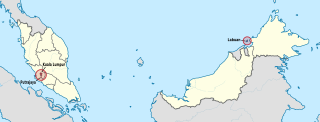
The Federal Territories (FT), in Malaysia comprise three territories—Kuala Lumpur, Labuan, and Putrajaya—governed directly by the Federal Government of Malaysia. Kuala Lumpur is the national capital of Malaysia, Putrajaya is the administrative capital, and Labuan is an offshore international financial centre. Kuala Lumpur and Putrajaya are enclaves in the state of Selangor. Labuan is an island off the coast of Sabah.

The Federal Constitution of Malaysia, which came into force in 1957 as the Constitution of the Federation of Malaya and was amended in 1963 to form the Constitution of Malaysia, is the supreme law of Malaysia and contains a total of 183 articles. It is a written legal document influenced by two previous documents, the Federation of Malaya Agreement 1948 and the Independence Constitution of 1957. The Federation was initially called the Federation of Malaya and it adopted its present name, Malaysia, when the states of Sabah, Sarawak and Singapore became part of the Federation. The Constitution establishes the Federation as a constitutional monarchy, having the Yang di-Pertuan Agong as the Head of State with largely ceremonial roles. It provides for the establishment and organisation of three main branches of the government: the bicameral legislative branch called the Parliament, which consists of the House of Representatives and the Senate ; the executive branch led by the Prime Minister and his Cabinet Ministers and the judicial branch headed by the Federal Court.
The states and federal territories of Malaysia are the principal administrative divisions of Malaysia. Malaysia is a federation of 13 states (Negeri) and 3 federal territories.

Public holidays in Malaysia are regulated at both federal and state levels, mainly based on a list of federal holidays observed nationwide plus a few additional holidays observed by each individual state and federal territory. The public holidays are a mix of secular holidays celebrating the nation and its history, and selected traditional holidays of the various ethnic and religious groups that make up the country.

The Ministry of Home Affairs, or simply the Home Ministry, is a ministry of the Government of India. It is mainly responsible for the maintenance of internal security and domestic policy. It is headed by Minister of Home Affairs.

The Fisheries Act 1985 is a Malaysian federal act relating to the administration and management of fisheries, including the conservation and development of maritime and estuarine fishing and fisheries in Malaysia waters, protection to aquatic mammals and turtles and riverine fishing in Malaysia and to matters connected to establishment of marine parks and marine reserves.
The local government in Malaysia is the lowest tier of government in Malaysia administered under the states and federal territories which in turn are beneath the federal tier. Local governments are generally under the exclusive purview of the state governments as provided in the Constitution of Malaysia, except for local governments in the federal territories. The federal Ministry of Local Government Development plays a role in co-ordinating and standardising the practices of local governments across the country.

Perbadanan Putrajaya (PPj) or Putrajaya Corporation (PjC) is a local authority that administers the Federal Territory of Putrajaya and is under the Department of Federal Territories of Malaysia. Founded in 1995, the corporation is responsible for public health and sanitation, waste removal and management, capital planning, environmental protection and building control, social and economic development, and the general maintenance functions of the urban infrastructure of Putrajaya. The main headquarters of the PPj is located at Precinct 3, Persiaran Perdana, Putrajaya.

Labuan Corporation or Perbadanan Labuan(PL) is a local authority which administers the Federal Territory of Labuan, Malaysia. This agency is under Department of Federal Territories Malaysia. PL are responsible for public health and sanitation, waste removal and management, town planning, environmental protection and building control, social and economic development and general maintenance functions of urban infrastructure. The PL main headquarters that is Wisma Perbadanan Labuan located at Jalan Dewan, Victoria. PL has another office building, Menara Perbadanan Labuan at Jalan OKK Awang Besar.

The Ministry of Health is a ministry of the Government of Malaysia that is responsible for health system: health behaviour, cancer, public health, health management, medical research, health systems research, respiratory medicine, health promotion, healthcare tourism, medical device, blood collection, leprosy control, clinical research, health care, dental care, health institution, laboratory, pharmaceutical, patient safety.

The 1974 Federal Territory of Kuala Lumpur Agreement was signed on 1 February 1974 by the fifth Yang di-Pertuan Agong, Abdul Halim of Kedah, on behalf of the Federal Government of Malaysia; and the Sultan of Selangor, Salahuddin, on behalf of the State Government of Selangor. This agreement was signed at the Istana Negara, Kuala Lumpur, and signified the official handing of Kuala Lumpur territory over to the Federal Government, which resulted in the establishment of the Federal Territory.

The Ministry of Finance, abbreviated MOF, is a ministry of the Government of Malaysia that is charged with the responsibility for government expenditure and revenue raising. The ministry's role is to develop economic policy and prepare the Malaysian federal budget. The Ministry of Finance also oversees financial legislation and regulation. Each year in October, the Minister of Finance presents the Malaysian federal budget to the Parliament.

The Ministry of Housing and Local Government, abbreviated KPKT, is a ministry of the Government of Malaysia that is responsible for urban well-being, housing, local government, town planning, country planning, fire and rescue authority, landscape, solid waste management, strata management, moneylenders, pawnbrokers.
The state governments in Malaysia are the governments ruling the 13 states in the federation of Malaysia. All 13 states adopts the Westminster Parliamentary system and each has a unicameral state legislative assembly. Each of the States of Malaya is run by an EXCO, while Sabah and Sarawak have their respective Cabinet and Ministry. The state government structure in all 13 states is similar to the government system of the federal government of Malaysia and that the state legislatures consist of only a single chamber.

The Local Government Act 1976 is an Act of the Parliament of Malaysia, which was enacted to revise and consolidate the laws relating to local government.

The Strata Management Act 2013, is a Malaysian laws which enacted to provide for the proper maintenance and management of buildings and common property, and for related matters.

The Ministry of Federal Territories(Malay: Kementerian Wilayah Persekutuan; Jawi: كمنترين ولايه ڤرسكوتوان), abbreviated KWP, was a ministry and is now a department under the Prime Minister's Department of the Government of Malaysia that is in charge of overseeing the administration and development of all three Federal Territories in Malaysia; Kuala Lumpur, Labuan and Putrajaya.
Alam Flora Sdn Bhd is a Malaysian solid waste management and public cleansing privatisation state-owned enterprise. Established in 1995 under the Malaysian government, it was established as a wholly-owned subsidiary of DRB-HICOM, a Malaysian infrastructure conglomerate, and was sold in 2019 to Malakoff.









