
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing. In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing. It defines a material's suitability for certain manufacturing operations and its capacity to absorb mechanical overload. Some metals that are generally described as ductile include gold and copper, while platinum is the most ductile of all metals in pure form. However, not all metals experience ductile failure as some can be characterized with brittle failure like cast iron. Polymers generally can be viewed as ductile materials as they typically allow for plastic deformation.

Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displacement develops perpendicular to the surface, it is called a normal tensile crack or simply a crack; if a displacement develops tangentially, it is called a shear crack, slip band, or dislocation.

In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface. The crack will continue to grow until it reaches a critical size, which occurs when the stress intensity factor of the crack exceeds the fracture toughness of the material, producing rapid propagation and typically complete fracture of the structure.

In materials science and metallurgy, toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing. Toughness is the strength with which the material opposes rupture. One definition of material toughness is the amount of energy per unit volume that a material can absorb before rupturing. This measure of toughness is different from that used for fracture toughness, which describes the capacity of materials to resist fracture. Toughness requires a balance of strength and ductility.

Hydrogen embrittlement (HE), also known as hydrogen-assisted cracking or hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC), is a reduction in the ductility of a metal due to absorbed hydrogen. Hydrogen atoms are small and can permeate solid metals. Once absorbed, hydrogen lowers the stress required for cracks in the metal to initiate and propagate, resulting in embrittlement. Hydrogen embrittlement occurs most notably in steels, as well as in iron, nickel, titanium, cobalt, and their alloys. Copper, aluminium, and stainless steels are less susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement.

Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) is the growth of crack formation in a corrosive environment. It can lead to unexpected and sudden failure of normally ductile metal alloys subjected to a tensile stress, especially at elevated temperature. SCC is highly chemically specific in that certain alloys are likely to undergo SCC only when exposed to a small number of chemical environments. The chemical environment that causes SCC for a given alloy is often one which is only mildly corrosive to the metal. Hence, metal parts with severe SCC can appear bright and shiny, while being filled with microscopic cracks. This factor makes it common for SCC to go undetected prior to failure. SCC often progresses rapidly, and is more common among alloys than pure metals. The specific environment is of crucial importance, and only very small concentrations of certain highly active chemicals are needed to produce catastrophic cracking, often leading to devastating and unexpected failure.
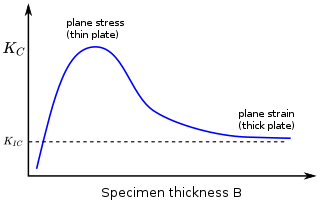
In materials science, fracture toughness is the critical stress intensity factor of a sharp crack where propagation of the crack suddenly becomes rapid and unlimited. A component's thickness affects the constraint conditions at the tip of a crack with thin components having plane stress conditions and thick components having plane strain conditions. Plane strain conditions give the lowest fracture toughness value which is a material property. The critical value of stress intensity factor in mode I loading measured under plane strain conditions is known as the plane strain fracture toughness, denoted . When a test fails to meet the thickness and other test requirements that are in place to ensure plane strain conditions, the fracture toughness value produced is given the designation . Fracture toughness is a quantitative way of expressing a material's resistance to crack propagation and standard values for a given material are generally available.
In materials science, environmental stress fracture or environment assisted fracture is the generic name given to premature failure under the influence of tensile stresses and harmful environments of materials such as metals and alloys, composites, plastics and ceramics.
Liquid metal embrittlement is a phenomenon of practical importance, where certain ductile metals experience drastic loss in tensile ductility or undergo brittle fracture when exposed to specific liquid metals. Generally, a tensile stress, either externally applied or internally present, is needed to induce embrittlement. Exceptions to this rule have been observed, as in the case of aluminium in the presence of liquid gallium. This phenomenon has been studied since the beginning of the 20th century. Many of its phenomenological characteristics are known and several mechanisms have been proposed to explain it. The practical significance of liquid metal embrittlement is revealed by the observation that several steels experience ductility losses and cracking during hot-dip galvanizing or during subsequent fabrication. Cracking can occur catastrophically and very high crack growth rates have been measured.
Corrosion fatigue is fatigue in a corrosive environment. It is the mechanical degradation of a material under the joint action of corrosion and cyclic loading. Nearly all engineering structures experience some form of alternating stress, and are exposed to harmful environments during their service life. The environment plays a significant role in the fatigue of high-strength structural materials like steel, aluminum alloys and titanium alloys. Materials with high specific strength are being developed to meet the requirements of advancing technology. However, their usefulness depends to a large extent on the degree to which they resist corrosion fatigue.

Embrittlement is a significant decrease of ductility of a material, which makes the material brittle. Embrittlement is used to describe any phenomena where the environment compromises a stressed material's mechanical performance, such as temperature or environmental composition. This is oftentimes undesirable as brittle fracture occurs quicker and can much more easily propagate than ductile fracture, leading to complete failure of the equipment. Various materials have different mechanisms of embrittlement, therefore it can manifest in a variety of ways, from slow crack growth to a reduction of tensile ductility and toughness.
6061 aluminium alloy is a precipitation-hardened aluminium alloy, containing magnesium and silicon as its major alloying elements. Originally called "Alloy 61S", it was developed in 1935. It has good mechanical properties, exhibits good weldability, and is very commonly extruded. It is one of the most common alloys of aluminium for general-purpose use.
7075 aluminium alloy (AA7075) is an aluminium alloy with zinc as the primary alloying element. It has excellent mechanical properties and exhibits good ductility, high strength, toughness, and good resistance to fatigue. It is more susceptible to embrittlement than many other aluminium alloys because of microsegregation, but has significantly better corrosion resistance than the alloys from the 2000 series. It is one of the most commonly used aluminium alloys for highly stressed structural applications and has been extensively used in aircraft structural parts.

Environmental Stress Cracking (ESC) is one of the most common causes of unexpected brittle failure of thermoplastic polymers known at present. According to ASTM D883, stress cracking is defined as "an external or internal crack in a plastic caused by tensile stresses less than its short-term mechanical strength". This type of cracking typically involves brittle cracking, with little or no ductile drawing of the material from its adjacent failure surfaces. Environmental stress cracking may account for around 15-30% of all plastic component failures in service. This behavior is especially prevalent in glassy, amorphous thermoplastics. Amorphous polymers exhibit ESC because of their loose structure which makes it easier for the fluid to permeate into the polymer. Amorphous polymers are more prone to ESC at temperature higher than their glass transition temperature (Tg) due to the increased free volume. When Tg is approached, more fluid can permeate into the polymer chains.
Low hydrogen annealing, commonly known as "baking" is a heat treatment in metallurgy for the reduction or elimination of hydrogen in a material to prevent hydrogen embrittlement. Hydrogen embrittlement is the hydrogen-induced cracking of metals, particularly steel which results in degraded mechanical properties such as plasticity, ductility and fracture toughness at low temperature. Low hydrogen annealing is called a de-embrittlement process. Low hydrogen annealing is an effective method compared to alternatives such as electroplating the material with zinc to provide a barrier for hydrogen ingress which results in coating defects.
Metallurgical failure analysis is the process to determine the mechanism that has caused a metal component to fail. It can identify the cause of failure, providing insight into the root cause and potential solutions to prevent similar failures in the future, as well as culpability, which is important in legal cases. Resolving the source of metallurgical failures can be of financial interest to companies. The annual cost of corrosion in the United States was estimated by NACE International in 2012 to be $450 billion a year, a 67% increase compared to estimates for 2001. These failures can be analyzed to determine their root cause, which if corrected, would save reduce the cost of failures to companies.
Rising Step Load Testing is a testing system that can apply loads in tension or bending to evaluate hydrogen-induced cracking. It was specifically designed to conduct the accelerated ASTM F1624 step-modified, slow strain rate tests on a variety of test coupons or structural components. It can also function to conduct conventional ASTM E8 tensile tests; ASTM F519 200-hr Sustained Load Tests with subsequent programmable step loads to rupture for increased reliability; and ASTM G129 Slow Strain Rate Tensile tests.

Tensile testing, also known as tension testing, is a fundamental materials science and engineering test in which a sample is subjected to a controlled tension until failure. Properties that are directly measured via a tensile test are ultimate tensile strength, breaking strength, maximum elongation and reduction in area. From these measurements the following properties can also be determined: Young's modulus, Poisson's ratio, yield strength, and strain-hardening characteristics. Uniaxial tensile testing is the most commonly used for obtaining the mechanical characteristics of isotropic materials. Some materials use biaxial tensile testing. The main difference between these testing machines being how load is applied on the materials.
Metal-induced embrittlement (MIE) is the embrittlement caused by diffusion of metal, either solid or liquid, into the base material. Metal induced embrittlement occurs when metals are in contact with low-melting point metals while under tensile stress. The embrittler can be either solid (SMIE) or liquid. Under sufficient tensile stress, MIE failure occurs instantaneously at temperatures just above melting point. For temperatures below the melting temperature of the embrittler, solid-state diffusion is the main transport mechanism. This occurs in the following ways:










