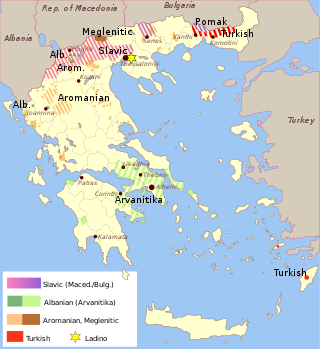
The Slavic dialects of Greece are the Eastern South Slavic dialects of Macedonian and Bulgarian spoken by minority groups in the regions of Macedonia and Thrace in northern Greece. Usually, dialects in Thrace are classified as Bulgarian, while the dialects in Macedonia are classified as Macedonian, with the exception of some eastern dialects which can also be classified as Bulgarian. Before World War II, most linguists considered all of these dialects to be Bulgarian dialects. However, other linguists opposed this view and considered Macedonian dialects as comprising an independent language distinct from both Bulgarian and Serbo-Croatian.

The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities.

The early Slavs were an Indo-European peoples who lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages in Central, Eastern and Southeast Europe and established the foundations for the Slavic nations through the Slavic states of the Early and High Middle Ages. The Slavs' original homeland is still a matter of debate due to a lack of historical records; however, scholars believe that it was in Eastern Europe, with Polesia being the most commonly accepted location.
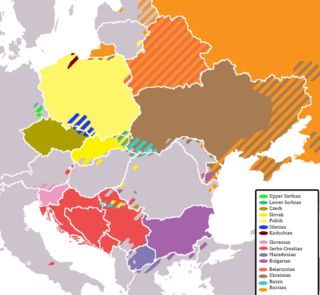
A pan-Slavic language is a zonal auxiliary language for communication among the Slavic peoples.
The Proto-Slavic language, the hypothetical ancestor of the modern-day Slavic languages, developed from the ancestral Proto-Balto-Slavic language, which is the parent language of the Balto-Slavic languages. The first 2,000 years or so consist of the pre-Slavic era, a long period during which none of the later dialectal differences between Slavic languages had yet emerged. The last stage in which the language remained without internal differences that later characterize different Slavic languages can be dated around AD 500 and is sometimes termed Proto-Slavic proper or Early Common Slavic. Following this is the Common Slavic period, during which the first dialectal differences appeared but the entire Slavic-speaking area continued to function as a single language, with sound changes tending to spread throughout the entire area. By around 1000, the area had broken up into separate East Slavic, West Slavic and South Slavic languages, and in the following centuries it broke up further into the various modern Slavic languages of which the following are extant: Belarusian, Russian, Rusyn and Ukrainian in the East; Czech, Slovak, Polish, Kashubian and the Sorbian languages in the West, and Bulgarian, Macedonian, Serbo-Croatian and Slovenian in the South.

The Slavs were Christianized in waves from the 7th to 12th century, though the process of replacing old Slavic religious practices began as early as the 6th century. Generally speaking, the monarchs of the South Slavs adopted Christianity in the 9th century, the East Slavs in the 10th, and the West Slavs between the 9th and 12th century. Saints Cyril and Methodius are attributed as "Apostles to the Slavs", having introduced the Byzantine-Slavic rite and Glagolitic alphabet, the oldest known Slavic alphabet and basis for the Early Cyrillic alphabet.
Topical outline of articles about Slavic history and culture. This outline is an overview of Slavic topics; for outlines related to specific Slavic groups and topics, see the links in the Other Slavic outlines section below.