
A yacht is a sailing or power vessel used for pleasure, cruising, or racing. There is no standard definition, though the term generally applies to vessels with a cabin intended for overnight use. To be termed a yacht, as opposed to a boat, such a pleasure vessel is likely to be at least 33 feet (10 m) in length and may have been judged to have good aesthetic qualities.
A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture.

A sailing vessel's rig is its arrangement of masts, sails and rigging. Examples include a schooner rig, cutter rig, junk rig, etc. A rig may be broadly categorized as "fore-and-aft", "square", or a combination of both. Within the fore-and-aft category there is a variety of triangular and quadrilateral sail shapes. Spars or battens may be used to help shape a given kind of sail. Each rig may be described with a sail plan—formally, a drawing of a vessel, viewed from the side.

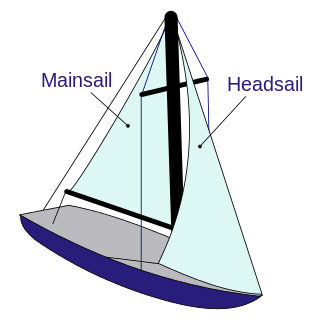
A mainsail is a sail rigged on the main mast of a sailing vessel.

Sail components include the features that define a sail's shape and function, plus its constituent parts from which it is manufactured. A sail may be classified in a variety of ways, including by its orientation to the vessel and its shape,. Sails are typically constructed out of flexible material that is shaped by various means, while in use, to offer an appropriate airfoil, according to the strength and apparent direction of the wind. A variety of features and fittings allow the sail to be attached to lines and spars.

Hobie Cat is a company that manufactures sailing catamarans, surfboards, sailboats, kayaks, stand-up paddle boards, and pedalboards as the Hobie Cat Company. It was founded in 1961 by Hobart Alter, who originally manufactured surfboards. Its line of products has included more than twenty sailing craft, plus a variety of other watercraft.

The junk rig, also known as the Chinese lugsail, Chinese balanced lug sail, or sampan rig, is a type of sail rig in which rigid members, called battens, span the full width of the sail and extend the sail forward of the mast.
A mast-aft rig is a sailboat sail-plan that uses a single mast set in the aft half of the hull. The mast supports fore-sails that may consist of a single jib, multiple staysails, or a crab claw sail. The mainsail is either small or completely absent. Mast-aft rigs are uncommon, but are found on a few custom, and production sailboats.

A sailing yacht, is a leisure craft that uses sails as its primary means of propulsion. A yacht may be a sail or power vessel used for pleasure, cruising, or racing. There is no standard definition, so the term applies here to sailing vessels that have a cabin with amenities that accommodate overnight use. To be termed a "yacht", as opposed to a "boat", such a vessel is likely to be at least 33 feet (10 m) in length and have been judged to have good aesthetic qualities. Sailboats that do not accommodate overnight use or are smaller than 30 feet (9.1 m) are not universally called yachts. Sailing yachts in excess of 130 feet (40 m) are generally considered to be superyachts.

The NS14 is an Australian restricted development class of sailing dinghy. Measuring 14 feet in length, the class was designed the 1960 and introduced at the Northbridge sailing club in Sydney, Australia, with control of the class transferred to the NS14 Association of New South Wales in 1965. Subsequently the boat was introduced to the other states, prior to being taken to New Zealand in 1995 and the United States in 1998.

A sail is a tensile structure, which is made from fabric or other membrane materials, that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails may be made from a combination of woven materials—including canvas or polyester cloth, laminated membranes or bonded filaments, usually in a three- or four-sided shape.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to sailing:
The Freedom 25 is an American sailboat that was designed by Gary Hoyt as a single-handed racer-cruiser and first built in 1980.
The Stiletto 27 is an American trailerable catamaran sailboat that was designed by Bill Higgins and Don Ansley as a racer/cruiser and first built in 1976.
The Gougeon 32 is an American trailerable catamaran that was designed by Jan Gougeon and first built in 1990.

The Hobie 14 is an American catamaran sailing dinghy that was designed by Hobie Alter and first built in 1967.
The Trac 14 is an American catamaran sailing dinghy that was designed by Australians Richard McFarlane and Jay McFarlane as a one-design racer and first built in 1980.
The Nacra 5.2 is an American catamaran sailing dinghy that was designed by Tom Roland as a one-design racer and first built in 1975. Other than the small production run Nacra 36, the Nacra 5.2 was the first Nacra brand boat and established its reputation.
The Isotope is an American catamaran sailing dinghy that was designed by Frank Meldau as a one-design racer and first built in 1962.
The Prindle 18 is an American catamaran sailing dinghy that was designed by Geoffrey Prindle as a racer and first built in 1977.












