Related Research Articles
An evoked potential or evoked response is an electrical potential in a specific pattern recorded from a specific part of the nervous system, especially the brain, of a human or other animals following presentation of a stimulus such as a light flash or a pure tone. Different types of potentials result from stimuli of different modalities and types. EP is distinct from spontaneous potentials as detected by electroencephalography (EEG), electromyography (EMG), or other electrophysiologic recording method. Such potentials are useful for electrodiagnosis and monitoring that include detections of disease and drug-related sensory dysfunction and intraoperative monitoring of sensory pathway integrity.

The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs and the auditory parts of the sensory system.

Sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are neurons in the nervous system, that convert a specific type of stimulus, via their receptors, into action potentials or graded potentials. This process is called sensory transduction. The cell bodies of the sensory neurons are located in the dorsal ganglia of the spinal cord.
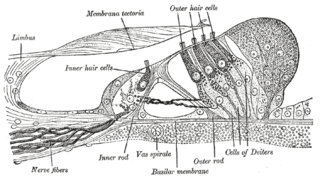
Hair cells are the sensory receptors of both the auditory system and the vestibular system in the ears of all vertebrates, and in the lateral line organ of fishes. Through mechanotransduction, hair cells detect movement in their environment.

The auditory cortex is the part of the temporal lobe that processes auditory information in humans and many other vertebrates. It is a part of the auditory system, performing basic and higher functions in hearing, such as possible relations to language switching. It is located bilaterally, roughly at the upper sides of the temporal lobes – in humans, curving down and onto the medial surface, on the superior temporal plane, within the lateral sulcus and comprising parts of the transverse temporal gyri, and the superior temporal gyrus, including the planum polare and planum temporale.
Audiometry is a branch of audiology and the science of measuring hearing acuity for variations in sound intensity and pitch and for tonal purity, involving thresholds and differing frequencies. Typically, audiometric tests determine a subject's hearing levels with the help of an audiometer, but may also measure ability to discriminate between different sound intensities, recognize pitch, or distinguish speech from background noise. Acoustic reflex and otoacoustic emissions may also be measured. Results of audiometric tests are used to diagnose hearing loss or diseases of the ear, and often make use of an audiogram.
Evoked fields are part of the magnetoencephalogram. They are brain signals evoked by sensory stimulation, but usually buried by the ongoing brain activity. Repeating the stimulus multiple times and averaging the signals reduces the uncorrelated ongoing activity and reveals the evoked field. Evoked fields are the magnetoencephalographic equivalent to evoked potentials, which are part of the electroencephalogram.
AEP may refer to:
Sensory gating describes neurological processes of filtering out redundant or unnecessary stimuli in the brain from all possible environmental stimuli. Also referred to as gating or filtering, sensory gating prevents an overload of irrelevant information in the higher cortical centers of the brain. Sensory gating can also occur in different forms through changes in both perception and sensation, affected by various factors such as "arousal, recent stimulus exposure, and selective attention.
Sensory neuroscience is a subfield of neuroscience which explores the anatomy and physiology of neurons that are part of sensory systems such as vision, hearing, and olfaction. Neurons in sensory regions of the brain respond to stimuli by firing one or more nerve impulses following stimulus presentation. How is information about the outside world encoded by the rate, timing, and pattern of action potentials? This so-called neural code is currently poorly understood and sensory neuroscience plays an important role in the attempt to decipher it. Looking at early sensory processing is advantageous since brain regions that are "higher up" contain neurons which encode more abstract representations. However, the hope is that there are unifying principles which govern how the brain encodes and processes information. Studying sensory systems is an important stepping stone in our understanding of brain function in general.
The auditory brainstem response (ABR) is an auditory evoked potential extracted from ongoing electrical activity in the brain and recorded via electrodes placed on the scalp. The measured recording is a series of six to seven vertex positive waves of which I through V are evaluated. These waves, labeled with Roman numerals in Jewett and Williston convention, occur in the first 10 milliseconds after onset of an auditory stimulus. The ABR is considered an exogenous response because it is dependent upon external factors.
In human neuroanatomy, brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BAEPs), also called brainstem auditory evoked responses (BAERs), are very small auditory evoked potentials in response to an auditory stimulus, which are recorded by electrodes placed on the scalp. They reflect neuronal activity in the auditory nerve, cochlear nucleus, superior olive, and inferior colliculus of the brainstem. They typically have a response latency of no more than six milliseconds with an amplitude of approximately one microvolt.

Cortical deafness is a rare form of sensorineural hearing loss caused by damage to the primary auditory cortex. Cortical deafness is an auditory disorder where the patient is unable to hear sounds but has no apparent damage to the anatomy of the ear, which can be thought of as the combination of auditory verbal agnosia and auditory agnosia. Patients with cortical deafness cannot hear any sounds, that is, they are not aware of sounds including non-speech, voices, and speech sounds. Although patients appear and feel completely deaf, they can still exhibit some reflex responses such as turning their head towards a loud sound.

Telaprevir (VX-950), marketed under the brand names Incivek and Incivo, is a pharmaceutical drug for the treatment of hepatitis C co-developed by Vertex Pharmaceuticals and Johnson & Johnson. It is a member of a class of antiviral drugs known as protease inhibitors. Specifically, telaprevir inhibits the hepatitis C viral enzyme NS3/4A serine protease. Telaprevir is only indicated for use against hepatitis C genotype 1 viral infections and has not been proven to have an effect on or being safe when used for other genotypes of the virus. The standard therapy of pegylated interferon and ribavirin is less effective than telaprevir in those with genotype 1.
In neuroscience, the N100 or N1 is a large, negative-going evoked potential measured by electroencephalography ; it peaks in adults between 80 and 120 milliseconds after the onset of a stimulus, and is distributed mostly over the fronto-central region of the scalp. It is elicited by any unpredictable stimulus in the absence of task demands. It is often referred to with the following P200 evoked potential as the "N100-P200" or "N1-P2" complex. While most research focuses on auditory stimuli, the N100 also occurs for visual, olfactory, heat, pain, balance, respiration blocking, and somatosensory stimuli.
Audio-visual entrainment (AVE), a subset of brainwave entrainment, uses flashes of lights and pulses of tones to guide the brain into various states of brainwave activity. AVE devices are often termed light and sound machines or mind machines. Altering brainwave activity is believed to aid in the treatment of psychological and physiological disorders.
In neuroscience, the visual P200 or P2 is a waveform component or feature of the event-related potential (ERP) measured at the human scalp. Like other potential changes measurable from the scalp, this effect is believed to reflect the post-synaptic activity of a specific neural process. The P2 component, also known as the P200, is so named because it is a positive going electrical potential that peaks at about 200 milliseconds after the onset of some external stimulus. This component is often distributed around the centro-frontal and the parieto-occipital areas of the scalp. It is generally found to be maximal around the vertex of the scalp, however there have been some topographical differences noted in ERP studies of the P2 in different experimental conditions.
BmKAEP is a neurotoxin from the venom of the Manchurian scorpion (Mesobuthus martensii). It is a β-toxin, which shift the activation voltage of sodium channels towards more negative potentials.
Electrocochleography is a technique of recording electrical potentials generated in the inner ear and auditory nerve in response to sound stimulation, using an electrode placed in the ear canal or tympanic membrane. The test is performed by an otologist or audiologist with specialized training, and is used for detection of elevated inner ear pressure or for the testing and monitoring of inner ear and auditory nerve function during surgery.
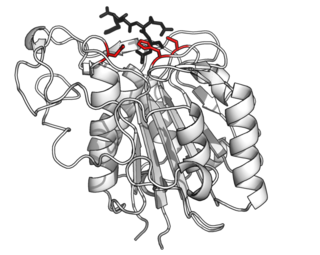
Asparagine endopeptidase is a proteolytic enzyme from C13 peptidase family which hydrolyses a peptide bond using the thiol group of a cysteine residue as a nucleophile. It is also known as asparaginyl endopeptidase, citvac, proteinase B, hemoglobinase, PRSC1 gene product or LGMN, vicilin peptidohydrolase and bean endopeptidase. In humans it is encoded by the LGMN gene.
References
| This biology article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |