This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2008) |
The Small-Order Execution System (SOES) was a system to facilitate clearing trades of low volume on Nasdaq. It has been phased out and is no longer necessary.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2008) |
The Small-Order Execution System (SOES) was a system to facilitate clearing trades of low volume on Nasdaq. It has been phased out and is no longer necessary.
SOES was first introduced in December 1984 for 25 stocks [1] to provide automatic order execution for individual traders with orders less than or equal to 1000 shares. The lack of liquidity after the 1987 market crash led Nasdaq to enforce mandatory use of the SOES by all market makers using the NASDAQ National Market System, [1] providing excellent liquidity for smaller investors and traders.
Initially, when SOES was mandatory, it was met with heavy pessimism from Nasdaq member firms because it forced them to execute all SOES trades that met the market maker's advertised price. There were also significant limitations implemented to prevent day traders from exploiting the system and taking advantage of old prices quoted by market makers.[ citation needed ]
SOES operated alongside another electronic system called SelectNet, launched in 1988, which enabled market participants to negotiate via computer instead of telephone and permitted larger orders than SOES. [2]
Although SOES was intended for use by retail investors, by 1995 more than 80% of its users were day traders, who used the system because its automatic execution gave them a trading advantage, [3] although licensed broker-dealers were prohibited by Nasdaq rules from using SOES to trade for themselves. [4] : 81 Since much trading on Nasdaq was still done by human market makers, day traders (derisively nicknamed "SOES bandits") could exploit slower human reaction times to profit from scalping outdated price quotes when the price for a stock shifted. [4] : 80–81
SOES's share of total Nasdaq trading volume was 5% in 1998. [3] In July 2001, Nasdaq rolled out an upgrade to SOES, dubbed "SuperSOES", that raised the cap on trades in a single transaction from 999 to 999,999. [5]
There were several restrictions for those who used SOES, rather than a traditional electronic communication network (ECN), to place their orders.[ citation needed ]
SOES revamped the trading market for individual investors. It gave small investors and traders the opportunity to compete on a level playing field with larger investors, such as institutions, for access to orders and execution.[ citation needed ]
The Nasdaq Stock Market is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the US by volume, and ranked second on the list of stock exchanges by market capitalization of shares traded, behind the New York Stock Exchange. The exchange platform is owned by Nasdaq, Inc., which also owns the Nasdaq Nordic stock market network and several U.S.-based stock and options exchanges.

Day trading is a form of speculation in securities in which a trader buys and sells a financial instrument within the same trading day, so that all positions are closed before the market closes for the trading day to avoid unmanageable risks and negative price gaps between one day's close and the next day's price at the open. Traders who trade in this capacity are generally classified as speculators. Day trading contrasts with the long-term trades underlying buy-and-hold and value investing strategies. Day trading may require fast trade execution, sometimes as fast as milli-seconds in scalping, therefore direct-access day trading software is often needed.

A market maker or liquidity provider is a company or an individual that quotes both a buy and a sell price in a tradable asset held in inventory, hoping to make a profit on the bid–ask spread, or turn. The benefit to the firm is that it makes money from doing so; the benefit to the market is that this helps limit price variation (volatility) by setting a limited trading price range for the assets being traded.

The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is a law governing the secondary trading of securities in the United States of America. A landmark of wide-ranging legislation, the Act of '34 and related statutes form the basis of regulation of the financial markets and their participants in the United States. The 1934 Act also established the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the agency primarily responsible for enforcement of United States federal securities law.
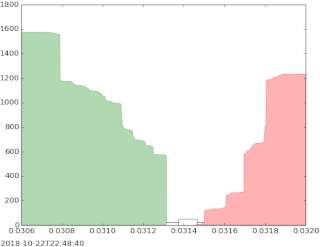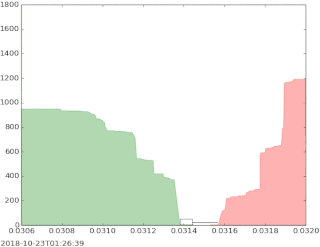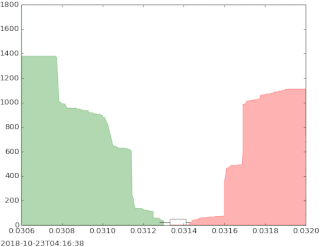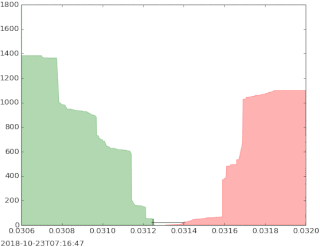
The bid–ask spread is the difference between the prices quoted for an immediate sale (ask) and an immediate purchase (bid) for stocks, futures contracts, options, or currency pairs in some auction scenario. The size of the bid–ask spread in a security is one measure of the liquidity of the market and of the size of the transaction cost. If the spread is 0 then it is a frictionless asset.
An electronic communication network (ECN) is a type of computerized forum or network that facilitates the trading of financial products outside traditional stock exchanges. An ECN is generally an electronic system that widely disseminates orders entered by market makers to third parties and permits the orders to be executed against in whole or in part. The primary products that are traded on ECNs are stocks and currencies. ECNs are generally passive computer-driven networks that internally match limit orders and charge a very small per share transaction fee.
Algorithmic trading is a method of executing orders using automated pre-programmed trading instructions accounting for variables such as time, price, and volume. This type of trading attempts to leverage the speed and computational resources of computers relative to human traders. In the twenty-first century, algorithmic trading has been gaining traction with both retail and institutional traders. A study in 2019 showed that around 92% of trading in the Forex market was performed by trading algorithms rather than humans.
A financial quotation refers to specific market data relating to a security or commodity. While the term quote specifically refers to the bid price or ask price of an instrument, it may be more generically used to relate to the last price which the security traded at. This may refer to both exchange-traded and over-the-counter financial instruments.
Direct market access (DMA) is a term used in financial markets to describe electronic trading facilities that give investors wishing to trade in financial instruments a way to interact with the order book of an exchange. Normally, trading on the order book is restricted to broker-dealers and market making firms that are members of the exchange. Using DMA, investment companies and other private traders use the information technology infrastructure of sell side firms such as investment banks and the market access that those firms possess, but control the way a trading transaction is managed themselves rather than passing the order over to the broker's own in-house traders for execution. Today, DMA is often combined with algorithmic trading giving access to many different trading strategies. Certain forms of DMA, most notably "sponsored access", have raised substantial regulatory concerns because of the possibility of a malfunction by an investor to cause widespread market disruption.
Regulation National Market System is a 2005 US financial regulation promulgated and described by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) as "a series of initiatives designed to modernize and strengthen the National Market System for equity securities". The Reg NMS is intended to assure that investors receive the best (NBBO) price executions for their orders by encouraging competition in the marketplace. Some contend that the rule has contributed to the rise of high-frequency trading, which is sometimes regarded as controversial.

In finance, a dark pool is a private forum for trading securities, derivatives, and other financial instruments. Liquidity on these markets is called dark pool liquidity. The bulk of dark pool trades represent large trades by financial institutions that are offered away from public exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange and the NASDAQ, so that such trades remain confidential and outside the purview of the general investing public. The fragmentation of electronic trading platforms has allowed dark pools to be created, and they are normally accessed through crossing networks or directly among market participants via private contractual arrangements. Generally, dark pools are not available to the public, but in some cases, they may be accessed indirectly by retail investors and traders via retail brokers.
The National Market System (NMS) is a regulatory mechanism that governs the operations of securities trading in the United States. Its primary focus is ensuring transparency and full disclosure regarding stock price quotations and trade executions. It was initiated in 1975, when, in the Securities Acts Amendments of 1975, Congress directed the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to use its authority to facilitate the establishment of a national market system. The system has been updated periodically, for example with the Regulation NMS in 2005 which took into account technological innovations and other market changes.
A multilateral trading facility (MTF) is a European Union regulatory term for a self-regulated financial trading venue. These are alternatives to the traditional stock exchanges where a market is made in securities, typically using electronic systems. The concept was introduced within the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID), a European Directive designed to harmonise retail investors protection and allow investment firms to provide services throughout the EU.

In finance, an electronic trading platform also known as an online trading platform, is a computer software program that can be used to place orders for financial products over a network with a financial intermediary. Various financial products can be traded by the trading platform, over a communication network with a financial intermediary or directly between the participants or members of the trading platform. This includes products such as stocks, bonds, currencies, commodities, derivatives and others, with a financial intermediary, such as brokers, market makers, Investment banks or stock exchanges. Such platforms allow electronic trading to be carried out by users from any location and are in contrast to traditional floor trading using open outcry and telephone based trading. Sometimes the term trading platform is also used in reference to the trading software alone.
Payment for order flow (PFOF) is the compensation that a stockbroker receives from a market maker in exchange for the broker routing its clients' trades to that market maker. It is a controversial practice that has been called a "kickback" by its critics. Policymakers supportive of PFOF and several people in finance who have a favorable view of the practice have defended it for helping develop new investment apps, low-cost trading, and more efficient execution.
High-frequency trading (HFT) is a type of algorithmic trading in finance characterized by high speeds, high turnover rates, and high order-to-trade ratios that leverages high-frequency financial data and electronic trading tools. While there is no single definition of HFT, among its key attributes are highly sophisticated algorithms, co-location, and very short-term investment horizons in trading securities. HFT uses proprietary trading strategies carried out by computers to move in and out of positions in seconds or fractions of a second.
Flash trading, otherwise known as a flash order, is a marketable order sent to a market center that is not quoting the industry's best price or that cannot fill that order in its entirety. The order is then flashed to recipients of the venue's proprietary data feed to see if any of those firms wants to take the other side of the order.

The Knight Capital Group was an American global financial services firm engaging in market making, electronic execution, and institutional sales and trading. With its high-frequency trading algorithms Knight was the largest trader in U.S. equities, with a market share of 17.3% on NYSE and 16.9% on NASDAQ. The company agreed to be acquired by Getco LLC in December 2012 after an August 2012 trading error lost $460 million. The merger was completed in July 2013, forming KCG Holdings.

The May 6, 2010, flash crash, also known as the crash of 2:45 or simply the flash crash, was a United States trillion-dollar flash crash which started at 2:32 p.m. EDT and lasted for approximately 36 minutes.
Island ECN was one of the first electronic communication networks established for the trading equities in the United States. Founded in 1996 by Datek Securities veterans Jeff Citron and Joshua Levine, Island executed its first trades in 1997.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)