
Rigging comprises the system of ropes, cables and chains, which support and control a sailing ship or sail boat's masts and sails. Standing rigging is the fixed rigging that supports masts including shrouds and stays. Running rigging is rigging which adjusts the position of the vessel's sails and spars including halyards, braces, sheets and vangs.
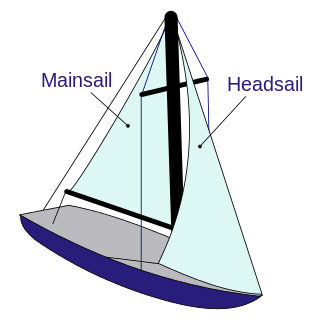
A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture.
A jib is a triangular sail that sets ahead of the foremast of a sailing vessel. Its tack is fixed to the bowsprit, to the bows, or to the deck between the bowsprit and the foremost mast. Jibs and spinnakers are the two main types of headsails on a modern boat.

On a sailing vessel, a forestay, sometimes just called a stay, is a piece of standing rigging which keeps a mast from falling backwards. It is attached either at the very top of the mast, or in fractional rigs between about 1/8 and 1/4 from the top of the mast. The other end of the forestay is attached to the bow of the boat.

A backstay is a piece of standing rigging on a sailing vessel that runs from the mast to either its transom or rear quarter, counteracting the forestay and jib. It is an important sail trim control and has a direct effect on the shape of the mainsail and the headsail. Backstays are generally adjusted by block and tackle, hydraulic adjusters, or lines leading to winches.

A spinnaker is a sail designed specifically for sailing off the wind on courses between a reach to downwind. Spinnakers are constructed of lightweight fabric, usually nylon, and are often brightly colored. They may be designed to perform best as either a reaching or a running spinnaker, by the shaping of the panels and seams. They are attached at only three points and said to be flown.

A mainsail is a sail rigged on the main mast of a sailing vessel.

In sailing, a boom is a spar (pole), along the of a fore and aft rigged sail, that greatly improves control of the angle and shape of the sail. The primary action of the boom is to keep the foot flatter when the sail angle is away from the centerline of the boat. The boom also serves as an attachment point for more sophisticated control lines. Because of the improved sail control it is rare to find a non-headsail without a boom, but lateen sails, for instance, are loose-footed. In some modern applications, the sail is rolled up into the boom for storage or reefing.

A fractional rig on a sailing vessel consists of a foresail, such as a jib or genoa sail, that does not reach all the way to the top of the mast.

The C Scow is an American sailing dinghy that was designed by John O. Johnson as a one-design racer and first built as early as 1905. Sources disagree as to the first-built date, with claims of 1905, 1906 and 1923.

The topping lift is a line which applies upward force on a boom on a sailboat.
A mast-aft rig is a sailboat sail-plan that uses a single mast set in the aft half of the hull. The mast supports fore-sails that may consist of a single jib, multiple staysails, or a crab claw sail. The mainsail is either small or completely absent. Mast-aft rigs are uncommon, but are found on a few custom, and production sailboats.

A trailer sailer is a type of sailboat that has been designed to be easily transported using a boat trailer towed by an automobile. They are generally larger than a sailing dinghy. Trailer sailers include day sailers and small cabin cruisers, suitable for living on.

A masthead rig on a sailing vessel consists of a forestay and backstay both attached at the top of the mast.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to sailing:

The B&R rig is a variant of the Bermuda sailboat rig, designed and patented by Swedish aeronautical engineers Lars Bergström and Sven Ridder. It employs swept spreaders that are usually angled aft, together with "stays" running diagonally downward from the tip of the spreaders to the attachment of the next pair of spreaders to the mast or to the intersection of the mast with the deck that facilitates a pre-bend of the mast that is sometimes tuned into the rig before it is stepped onto the boat. Conventional shrouds thereby contribute to both lateral and longitudinal stability, unlike rigs with unswept spreaders. A B&R rig can be a masthead or fractional rig depending on how stays are configured; a backstay is optional. Such rigs are employed in many of the models of at least one U.S. manufacturer and in many thousands of boats, worldwide.
The DB-1 is a West German sailboat that was designed by E. G. van de Stadt and Cees van Tongeren as an International Offshore Rule Three-Quarter Ton class racer and first built in 1980.
The DB-2 is a West German sailboat that was designed by E. G. van de Stadt and Cees van Tongeren as an International Offshore Rule Three-Quarter Ton class racer and first built in 1981.
A solent refers to a sail and rigging system on sailboats, typically sloops. Sailors, particularly British sailors, often refer to a 100% jib as a Solent, because its smaller size is preferable when sailing in the strong winds found in the Solent between the Isle of Wight and Britain. The common use of roller-furling headsails, or genoas, on modern cruising yachts allows the jib to be reduced in size, but partially-furled sails lack the efficiency of a sail that is actually cut to a smaller size. Accordingly, it is preferable to fly a separate, smaller jib—the solent—instead.
The Dolphin 17 is an American trailerable sailboat that was designed by Glenn Corcorran and Murray Corcorran and first built in 1970.











