
A sloop is a sailboat with a single mast typically having only one headsail in front of the mast and one mainsail aft of (behind) the mast. Such an arrangement is called a fore-and-aft rig, and can be rigged as a Bermuda rig with triangular sails fore and aft, or as a gaff-rig with triangular foresail(s) and a gaff rigged mainsail.

A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships carry square sails on each mast—the brig and full-rigged ship, said to be "ship-rigged" when there are three or more masts. Others carry only fore-and-aft sails on each mast, for instance some schooners. Still others employ a combination of square and fore-and-aft sails, including the barque, barquentine, and brigantine.
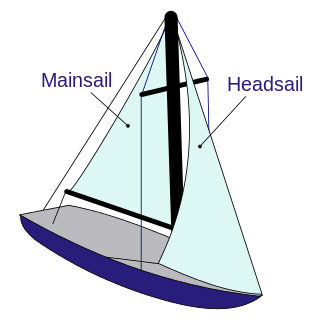
A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture.

A sailing vessel's rig is its arrangement of masts, sails and rigging. Examples include a schooner rig, cutter rig, junk rig, etc. A rig may be broadly categorized as "fore-and-aft", "square", or a combination of both. Within the fore-and-aft category there is a variety of triangular and quadrilateral sail shapes. Spars or battens may be used to help shape a given kind of sail. Each rig may be described with a sail plan—formally, a drawing of a vessel, viewed from the side.

A yawl is a type of boat. The term has several meanings. It can apply to the rig, to the hull type or to the use which the vessel is put.
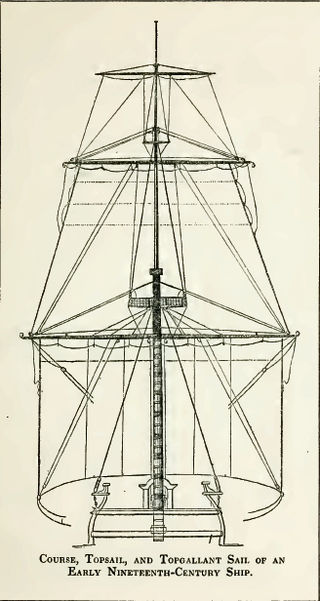
A topsail ("tops'l") is a sail set above another sail; on square-rigged vessels further sails may be set above topsails.

A staysail ("stays'l") is a fore-and-aft rigged sail whose luff can be affixed to a stay running forward from a mast to the deck, the bowsprit, or to another mast.
In sailing, a snow, snaw or snauw is a square-rigged vessel with two masts, complemented by a snow- or trysail-mast stepped immediately abaft (behind) the main mast.

A cutter is a name for various types of watercraft. It can apply to the rig of a sailing vessel, to a governmental enforcement agency vessel, to a type of ship's boat which can be used under sail or oars, or, historically, to a type of fast-sailing vessel introduced in the 18th century, some of which were used as small warships.

Running rigging is the rigging of a sailing vessel that is used for raising, lowering, shaping and controlling the sails on a sailing vessel—as opposed to the standing rigging, which supports the mast and bowsprit. Running rigging varies between vessels that are rigged fore and aft and those that are square-rigged.

A lugger is a sailing vessel defined by its rig, using the lug sail on all of its one or more masts. Luggers were widely used as working craft, particularly off the coasts of France, England, Ireland and Scotland. Luggers varied extensively in size and design. Many were undecked, open boats, some of which operated from beach landings. Others were fully decked craft. Some larger examples might carry lug topsails.

The mast of a sailing vessel is a tall spar, or arrangement of spars, erected more or less vertically on the centre-line of a ship or boat. Its purposes include carrying sails, spars, and derricks, giving necessary height to a navigation light, look-out position, signal yard, control position, radio aerial or signal lamp. Large ships have several masts, with the size and configuration depending on the style of ship. Nearly all sailing masts are guyed.

A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing vessel with a sail plan of three or more masts, all of them square-rigged. Such a vessel is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged, with each mast stepped in three segments: lower, top, and topgallant.

Gunter rig is a configuration of sail and spars used in sailing. It is a fore and aft sail set abaft (behind) the mast. The lower half of the luff (front) of the sail is attached to the mast, and the upper half is fastened to a spar which is approximately vertical and reaches above the top of the mast. This spar is called a "yard", but it is common for some to confuse it with a "gaff". The overall shape of a gunter sail is roughly triangular, so having a superficial resemblance to Bermuda rig.

A Thames sailing barge is a type of commercial sailing boat once common on the River Thames in London. The flat-bottomed barges, with a shallow draught and leeboards, were perfectly adapted to the Thames Estuary, with its shallow waters and narrow tributary rivers. The larger barges were seaworthy vessels, and were the largest sailing vessel to be handled by just two men. The average size was about 120 tons and they carried 4,200 square feet (390 m2) of canvas sail in six working sails. The mainsail was loose-footed and set up with a sprit, and was brailed to the mast when not needed. It is sheeted to a horse, as is the foresail; they require no attention when tacking. The foresail is often held back by the mate to help the vessel come about more swiftly.

Blackadder was a clipper, a sister ship to Hallowe'en, built in 1870 by Maudslay, Sons & Field at Greenwich for Jock Willis & Sons.

A polacca is a type of seventeenth- to nineteenth-century sailing vessel, similar to the xebec. The name is the feminine of "Polish" in the Italian language. The polacca was frequently seen in the Mediterranean. It had two or three single-pole masts, the three-masted vessels often with a lateen hoisted on the foremast and a gaff or lateen on the mizzen mast. The mainmast was square-rigged after the European style. Special polaccas were used by Murat Reis, whose ships had lateen sails in front and fore-and-aft rig behind.

A jackass-barque, sometimes spelled jackass bark, is a sailing ship with three masts, of which the foremast is square-rigged and the main is partially square-rigged and partially fore-and-aft rigged (course). The mizzen mast is fore-and-aft rigged.

Potosi was a five-masted steel barque built in 1865 by Joh. C. Tecklenborg ship yard in Geestemünde, Germany, for the sailing ship company F. Laeisz as a trading vessel. Its primary purpose was as a "nitrate clipper" collecting guano in South America for use in chemical companies in Germany. As its shipping route was between Germany, Bolivia until 1870 but, during the "pacific War" was transferred to Chile, it was designed to be capable of withstanding the rough weather encountered around Cape Horn.

Literally, the word pinisi refers to a type of rigging of Indonesian sailing vessels. A pinisi carries seven to eight sails on two masts, arranged like a gaff-ketch with what is called 'standing gaffs' — i.e., unlike most Western ships using such a rig, the two main sails are not opened by raising the spars they are attached to, but the sails are 'pulled out' like curtains along the gaffs which are fixed at around the centre of the masts.





















