
American Airlines Flight 587 was a regularly scheduled international passenger flight from New York's John F. Kennedy International Airport to Las Américas International Airport in Santo Domingo, the capital of the Dominican Republic. On November 12, 2001, the Airbus A300B4-605R flying the route crashed shortly after takeoff into the Belle Harbor neighborhood of Queens, a borough of New York City. All 260 people aboard the plane were killed, along with 5 people on the ground.

Aircraft flight control surfaces are aerodynamic devices allowing a pilot to adjust and control the aircraft's flight attitude.

The hammerhead turn, stall turn, or Fieseler is an aerobatics turn-around maneuver.

The empennage, also known as the tail or tail assembly, is a structure at the rear of an aircraft that provides stability during flight, in a way similar to the feathers on an arrow. The term derives from the French language word empenner which means "to feather an arrow". Most aircraft feature an empennage incorporating vertical and horizontal stabilising surfaces which stabilise the flight dynamics of yaw and pitch, as well as housing control surfaces.

Aerobatic maneuvers are flight paths putting aircraft in unusual attitudes, in air shows, dogfights or competition aerobatics. Aerobatics can be performed by a single aircraft or in formation with several others. Nearly all aircraft are capable of performing aerobatics maneuvers of some kind, although it may not be legal or safe to do so in certain aircraft.
Flight mechanics are relevant to fixed wing and rotary wing (helicopters) aircraft. An aeroplane, is defined in ICAO Document 9110 as, "a power-driven heavier than air aircraft, deriving its lift chiefly from aerodynamic reactions on surface which remain fixed under given conditions of flight".

A twin tail is a specific type of vertical stabilizer arrangement found on the empennage of some aircraft. Two vertical stabilizers—often smaller on their own than a single conventional tail would be—are mounted at the outside of the aircraft's horizontal stabilizer. This arrangement is also known as an H-tail, as it resembles a capital "H" when viewed from rear - these were used on a wide variety of World War II multi-engine designs that saw mass production, especially on the American B-24 Liberator and B-25 Mitchell bombers, the British Avro Lancaster and Handley-Page Halifax heavy bombers, and on the Soviet Union's Petlyakov Pe-2 attack bomber.

An aircraft stabilizer is an aerodynamic surface, typically including one or more movable control surfaces, that provides longitudinal (pitch) and/or directional (yaw) stability and control. A stabilizer can feature a fixed or adjustable structure on which any movable control surfaces are hinged, or it can itself be a fully movable surface such as a stabilator. Depending on the context, "stabilizer" may sometimes describe only the front part of the overall surface.

A barrel roll is an aerial maneuver in which an airplane makes a complete rotation on both its longitudinal and lateral axes, causing it to follow a helical path, approximately maintaining its original direction. It is sometimes described as a "combination of a loop and a roll." The g-force is kept positive on the object throughout the maneuver, commonly between 2–3 g, and no less than 0.5 g. The barrel roll is commonly confused with an aileron roll.
The term Immelmann turn refers to two different aircraft maneuvers:

The Pfalz D.III was a fighter aircraft used by the Luftstreitkräfte during the First World War. The D.III was the first major original design from Pfalz Flugzeugwerke. Though generally considered inferior to contemporary Albatros and Fokker fighters, the D.III was widely used by the Jagdstaffeln from late 1917 to mid-1918. It continued to serve as a training aircraft until the end of the war.
A Lomcovák is a family of extreme aerobatic maneuvers where the aircraft, with almost no forward speed, rotates on chosen axes due to the gyroscopic precession and torque of the rotating propeller.
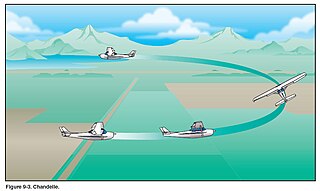
The chandelle is an aircraft control maneuver where the pilot combines a 180° turn with a climb.

Radio-controlled aerobatics is the practice of flying radio-controlled aircraft in maneuvers involving aircraft attitudes that are not used in normal flight.

The Parnall Puffin was an experimental amphibious fighter-reconnaissance biplane produced in the United Kingdom just after World War I. It had several unusual features, principally a single central float and an inverted vertical stabilizer and rudder, and showed promise, but at that time no new aircraft were being ordered in numbers for the RAF and only the three Puffins of the initial order were built.
3D Aerobatics or 3D flying is a form of flying using flying aircraft to perform specific aerial maneuvers. They are usually performed when the aircraft had been intentionally placed in a stalled position.
Royal Prussian Jagdstaffel 56, commonly abbreviated to Jasta 56, was a "hunting group" of the Luftstreitkräfte, the air arm of the Imperial German Army during World War I. The squadron would score 63 aerial victories during the war. The unit's victories came at the expense of seven killed in action, four wounded in action, two injured in accidents, and one taken prisoner of war.
A wingover is an aerobatic maneuver in which an airplane makes a steep climb, followed by a vertical flat-turn. The maneuver ends with a short dive as the plane gently levels out, flying in the opposite direction from which the maneuver began.















