
The Djibouti Armed Forces are the military forces of Djibouti. They consist of the Djiboutian National Army and its sub-branches the Djiboutian Air Force and Djiboutian Navy. As of 2018, the Djibouti Armed Forces consists of 20,470 ground troops, which are divided into several regiments and battalions garrisoned in various areas throughout the country. The Djibouti Armed Forces are an important player in the Bab-el-Mandeb and Red Sea.

The Somali Armed Forces are the military forces of the Federal Republic of Somalia. Headed by the president as commander-in-chief, they are constitutionally mandated to ensure the nation's sovereignty, independence and territorial integrity.

Somaliland, officially the Republic of Somaliland, is an unrecognised country in the Horn of Africa. It is located in the southern coast of the Gulf of Aden and bordered by Djibouti to the northwest, Ethiopia to the south and west, and Somalia to the east. Its claimed territory has an area of 176,120 square kilometres (68,000 sq mi), with approximately 6.2 million people as of 2024. The capital and largest city is Hargeisa.

British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate, was a protectorate of the United Kingdom in modern Somaliland. During its existence, the territory was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Somali Coast and Abyssinia. From 1940 to 1941, it was occupied by the Italians and was part of Italian East Africa.

The national flag of Somalia was adopted on October 12, 1954, and was designed by Mohammed Awale Liban. The flag was initially used within the Trust Territory of Somaliland before being adopted by the short-lived State of Somaliland and the Somali Republic. It is an ethnic flag for the Somali people; the flag's five-pointed star represents the five regions in which Somalis reside.

Las Anod is the administrative capital of the Sool region, currently controlled by Khatumo State forces aligned with Somalia.

Greater Somalia sometimes also called Greater Somaliland is the geographic location comprising the regions in the Horn of Africa in which ethnic Somalis live and have historically inhabited.

Mohamed Haji Ibrahim Egal was a Somali politician who served as the president of Somaliland from 1993 to his death in 2002. He previously served as the prime minister of the State of Somaliland between 26 June and 1 July 1960 and as the first prime minister of the Somali Republic for eleven days in 1960 and again from 1967 to 1969.

The Somali Republic was formed by the union of the Trust Territory of Somaliland and the State of Somaliland. A government was formed by Abdullahi Issa Mohamud and Muhammad Haji Ibrahim Egal and other members of the trusteeship and protectorate administrations, with Haji Bashir Ismail Yusuf as President of the Somali National Assembly and Aden Abdullah Osman Daar as President of the Somali Republic. On 22 July 1960, Daar appointed Abdirashid Ali Shermarke as prime minister. On 20 July 1961 and through a popular referendum, Somalia ratified a new constitution, which was first drafted in 1960. The new constitution was rejected by Somaliland.

Edna Adan Ismail is a nurse midwife, activist, and was the first female Foreign Minister of Somaliland from 2003 to 2006. She previously served as Somalia’s Minister of Family Welfare and Social Development.
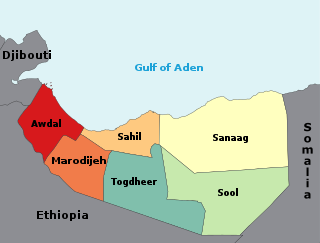
The regions of Somaliland is divided into six administrative regions, Awdal, Sahil, Maroodi-Jeeh, Togdheer, Sanaag and Sool. These are in turn subdivided into twenty-two districts. Regions of Somaliland are the primary geographical divisions through which Somaliland is administered. A distinction is made between districts of grades A, B, C and D, with the classification being based on population, area, economy and production.

The Somali National Army are the ground forces component of the Somali Armed Forces.

The Somaliland National Armed Forces are the military services of the Republic of Somaliland. The Somaliland National Armed Forces consist of the Somaliland National Army, the Somaliland Coast Guard, the Somaliland Police Force, the Somaliland Custodial Corps, the Somaliland Immigration and Border Control and the Somaliland Fire Brigade. There is no air force. The Armed Forces is under the command of President Muse Bihi Abdi, who is the Commander-in-chief. Minister of Defence Dr. Rooble Muuse Abdi is the designated minister that oversees the armed forces.

The Somali Youth League, initially known as the Somali Youth Club (SYC), was the first political party in Somalia.

The Somali Air Force is the air force of Somalia. Called the Somali Aeronautical Corps (SAC) during its pre-independence period (1954–1960), it was renamed as Somali Air Force (SAF) after Somalia gained independence in 1960. Ali Matan Hashi, Somalia's first pilot and person principally responsible for organizing the SAF, was its founder and served as its the country's first air chief. At one point, the Somali Air Force had the strongest airstrike capability in the Horn of Africa. But by the time President Siad Barre fled Mogadishu in 1991, it had completely collapsed. The SAF headquarters was technically reopened in 2015.

The Somali Police Force is the national police force and the main civil law enforcement agency of Somalia. As with most other police forces in the world, its duties include crime fighting, traffic control, maintaining public safety, counter-terrorism. It is under the jurisdiction of the Minister of Internal Security.

Abdirahman Ahmed Ali Tuur was a Somali politician who served as the first President of Somaliland from 1991 to 1993. Tuur previously served as the Chairman of the Somali National Movement from 1990 to 1991. He also served as the Vice President of Somaliland from 1993 to 1995.

The following is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Somalia. From the late 1800s to 1960, northwestern present-day Somalia was administered as British Somaliland, while the northeastern, central and southern part of the country were concurrently administered as Italian Somaliland. In 1960, the two territories were unified as the Somali Republic.

Somali nationality law is regulated by the Constitution of Somalia, as amended; the Somali Citizenship Law, and its revisions; and various international agreements to which the country is a signatory. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of Somalia. The legal means to acquire nationality, formal legal membership in a nation, differ from the domestic relationship of rights and obligations between a national and the nation, known as citizenship. Nationality describes the relationship of an individual to the nation under international law, whereas citizenship is the domestic relationship of an individual and the state. Somali nationality is typically obtained under the principle of jus soli, i.e. by birth in Somalia, or jus sanguinis, born to parents with Somali nationality. It can be granted to persons with an affiliation to the country, or to a permanent resident who has lived in the country for a given period of time through grant (naturalization).

The Somaliland Declaration of Independence was made on 18 May 1991 by Somali sultans from the Isaaq, Dhulbahante, Issa, Gadabursi, Warsangali clans, as well as the Somali National Movement.





















