
A ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system, there are both sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia which contain the cell bodies of postganglionic sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons respectively.

The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, its force of contraction, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal.

The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.
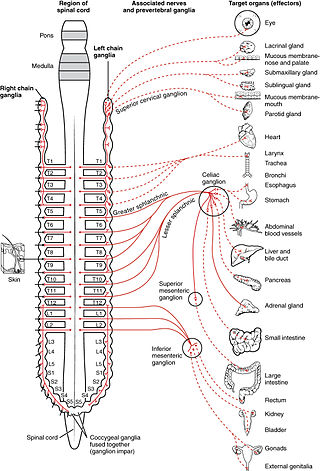
The sympathetic nervous system is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.

The enteric nervous system (ENS) or intrinsic nervous system is one of the three main divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), the others being the sympathetic (SNS) and parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS). It consists of a mesh-like system of neurons that governs the function of the gastrointestinal tract. It is capable of acting independently of the SNS and PSNS, although it may be influenced by them. The ENS is nicknamed the "second brain". It is derived from neural crest cells.
Nervous tissue, also called neural tissue, is the main tissue component of the nervous system. The nervous system regulates and controls body functions and activity. It consists of two parts: the central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) comprising the branching peripheral nerves. It is composed of neurons, also known as nerve cells, which receive and transmit impulses, and neuroglia, also known as glial cells or glia, which assist the propagation of the nerve impulse as well as provide nutrients to the neurons.

The adrenal medulla is the inner part of the adrenal gland. It is located at the center of the gland, being surrounded by the adrenal cortex. It is the innermost part of the adrenal gland, consisting of chromaffin cells that secrete catecholamines, including epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and a small amount of dopamine, in response to stimulation by sympathetic preganglionic neurons.

The pterygopalatine ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion in the pterygopalatine fossa. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck,.

The ciliary ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion located just behind the eye in the posterior orbit. It is 1–2 mm in diameter and in humans contains approximately 2,500 neurons. The ganglion contains postganglionic parasympathetic neurons. These neurons supply the pupillary sphincter muscle, which constricts the pupil, and the ciliary muscle which contracts to make the lens more convex. Both of these muscles are involuntary since they are controlled by the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.
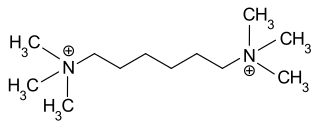
Hexamethonium is a non-depolarising ganglionic blocker, a neuronal nicotinic (nAChR) receptor antagonist that acts in autonomic ganglia by binding mostly in or on the nAChR receptor, and not the acetylcholine binding site itself. It does not have any effect on the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChR) located on target organs of the parasympathetic nervous system, nor on the nicotinic receptors at the skeletal neuromuscular junction, but acts as antagonist at the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors located in sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia (nAChR).

The superior cervical ganglion (SCG) is the upper-most and largest of the cervical sympathetic ganglia of the sympathetic trunk. It probably formed by the union of four sympathetic ganglia of the cervical spinal nerves C1–C4. It is the only ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system that innervates the head and neck. The SCG innervates numerous structures of the head and neck.
Each spinal nerve receives a branch called a gray ramus communicans from the adjacent paravertebral ganglion of the sympathetic trunk. The gray rami communicantes contain postganglionic nerve fibers of the sympathetic nervous system and are composed of largely unmyelinated neurons. This is in contrast to the white rami communicantes, in which heavily myelinated neurons give the rami their white appearance.

In the autonomic nervous system, nerve fibers from the ganglion to the effector organ are called postganglionic nerve fibers.

In the autonomic nervous system, nerve fibers from the central nervous system to the ganglion are known as preganglionic nerve fibers. All preganglionic fibers, whether they are in the sympathetic division or in the parasympathetic division, are cholinergic and they are myelinated.

The celiac ganglia or coeliac ganglia are two large irregularly shaped masses of nerve tissue in the upper abdomen. Part of the sympathetic subdivision of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), the two celiac ganglia are the largest ganglia in the ANS, and they innervate most of the digestive tract.

The sympathetic ganglia, or paravertebral ganglia, are autonomic ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system. Ganglia are 20,000 to 30,000 afferent and efferent nerve cell bodies that run along on either side of the spinal cord. Afferent nerve cell bodies bring information from the body to the brain and spinal cord, while efferent nerve cell bodies bring information from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. The cell bodies create long sympathetic chains that are on either side of the spinal cord. They also form para- or pre-vertebral ganglia of gross anatomy.

The lateral grey column is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord ; the others being the anterior and posterior grey columns. The lateral grey column is primarily involved with activity in the sympathetic division of the autonomic motor system. It projects to the side as a triangular field in the thoracic and upper lumbar regions of the postero-lateral part of the anterior grey column.

Satellite glial cells, formerly called amphicytes, are glial cells that cover the surface of neuron cell bodies in ganglia of the peripheral nervous system. Thus, they are found in sensory, sympathetic, and parasympathetic ganglia. Both satellite glial cells (SGCs) and Schwann cells are derived from the neural crest of the embryo during development. SGCs have been found to play a variety of roles, including control over the microenvironment of sympathetic ganglia. They are thought to have a similar role to astrocytes in the central nervous system (CNS). They supply nutrients to the surrounding neurons and also have some structural function. Satellite cells also act as protective, cushioning cells. Additionally, they express a variety of receptors that allow for a range of interactions with neuroactive chemicals. Many of these receptors and other ion channels have recently been implicated in health issues including chronic pain and herpes simplex. There is much more to be learned about these cells, and research surrounding additional properties and roles of the SGCs is ongoing.

The lumbar ganglia are paravertebral ganglia located in the inferior portion of the sympathetic trunk. The lumbar portion of the sympathetic trunk typically has 4 lumbar ganglia. The lumbar splanchnic nerves arise from the ganglia here, and contribute sympathetic efferent fibers to the nearby plexuses. The first two lumbar ganglia have both white and gray rami communicates.

The ciliary ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion located just behind the eye in the posterior orbit. Three types of axons enter the ciliary ganglion but only the preganglionic parasympathetic axons synapse there. The entering axons are arranged into three roots of the ciliary ganglion, which join enter the posterior surface of the ganglion.
















