A jib is a triangular sail that sets ahead of the foremast of a sailing vessel. Its tack is fixed to the bowsprit, to the bows, or to the deck between the bowsprit and the foremost mast. Jibs and spinnakers are the two main types of headsails on a modern boat.

Mayflower II is a reproduction of the 17th-century ship Mayflower, celebrated for transporting the Pilgrims to the New World in 1620. The reproduction was built in Devon, England during 1955–1956, in a collaboration between Englishman Warwick Charlton and Plimoth Patuxet, a living history museum. The work drew upon reconstructed ship blueprints held by the American museum, along with hand construction by English shipbuilders using traditional methods. Mayflower II was sailed from Plymouth, Devon on April 20, 1957, recreating the original voyage across the Atlantic Ocean, under the command of Alan Villiers. According to the ship's log, Mayflower II arrived at Plymouth on June 22; it was towed up the East River into New York City on Monday, July 1, 1957, where Villiers and crew received a ticker-tape parade. The ship was listed on the US National Register of Historic Places in 2020.

Boat building is the design and construction of boats and their systems. This includes at a minimum a hull, with propulsion, mechanical, navigation, safety and other systems as a craft requires.

A spinnaker is a sail designed specifically for sailing off the wind on courses between a reach to downwind. Spinnakers are constructed of lightweight fabric, usually nylon, and are often brightly colored. They may be designed to perform best as either a reaching or a running spinnaker, by the shaping of the panels and seams. They are attached at only three points and said to be flown.

A cutter is a name for various types of watercraft. It can apply to the rig of a sailing vessel, to a governmental enforcement agency vessel, to a type of ship's boat which can be used under sail or oars, or, historically, to a type of fast-sailing vessel introduced in the 18th century, some of which were used as small warships.
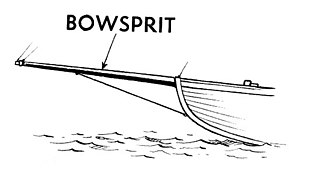
The bowsprit of a sailing vessel is a spar extending forward from the vessel's prow. The bowsprit is typically held down by a bobstay that counteracts the forces from the forestays. The bowspirit’s purpose is to create anchor points for the sails that extend beyond the vessel’s bow, increasing the size of sail that may be held taut.

A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing vessel with a sail plan of three or more masts, all of them square-rigged. Such a vessel is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged, with each mast stepped in three segments: lower, top, and topgallant.

Stays are ropes, wires, or rods on sailing vessels that run fore-and-aft along the centerline from the masts to the hull, deck, bowsprit, or to other masts which serve to stabilize the masts.

A gennaker is a sail that was developed around 1990. Used when sailing downwind, it is a cross between a genoa and a spinnaker. It is not symmetric like a true spinnaker but is asymmetric like a genoa, but the gennaker is not attached to the forestay like a jib or genoa. The gennaker is rigged like a spinnaker but the tack is fastened to the hull or to a bowsprit. It has greater camber than a genoa. This is optimal for generating lift at larger angles of attack. An early form of gennaker was the "gollywhomper", used briefly in the 1870s.

A Thames sailing barge is a type of commercial sailing boat once common on the River Thames in London. The flat-bottomed barges, with a shallow draught and leeboards, were perfectly adapted to the Thames Estuary, with its shallow waters and narrow tributary rivers. The larger barges were seaworthy vessels, and were the largest sailing vessel to be handled by just two men. The average size was about 120 tons and they carried 4,200 square feet (390 m2) of canvas sail in six working sails. The mainsail was loose-footed and set up with a sprit, and was brailed to the mast when not needed. It is sheeted to a horse, as is the foresail; they require no attention when tacking. The foresail is often held back by the mate to help the vessel come about more swiftly.

Length overall is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, and is also used for calculating the cost of a marina berth.

The 3000 is a racing sailing dinghy crewed by two persons with a trapeze for the crew. Launched in 1996 as the Laser 3000, the 3000 was developed from the Laser 2, using the original Frank Bethwaite-designed planing hull combined with a new designed self-draining deck by Derek Clark. Clark also re-designed the rig, using spars and sails from premium proprietary sources and replacing the symmetric spinnaker of the Laser 2 by a larger asymmetric spinnaker (gennaker). The gennaker is chute-launched and retrieved using a single halyard line, and is set on a retractable bowsprit. Helm balance and handling were improved using a shorter-footed mainsail with two full-width battens giving a larger roach. A mast with conventional spreaders replaced the now-unusual diamond arrangement of the Laser 2.

Baron of Renfrew was a four-masted barque of 5,294 gross register tonnage (GRT), built of wood in 1825 by Charles Wood in Quebec, Canada. She was one of the largest wooden ships ever built, although she was a disposable ship built for a one-way voyage to transport timber to England and did not complete a single voyage before breaking up.

A jibboom is a spar used to extend the length of a bowsprit on sailing ships. It can itself be extended further by a flying jib-boom. The heel end of the flying jib-boom is attached to the jib-boom, and the heel of the jib-boom to the bowsprit. The point of the flying jib-boom is generally the fore-most extent of a ship. The jib- and flying jib- booms carry the tacks of the jib and flying jib sails, respectively, and the stay for the fore topgallant mast and the royal stay.

The pinas, sometimes called "pinis" as well, is a type of schooner of the east coast of the Malay peninsula, built in the Terengganu area. This kind of vessel was built of Chengal wood by the Malays since the 19th century and roamed the South China Sea and adjacent oceans as one of the two types of traditional sailing vessels the late Malay maritime culture has developed: The bedar and the pinas.

The term bedar is applied to a wide variety of boats of the east coast of Malaysia that carry one or two junk sails and lack the typical transom stern of the perahu pinas. These junk rigged boats are usually built in the Terengganu area. The stern of the bedar is a classical "canu" or "pinky stern," being a typical "double ender", a bit like a modern ship's lifeboat, with a very full turn of the bilge and with markedly raked stem and stern. They came in small versions as small one-masted fishing vessels — anak bedar and were built as big as 90 feet over deck (LOD). The majority of the bedars were usually 45 to 60 feet over deck. The bedar, like all Terengganu boats, was built of Chengal wood by the Malays since the 19th century and roamed the South China Sea and adjacent oceans as a highly seaworthy traditional sailing vessel.

The Falmouth Working Boat is a type of small traditional sailing craft that evolved for fishing in the waters of Falmouth, Cornwall.
The Lord Nelson 41 is an American sailboat that was designed by Loren Hart as a cruiser and first built in 1982.

The Sprinto is a French trailerable sailboat that was designed by Joubert Nivelt Design as a racer and first built in 2000.
The Herreshoff Eagle, also called the Herreshoff Eagle 21, is an American trailerable sailboat that was designed by Halsey Chase Herreshoff as a cruiser and first built in 1976.


















