Related Research Articles

A sloop is a sailboat with a single mast typically having only one headsail in front of the mast and one mainsail aft of (behind) the mast. Such an arrangement is called a fore-and-aft rig, and can be rigged as a Bermuda rig with triangular sails fore and aft, or as a gaff-rig with triangular foresail(s) and a gaff rigged mainsail.
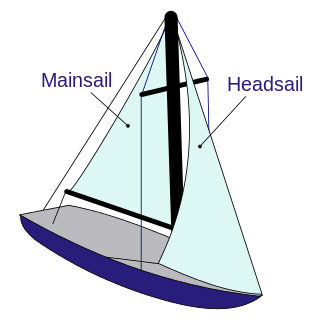
A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture.

A sailing vessel's rig is its arrangement of masts, sails and rigging. Examples include a schooner rig, cutter rig, junk rig, etc. A rig may be broadly categorized as "fore-and-aft", "square", or a combination of both. Within the fore-and-aft category there is a variety of triangular and quadrilateral sail shapes. Spars or battens may be used to help shape a given kind of sail. Each rig may be described with a sail plan—formally, a drawing of a vessel, viewed from the side.
A jib is a triangular sail that sets ahead of the foremast of a sailing vessel. Its forward corner (tack) is fixed to the bowsprit, to the bows, or to the deck between the bowsprit and the foremost mast. Jibs and spinnakers are the two main types of headsails on a modern boat.

On a sailing vessel, a forestay, sometimes just called a stay, is a piece of standing rigging which keeps a mast from falling backwards. It is attached either at the very top of the mast, or in fractional rigs between about 1/8 and 1/4 from the top of the mast. The other end of the forestay is attached to the bow of the boat.

A staysail ("stays'l") is a fore-and-aft rigged sail whose luff can be affixed to a stay running forward from a mast to the deck, the bowsprit, or to another mast.

A genoa sail is a type of large jib or staysail that extends past the mast and so overlaps the main sail when viewed from the side, sometimes eliminating it. It was originally called an "overlapping jib" and later a genoa jib. It is used on single-masted sloops and twin-masted boats such as yawls and ketches. Its larger surface area increases the speed of the craft in light to moderate winds; in high wind, a smaller jib is usually substituted, and downwind a spinnaker may be used.

A spinnaker is a sail designed specifically for sailing off the wind on courses between a reach to downwind. Spinnakers are constructed of lightweight fabric, usually nylon, and are often brightly colored. They may be designed to perform best as either a reaching or a running spinnaker, by the shaping of the panels and seams. They are attached at only three points and said to be flown.

A mainsail is a sail rigged on the main mast of a sailing vessel.

A cutter is a name for various types of watercraft. It can apply to the rig of a sailing vessel, to a governmental enforcement agency vessel, to a type of ship's boat which can be used under sail or oars, or, historically, to a type of fast-sailing vessel introduced in the 18th century, some of which were used as small warships.

Gaff rig is a sailing rig in which the sail is four-cornered, fore-and-aft rigged, controlled at its peak and, usually, its entire head by a spar (pole) called the gaff. Because of the size and shape of the sail, a gaff rig will have running backstays rather than permanent backstays.

Sail components include the features that define a sail's shape and function, plus its constituent parts from which it is manufactured. A sail may be classified in a variety of ways, including by its orientation to the vessel and its shape,. Sails are typically constructed out of flexible material that is shaped by various means, while in use, to offer an appropriate airfoil, according to the strength and apparent direction of the wind. A variety of features and fittings allow the sail to be attached to lines and spars.

A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing vessel with a sail plan of three or more masts, all of them square-rigged. Such a vessel is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged, with each mast stepped in three segments: lower, top, and topgallant.

A fractional rig on a sailing vessel consists of a foresail, such as a jib or genoa sail, that does not reach all the way to the top of the mast.
A mast-aft rig is a sailboat sail-plan that uses a single mast set in the aft half of the hull. The mast supports fore-sails that may consist of a single jib, multiple staysails, or a crab claw sail. The mainsail is either small or completely absent. Mast-aft rigs are uncommon, but are found on a few custom, and production sailboats.

Roller furling is a method of furling a yacht's staysail by rolling the sail around a stay. Roller furling is typically used for foresails such as jibs or genoas.

An asymmetrical spinnaker is a sail used when sailing between about 90 and 165 degrees from the angle of the wind. Also known as an "asym", "aspin", or "A-sail" it can be described as a cross between a genoa jib and a spinnaker. It is asymmetric like a genoa, but like a spinnaker, its luff is unstructured; its leading edge is allowed to float freely, unencumbered by an internal wire or hanks attaching it to a stay. Unlike a symmetric spinnaker, the asymmetric does not require a spinnaker pole, since it is fixed (tacked) to the bow or a bowsprit.

A masthead rig on a sailing vessel consists of a forestay and backstay both attached at the top of the mast.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to sailing:

A sail plan is a drawing of a sailing craft, viewed from the side, depicting its sails, the spars that carry them and some of the rigging that supports the rig. By extension, "sail plan" describes the arrangement of sails on a craft. A sailing craft may be waterborne, an iceboat, or a sail-powered land vehicle.
References
- ↑ "The Solent Has Its Own Stay!". The Rigging Company. April 10, 2017.
- ↑ "Solent Stay". www.svsarah.com.
- ↑ "Bluewater Cruising: Cutter Rig versus Solent Rig - Part 2". www.sail-world.com.
- ↑ "Hank on vs Furling". Rigging Doctor. 14 September 2015.