Related Research Articles
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard that is used for exchanging data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and building personal area networks (PANs). In the most widely used mode, transmission power is limited to 2.5 milliwatts, giving it a very short range of up to 10 metres (33 ft). It employs UHF radio waves in the ISM bands, from 2.402 GHz to 2.48 GHz. It is mainly used as an alternative to wire connections, to exchange files between nearby portable devices and connect cell phones and music players with wireless headphones.
Adobe Flash is a multimedia software platform used for production of animations, rich internet applications, desktop applications, mobile apps, mobile games, and embedded web browser video players.

OSGi is an open specification and open source project under the Eclipse Foundation. It is a continuation of the work done by the OSGi Alliance, which was an open standards organization for computer software founded in March 1999. The foundation originally specified and maintained the OSGi standard. The alliance transferred its work to the Eclipse Foundation at the end of 2020. The OSGi specification describes a modular system and a service platform for the Java programming language that implements a complete and dynamic component model, something that does not exist in standalone Java or VM environments. It has a service-oriented architecture based on micro services each implemented as an extended Java class file archive.
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. Based on the PostScript language, each PDF file encapsulates a complete description of a fixed-layout flat document, including the text, fonts, vector graphics, raster images and other information needed to display it. PDF has its roots in "The Camelot Project" initiated by Adobe co-founder John Warnock in 1991.
Zigbee is an IEEE 802.15.4-based specification for a suite of high-level communication protocols used to create personal area networks with small, low-power digital radios, such as for home automation, medical device data collection, and other low-power low-bandwidth needs, designed for small scale projects which need wireless connection. Hence, Zigbee is a low-power, low data rate, and close proximity wireless ad hoc network.
OpenMAX, often shortened as "OMX", is a non-proprietary and royalty-free cross-platform set of C-language programming interfaces. It provides abstractions for routines that are especially useful for processing of audio, video, and still images. It is intended for low power and embedded system devices that need to efficiently process large amounts of multimedia data in predictable ways, such as video codecs, graphics libraries, and other functions for video, image, audio, voice and speech.
OMA SpecWorks, previously the Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) is a standards organization which develops open, international technical standards for the mobile phone industry. It is a nonprofit Non-governmental organization (NGO), not a formal government-sponsored standards organization as is the International Telecommunication Union (ITU): a forum for industry stakeholders to agree on common specifications for products and services.
Digital Living Network Alliance was founded by a group of PC and consumer electronics companies in June 2003 to develop and promote a set of interoperability guidelines for sharing digital media among multimedia devices under the auspices of a certification standard. DLNA certified devices include smartphones, tablets, PCs, TV sets and storage servers.
OMA DRM is a digital rights management (DRM) system invented by the Open Mobile Alliance, whose members represent mobile phone manufacturers, mobile system manufacturers, mobile phone network operators, and information technology companies. DRM provides a way for content creators to set enforced limits on the use and duplication of their content by customers. The system is implemented on many recent phones. To date, two versions of OMA DRM have been released: OMA DRM 1.0 and OMA DRM 2.0.

Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) is an open standard that operating systems can use to discover and configure computer hardware components, to perform power management, auto configuration, and status monitoring. First released in December 1996, ACPI aims to replace Advanced Power Management (APM), the MultiProcessor Specification, and the Plug and Play BIOS (PnP) Specification. ACPI brings power management under the control of the operating system, as opposed to the previous BIOS-centric system that relied on platform-specific firmware to determine power management and configuration policies. The specification is central to the Operating System-directed configuration and Power Management (OSPM) system. ACPI defines hardware abstraction interfaces between the device's firmware, the computer hardware components, and the operating systems.
The Trusted Computing Group is a group formed in 2003 as the successor to the Trusted Computing Platform Alliance which was previously formed in 1999 to implement Trusted Computing concepts across personal computers. Members include Intel, AMD, IBM, Microsoft, and Cisco.
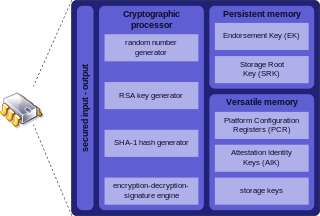
Trusted Platform Module is an international standard for a secure cryptoprocessor, a dedicated microcontroller designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. The term can also refer to a chip conforming to the standard.
OMA Device Management is a device management protocol specified by the Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) Device Management (DM) Working Group and the Data Synchronization (DS) Working Group. The current approved specification of OMA DM is version 1.2.1, the latest modifications to this version released in June 2008. The candidate release 2.0 was scheduled to be finalized in September 2013.
Mobile device management (MDM) is the administration of mobile devices, such as smartphones, tablet computers, and laptops. MDM is usually implemented with the use of a third-party product that has management features for particular vendors of mobile devices. Though closely related to Enterprise Mobility Management and Unified Endpoint Management, MDM differs slightly from both: unlike MDM, EMM includes mobile information management, BYOD, mobile application management and mobile content management, whereas UEM provides device management for endpoints like desktops, printers, IoT devices, and wearables as well.
Red Bend Software is a software company providing mobile software management technology to mobile phone manufacturers and operators. Its software has been deployed by handset manufacturers including Kyocera, LG Electronics, Motorola, Sharp, Sony Mobile, and ZTE, as well as companies in the mobile industry, M2M, automotive and enterprise markets. The company's initial funding was provided by Carmel Ventures.

The .NET Framework is a proprietary software framework developed by Microsoft that runs primarily on Microsoft Windows. It was the predominant implementation of the Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) until being superseded by the cross-platform .NET project. It includes a large class library called Framework Class Library (FCL) and provides language interoperability across several programming languages. Programs written for .NET Framework execute in a software environment named the Common Language Runtime (CLR). The CLR is an application virtual machine that provides services such as security, memory management, and exception handling. As such, computer code written using .NET Framework is called "managed code". FCL and CLR together constitute the .NET Framework.
The Experience API (xAPI) is an e-learning software specification that records and tracks various types of learning experiences for learning systems. Learning experiences are recorded in a Learning Record Store (LRS), which can exist within traditional learning management systems (LMSs) or on their own.
The Physical Security Interoperability Alliance (PSIA) is a global consortium of more than 65 physical security manufacturers and systems integrators focused on promoting interoperability of IP-enabled security devices and systems across the physical security ecosystem as well as enterprise and building automation systems.
OMA Lightweight M2M (LwM2M) is a protocol from the Open Mobile Alliance for machine to machine (M2M) or Internet of things (IoT) device management and service enablement. The LwM2M standard defines the application layer communication protocol between an LwM2M Server and an LwM2M Client which is located in an IoT device. It offers an approach for managing IoT devices and allows devices and systems from different vendors to co-exist in an IoT- ecosystem. LwM2M was originally built on Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) but later LwM2M versions also support additional transfer protocols.
Matter is an open-source connectivity standard for smart home and Internet of things devices, which aims to improve their compatibility and security.
References
- ↑ "ProSyst mBS SDK 8.2: Software Component Management Object". documentation.bosch-si.com. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ↑ "Software Component Management Object: Candidate Version 1.0 – 24 Oct 2008" (PDF). Open Mobile Alliance. 2008. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ↑ Enabler Test Report: Software Component Management Object v1.0 (PDF) (Report). Open Mobile Alliance. 27 Sep 2009. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ↑ "US20130097226A1 - Software Component Information Retrieving Method for SCOMO and Related Service System". Google Patents. 9 April 2012. Retrieved 15 August 2020.