
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. Houses use a range of different roofing systems to keep precipitation such as rain from getting into the dwelling space. Houses generally have doors or locks to secure the dwelling space and protect its inhabitants and contents from burglars or other trespassers. Most conventional modern houses in Western cultures will contain one or more bedrooms and bathrooms, a kitchen or cooking area, and a living room. A house may have a separate dining room, or the eating area may be integrated into the kitchen or another room. Some large houses in North America have a recreation room. In traditional agriculture-oriented societies, domestic animals such as chickens or larger livestock may share part of the house with humans.

Shikumen is a traditional Shanghainese architectural style combining Western and Chinese elements that first appeared in the 1860s.

McMansion is a pejorative term for a large, "mass-produced" house in a suburban community that is marketed to the upper middle class in developed countries.

A parking space, parking place or parking spot is a location that is designated for parking, either paved or unpaved. It can be in a parking garage, in a parking lot or on a city street. The space may be delineated by road surface markings. The automobile fits inside the space, either by parallel parking, perpendicular parking or angled parking.
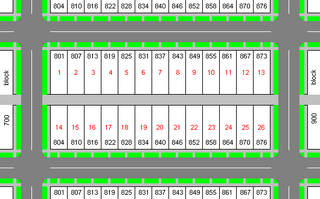
A city block, residential block, urban block, or simply block is a central element of urban planning and urban design.

A multistorey car park or parking garage, also called a multistorey, parking building, parking structure, parkade, parking ramp, parking deck, or indoor parking, is a building designed for car, motorcycle, and bicycle parking in which parking takes place on more than one floor or level. The first known multistorey facility was built in London in 1901, and the first underground parking was built in Barcelona in 1904. The term multistorey is almost never used in the US, because almost all parking structures have multiple parking levels. Parking structures may be heated if they are enclosed.

A single-family detached home, also called a single-detached dwelling,single-family residence (SFR) or separate house is a free-standing residential building. It is defined in opposition to a multi-family residential dwelling.

Ranch is a domestic architectural style that originated in the United States. The ranch-style house is noted for its long, close-to-the-ground profile, and wide open layout. The style fused modernist ideas and styles with notions of the American Western period of wide open spaces to create a very informal and casual living style. While the original ranch style was informal and basic in design, ranch-style houses built in the United States from around the early 1960s increasingly had more dramatic features such as varying roof lines, cathedral ceilings, sunken living rooms, and extensive landscaping and grounds.

A residential garage is a walled, roofed structure with a door for storing a vehicle or vehicles that may be part of or attached to a home, or a separate outbuilding or shed. Residential garages typically have space for one or two cars, although three-car garages are used. When a garage is attached to a house, the garage typically has an entry door into the house, called the person door or man door, in contrast with the wider and taller door for vehicles, called the garage door, which can be opened to permit the entry and exit of a vehicle and then closed to secure the vehicle. A garage protects a vehicle from precipitation, and, if it is equipped with a locking garage door, it also protects the vehicle(s) from theft and vandalism. Most garages also serve multifunction duty as workshops for a variety of projects, including painting, woodworking, and assembly. Garages also may be used for other purposes as well, such as storage or entertainment.

Coving is a method of suburban planning used in subdivision and redevelopment of cities characterized by organic lot shapes and home placement along meandering setbacks. When combined with a new form of street patterns, lot area is increased and road area and length is reduced – a demonstrated average 25% compared to conventional suburban platting. Coving is used as an alternative to conventional urban "grid" and suburban land development layouts to enhance curb appeal, eliminate monotony, reduce costs, such as road surfacing and street length, while increasing the amount of land available for construction. Coving is unique because it gains its efficiency by increasing instead of decreasing existing regulatory minimums.

The American Foursquare is an American house vernacular under the Arts and Crafts style popular from the mid-1890s to the late 1930s. A reaction to the ornate and mass-produced elements of the Victorian and other Revival styles popular throughout the last half of the 19th century, the American Foursquare was plain, often incorporating handcrafted "honest" woodwork. This architectural vernacular incorporates elements of the Prairie School and the Craftsman styles. It is also sometimes called Transitional Period.

A structure gauge, also called the minimum structure outline, is a diagram or physical structure that sets limits to the extent that bridges, tunnels and other infrastructure can encroach on rail vehicles. It specifies the height and width of station platforms, tunnels and bridges, and the width of the doors that allow access to a warehouse from a rail siding. Specifications may include the minimum distance from rail vehicles to railway platforms, buildings, lineside electrical equipment cabinets, signalling equipment, third rails or supports for overhead lines.

In real estate, a Land lot or plot of land is a tract or parcel of land owned or meant to be owned by some owner(s). A plot is essentially considered a parcel of real property in some countries or immovable property in other countries. Possible owners of a plot can be one or more persons or another legal entity, such as a company, corporation, organization, government, or trust. A common form of ownership of a plot is called fee simple in some countries.

A carriage house, also called a remise or coach house, is a term used in North America to describe an outbuilding which was originally built to house horse-drawn carriages and their related tack. Carriage houses were often two stories, with related staff quarters above.
The Blackstone Boulevard Realty Plat Historic District is a historic district roughly bounded by Blackstone Blvd., Rochambeau Ave., Holly St. and Elmgrove Ave. in Providence, Rhode Island.

The bay-and-gable is a distinct residential architectural style that is ubiquitous in the older portions of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The most prominent feature of the style is a large bay window that usually covers more than half the front façade of the home, surmounted by a gable roof. The bay window typically extends from the ground level towards the roof, although a variant of the housing form exists where the bay window fronts only the first level; known as a half-bay-and-gable. The housing form may be built as a stand-alone structure, although it is more often built as a semi-detached, or as terraced houses.

The Normandy is a cooperative apartment building at 140 Riverside Drive, between 86th and 87th Streets, adjacent to Riverside Park on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. Designed by architect Emery Roth in a mixture of the Art Moderne and Renaissance Revival styles, it was constructed from 1938 to 1939. The building was developed by a syndicate composed of Henry Kaufman, Emery Roth, Samson Rosenblatt, and Herman Wacht. The Normandy is 20 stories tall, with small twin towers rising above the 18th story. The building is a New York City designated landmark.

The Middlesex Plat Historic District is located in Des Moines, Iowa, United States. It was an upper-middle-class neighborhood of two-story square houses and bungalows that were built from 1910 to 1923. The district has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places since 2000. It is part of The Bungalow and Square House--Des Moines Residential Growth and Development MPS.

The Fairglen Additions is an example of Mid-century modern-style tract housing located in San Jose, California, US. Comprising 218 single-family houses within the Willow Glen neighborhood of San Jose, this district was built between 1959 and 1961. The additions were developed by real estate developer Joseph Eichler and designed by architectural firms Anshen & Allen, Jones Emmons & Associates, and Claude Oakland Architect & Associates. Thirteen distinct home plans were executed on approximately 6,000 square feet (560 m2) lots. These residences feature open floor plans that accentuate privacy and the seamless transition between indoor and outdoor living, characteristic of Eichler homes and subdivisions. The Fairglen Additions was officially recognized and listed on the National Register of Historic Places on June 6, 2019.



















