Related Research Articles

Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the water, on ice (iceboat) or on land over a chosen course, which is often part of a larger plan of navigation.

A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships carry square sails on each mast—the brig and full-rigged ship, said to be "ship-rigged" when there are three or more masts. Others carry only fore-and-aft sails on each mast, for instance some schooners. Still others employ a combination of square and fore-and-aft sails, including the barque, barquentine, and brigantine.

A sailing vessel's rig is its arrangement of masts, sails and rigging. Examples include a schooner rig, cutter rig, junk rig, etc. A rig may be broadly categorized as "fore-and-aft", "square", or a combination of both. Within the fore-and-aft category there is a variety of triangular and quadrilateral sail shapes. Spars or battens may be used to help shape a given kind of sail. Each rig may be described with a sail plan—formally, a drawing of a vessel, viewed from the side.

A point of sail is a sailing craft's direction of travel under sail in relation to the true wind direction over the surface.

A jibe (US) or gybe (Britain) is a sailing maneuver whereby a sailing craft reaching downwind turns its stern through the wind, which then exerts its force from the opposite side of the vessel. It stands in contrast with tacking, whereby the sailing craft turns its bow through the wind.
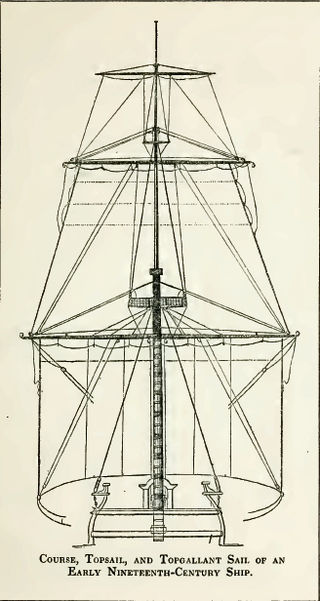
A topsail ("tops'l") is a sail set above another sail; on square-rigged vessels further sails may be set above topsails.

A barquentine or schooner barque is a sailing vessel with three or more masts; with a square rigged foremast and fore-and-aft rigged main, mizzen and any other masts.

Gaff rig is a sailing rig in which the sail is four-cornered, fore-and-aft rigged, controlled at its peak and, usually, its entire head by a spar (pole) called the gaff. Because of the size and shape of the sail, a gaff rig will have running backstays rather than permanent backstays.
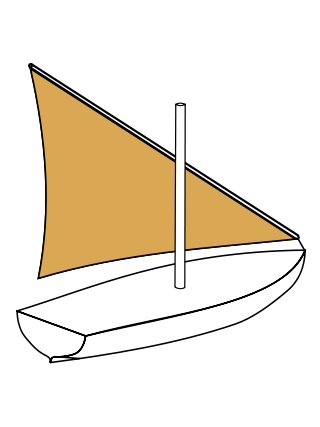
A lateen or latin-rig is a triangular sail set on a long yard mounted at an angle on the mast, and running in a fore-and-aft direction. The settee can be considered to be an associated type of the same overall category of sail.

Running rigging is the rigging of a sailing vessel that is used for raising, lowering, shaping and controlling the sails on a sailing vessel—as opposed to the standing rigging, which supports the mast and bowsprit. Running rigging varies between vessels that are rigged fore and aft and those that are square-rigged.

The mast of a sailing vessel is a tall spar, or arrangement of spars, erected more or less vertically on the centre-line of a ship or boat. Its purposes include carrying sails, spars, and derricks, giving necessary height to a navigation light, look-out position, signal yard, control position, radio aerial or signal lamp. Large ships have several masts, with the size and configuration depending on the style of ship. Nearly all sailing masts are guyed.

A yard is a spar on a mast from which sails are set. It may be constructed of timber or steel or from more modern materials such as aluminium or carbon fibre. Although some types of fore and aft rigs have yards, the term is usually used to describe the horizontal spars used on square rigged sails. In addition, for some decades after square sails were generally dispensed with, some yards were retained for deploying wireless (radio) aerials and signal flags.

Sail components include the features that define a sail's shape and function, plus its constituent parts from which it is manufactured. A sail may be classified in a variety of ways, including by its orientation to the vessel and its shape,. Sails are typically constructed out of flexible material that is shaped by various means, while in use, to offer an appropriate airfoil, according to the strength and apparent direction of the wind. A variety of features and fittings allow the sail to be attached to lines and spars.

A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing vessel with a sail plan of three or more masts, all of them square-rigged. Such a vessel is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged, with each mast stepped in three segments: lower, top, and topgallant.
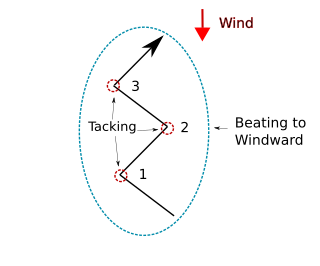
Tacking or coming about is a sailing maneuver by which a sailing craft, whose next destination is into the wind, turns its bow toward and through the wind so that the direction from which the wind blows changes from one side of the boat to the other, allowing progress in the desired direction. Sailing vessels are unable to sail higher than a certain angle towards the wind, so "beating to windward" in a zig-zag fashion with a series of tacking maneuvers, allows a vessel to sail towards a destination that is closer to the wind than the vessel can sail directly.
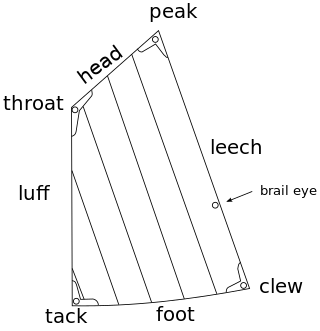
The spritsail is a four-sided, fore-and-aft sail that is supported at its highest points by the mast and a diagonally running spar known as the sprit. The foot of the sail can be stretched by a boom or held loose-footed just by its sheets. A spritsail has four corners: the throat, peak, clew, and tack. The Spritsail can also be used to describe a rig that uses a spritsail.

The junk rig, also known as the Chinese lugsail, Chinese balanced lug sail, or sampan rig, is a type of sail rig in which rigid members, called battens, span the full width of the sail and extend the sail forward of the mast. While relatively uncommon in use among modern production sailboats, the rig's advantages of easier use and lower maintenance for blue-water cruisers have been explored by individuals such as trans-Atlantic racer Herbert "Blondie" Hasler and author Annie Hill.
The term to square a yard is used when sailing a square-rigged ship.
The settee sail was a lateen sail with the front corner cut off, giving it a quadrilateral shape. The settee sail requires a shorter yard than does the lateen, and both settee and lateen have shorter masts than square-rigged sails.

A sail is a tensile structure, which is made from fabric or other membrane materials, that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails may be made from a combination of woven materials—including canvas or polyester cloth, laminated membranes or bonded filaments, usually in a three- or four-sided shape.