| Type | Private company |
|---|---|
| Industry | Solar panel energy systems |
| Founded | 2003 [1] |
| Founder | Adam Rizzo and Nathan Rizzo |
| Headquarters | Williamsville, NY, , United states |
| Website | solarliberty |
Solar Liberty is an American company that installs, sells and leases solar panel energy systems, known as photovoltaic (PV) systems, for homes, businesses, schools, universities, municipalities, non-profits, and other facilities and properties. [2]
Solar Liberty was founded in 2003 in Buffalo, New York by brothers Adam Rizzo and Nathan Rizzo. Solar Liberty was named #1 Largest Solar Installer in New York State in 2018 (http://www.solarliberty.com/news/335-solar-liberty-recognized-as-top-solar-contractor-in-new-york.html). [3] In 2008 it was ranked number 92 by Inc. Magazine in its annual list of fastest growing private companies in the U.S. [4] In 2012, it was ranked the number 6 fastest-growing private company in Western New York by the Business First publication. [5]
The company headquarters is in Buffalo, NY—with offices in Rochester, Albany, Corning, Syracuse, Binghamton, and Plattsburgh (all in New York).
Solar Liberty is currently the #1 Largest Solar Installer in New York State. Installations are predominantly located in Western, Central New York State, New York City area and Northern Pennsylvania. Notable installations include, but are not limited to: Buffalo City Mission (48 kW, Donated in 2010), University at Buffalo Interactive 'Solar Strand' (2014), Cummins Engines (2013), Rochester Institute of Technology (RIT, 2 MW, 2014), Life Storage (formerly Uncle Bobs Storage, 27 locations, 2015), Town of Holland (2017), City of Rochester (Landfill, 2017), Monroe County (2017), and St. John's Annex Cemetery in Long Island (10 MW, Acquired by PSEG Solar Source, 2017) which is the 'Second-Largest Solar System in New York State).
[6] at the University at Buffalo in Amherst, NY. It is a 750-kilowatt, 3,200 panel photovoltaic array on the university’s north campus. [6] [7]
The Solar Liberty Foundation provides funding for renewable energy projects in developing nations. Completed projects include a health clinic, school and orphanage in Haiti, solar cookers in Kenya, and more solar donations to Liberia and Tanzania. During Fall 2017, a group of Solar Liberty volunteers traveled to Africa to provide solar energy to an all-girls school in Kitenga which is in Tanzania, Africa. This was the first time in history Kitenga has seen electricity. The Solar Liberty Foundation will continue to provide solar energy to underdeveloped communities throughout the world. [8]

Many countries and territories have installed significant solar power capacity into their electrical grids to supplement or provide an alternative to conventional energy sources. Solar power plants use one of two technologies:

First Solar, Inc. is an American manufacturer of solar panels, and a provider of utility-scale PV power plants and supporting services that include finance, construction, maintenance and end-of-life panel recycling. First Solar uses rigid thin-film modules for its solar panels, and produces CdTe panels using cadmium telluride (CdTe) as a semiconductor. The company was founded in 1990 by inventor Harold McMaster as Solar Cells, Inc. and the Florida Corporation in 1993 with JD Polk. In 1999 it was purchased by True North Partners, LLC, who rebranded it as First Solar, Inc.
Blue Oak Energy is an American full-service photovoltaic system design, engineering and consulting firm. The company engineers and commercial and utility solar photovoltaic (PV) energy systems in the United States and abroad.

Solar power represented a very small part of electricity production in the United Kingdom until the 2010s when it increased rapidly, thanks to feed-in tariff (FIT) subsidies and the falling cost of photovoltaic (PV) panels.
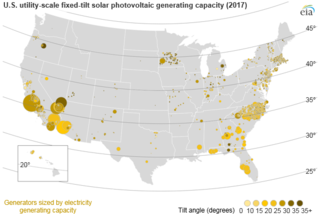
Solar power in the United States includes utility-scale solar power plants as well as local distributed generation, mostly from rooftop photovoltaics and increasingly from community solar arrays. As of the end of 2021, the United States had 121,475 megawatts (MW) of installed photovoltaic and concentrated solar power capacity combined. In 2018, utility-scale solar power generated 66.6 terawatt-hours (TWh), 1.66% of total U.S. electricity. During the same time period total solar generation, including estimated small-scale photovoltaic generation, was 96.1 TWh, 2.30% of total U.S. electricity. In terms of total cumulative installed capacity, by year end 2017 the United States ranked 2nd in the world behind China. In 2016, 39% of all new electricity generation capacity in the country came from solar, more than any other source and ahead of natural gas (29%). By 2015, solar employment had overtaken oil and gas as well as coal employment in the United States. In 2016, more than 260,000 Americans were employed in the solar industry.
SolarCity Corporation was a publicly traded company headquartered in Fremont, California that sold and installed solar energy generation systems as well as other related products and services to residential, commercial, and industrial customers. The company was founded on July 4, 2006, by Peter and Lyndon Rive, the cousins of SpaceX and Tesla, Inc. CEO Elon Musk, and nephews of model Maye Musk. Tesla acquired SolarCity in 2016, at a cost of approximately $2.6 billion and reorganized its solar business into Tesla Energy.

Solar power in New Jersey has grown significantly, increasing from less than 50 megawatts (MW) in 2007 to over 2,800 MW in 2018, such that solar power provided 4.17% of the state's electricity consumption. This is aided by a Renewable Portfolio Standard which requires that 22.5% of New Jersey's electricity come from renewable resources by 2021, and by one of the most favorable net metering standards in the country, along with Arizona, allowing unlimited customers of any size array to use net metering, although generation may not exceed annual demand. Best practices recommend limiting net metering only to the size of the customer’s service entrance capacity. As of 2018, New Jersey has the sixth-largest installed solar capacity of all U.S. states and the largest installed solar capacity of the Northeastern States.

Solar power in Arizona has the potential to, according to then-Governor Janet Napolitano, make Arizona "the Persian Gulf of solar energy". In 2012, Arizona had 1,106 MW of photovoltaic (PV) solar power systems, and 6 MW of concentrated solar power (CSP), bringing the total to over 1,112 megawatts (MW) of solar power. As an example, the Solana Generating Station, a 280 MW parabolic trough solar plant, when commissioned in 2013, was the largest parabolic trough plant in the world and the first U.S. solar plant with molten salt thermal energy storage.
REC Solar was a solar energy contractor specializing in commercial solar and storage systems, including the installation of commercial solar electric systems in the United States. The company focused on providing products and services to support commercial, government and utility scale solar photovoltaic (PV) installations.

The energy sector in Hawaii has rapidly adopted solar power due to the high costs of electricity, and good solar resources, and has one of the highest per capita rates of solar power in the United States. Hawaii's imported energy costs, mostly for imported petroleum and coal, are three to four times higher than the mainland, so Hawaii has motivation to become one of the highest users of solar energy. Hawaii was the first state in the United States to reach grid parity for photovoltaics. Its tropical location provides abundant ambient energy.

Sunetric is a Hawaii-based photovoltaic solar power company that performs consultation, design, and installation of photovoltaic systems for residential, commercial, military, and non-profit customers. Sunetric operates on all of the Hawaiian islands and in several states in the continental US. The company was founded in 2004 as Suntech Hawaii by Sean Mullen. Alex Tiller is the company's CEO. The company handles system consulting, design, and installation, and remains responsible for maintenance, monitoring, and repairs.

A photovoltaic power station, also known as a solar park, solar farm, or solar power plant, is a large-scale grid-connected photovoltaic power system designed for the supply of merchant power. They are differentiated from most building-mounted and other decentralised solar power because they supply power at the utility level, rather than to a local user or users. The generic expression utility-scale solar is sometimes used to describe this type of project.

Solar power in Ohio has been increasing, as the cost of photovoltaics has decreased. Ohio installed 10 MW of solar in 2015. Ohio adopted a net metering rule which allows any customer generating up to 25 kW to use net metering, with the kilowatt hour surplus rolled over each month, and paid by the utility once a year at the generation rate upon request. For hospitals there is no limit on size, but two meters are required, one for generation, the other for utility supplied power.

Solar power in New Zealand is on the rise, but there are no of subsidies or intervention from the New Zealand Government. As at the end of December 2021, New Zealand has 186.7 MW of grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) solar power installed, of which 72.4 MW (8.8%) was installed in the preceding 24 months. In the year to December 2020, 159,000 megawatt-hours of electricity was generated by solar power, or 0.37% of all electricity generated in the country.

Solar power in New Hampshire provides a small percentage of the state's electricity. State renewable requirements and declining prices have led to some installations. Photovoltaics on rooftops can provide 53.4% of all electricity used in New Hampshire, from 5,300 MW of solar panels, and 72% of the electricity used in Concord, New Hampshire. A 2016 estimate suggests that a typical 5 kW system costing $25,000 before credits and utility savings will pay for itself in 9 years, and generate a profit of $34,196 over the rest of its 25-year life. A loan or lease provides a net savings each year, including the first year. New Hampshire has a rebate program which pays $0.75/W for residential systems up to 5 kW, for up to 50% of the system cost, up to $3,750. However, New Hampshire's solar installation lagged behind nearby states such as Vermont and New York, which in 2013 had 10 times and 25 times more solar, respectively.

The Hickory Ridge Landfill is a municipal solid waste landfill located in Conley, Georgia, United States and privately owned by Republic Services. The site was opened in 1993 and closed in 2006; it contains nearly 9,000,000 cubic yards of waste.

Tesla Energy is the clean energy subsidiary of Tesla, Inc., headquartered in Fremont, California, that develops, manufactures, sells and installs photovoltaic solar energy generation systems, battery energy storage products, as well as other related products and services to residential, commercial and industrial customers.

Zep Solar was a manufacturer of mounting and grounding equipment for photovoltaic solar energy generation systems. The company was founded by entrepreneur and inventor Jack West in 2009 in San Rafael, California. In 2013, Zep Solar was acquired by SolarCity, which was, at the time, the largest solar power installer in the United States. Zep Solar operated as an independent business unit of SolarCity until SolarCity was acquired by Tesla, Inc. in 2016, at which time Zep Solar was merged into the company's Tesla Energy subsidiary.

Agrivoltaics,agrophotovoltaics,agrisolar, or dual-use solar is the simultaneous use of areas of land for both solar photovoltaic power generation and agriculture. The coexistence of solar panels and crops implies a sharing of light between these two types of production, so the design of agrivoltaic facilities may require trading off such objectives as optimizing crop yield, crop quality, and energy production. However, in some cases crop yield increases due to the shade of the solar panels mitigating some of the stress on plants caused by high temperatures and UV damage.
SunCommon is a Vermont-based installer of residential solar power systems. It is headquartered in Waterbury, Vermont. The business was co-founded by Duane Peterson and James Moore.
http://www.solarliberty.com/news/335-solar-liberty-recognized-as-top-solar-contractor-in-new-york.html https://www.wnypapers.com/news/article/current/2018/07/26/133485/buffalo-based-solar-liberty-recognized-as-top-solar-contractor-in-new-york