
With a land area of 93,030 square km, Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It measures about 250 km from north to south and 524 km from east to west. It has 2,106 km of boundaries, shared with Austria to the west, Serbia, Croatia and Slovenia to the south and southwest, Romania to the southeast, Ukraine to the northeast, and Slovakia to the north.
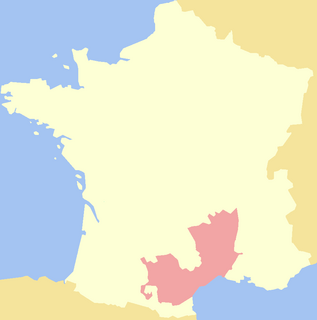
Languedoc is a former province of France. Its territory is now contained in the modern-day region of Occitanie in the south of France. Its capital city was Toulouse. It had an area of approximately 27,376 square kilometers.

Burgundy is a historical territory and a former administrative region of France. It takes its name from the Burgundians, an East Germanic people who moved westwards beyond the Rhine during the late Roman period.

Burgenland (German pronunciation: [ˈbʊʁɡen̩lant]; Hungarian: Őrvidék; Croatian: Gradišće; Slovene: Gradiščanska; Czech: Hradsko; is the easternmost and least populous state of Austria. It consists of two statutory cities and seven rural districts, with in total 171 municipalities. It is 166 km long from north to south but much narrower from west to east. The region is part of the Centrope Project.

Sparkling wine is a wine with significant levels of carbon dioxide in it, making it fizzy. While the phrase commonly refers to champagne, EU countries legally reserve that term for products exclusively produced in the Champagne region of France. Sparkling wine is usually either white or rosé, but there are examples of red sparkling wines such as the Italian Brachetto, Bonarda and Lambrusco, Australian sparkling Shiraz, and Azerbaijani "Pearl of Azerbaijan" made from Madrasa grapes. The sweetness of sparkling wine can range from very dry brut styles to sweeter doux varieties.

Hungarian or Magyar cuisine is the cuisine characteristic of the nation of Hungary and its primary ethnic group, the Magyars. Traditional Hungarian dishes are primarily based on meats, seasonal vegetables, fruits, fresh bread, dairy products and cheeses.

Goulash is a stew of meat and vegetables usually seasoned with paprika and other spices. Originating from medieval Hungary, goulash is a popular meal predominantly eaten in Central Europe but also in other parts of Europe.

Furmint is a white Hungarian wine grape variety that is most noted widely grown in the Tokaj-Hegyalja wine region where it is used to produce single-varietal dry wines as well as being the principal grape in the better known Tokaji dessert wines. It is also grown in the tiny Hungarian wine region of Somló. Furmint plays a similar role in the Slovakian wine region of Tokaj. It is also grown in Austria where it is known as Mosler. Smaller plantings are found in Slovenia where it is known as Šipon. The grape is also planted in Croatia where it is known as Moslavac. It is also found in Romania and in former republics of the Soviet Union. Furmint is a late ripening variety. For dry wines the harvest starts usually in September, however sweet wine specific harvest can start in the second half of October or even later, and is often affected by Botrytis.
The culture of Hungary varies across Hungary, starting from the capital city of Budapest on the Danube, to the Great Plains bordering Ukraine. Hungary has a rich folk crafts tradition, for example: embroidery, decorated pottery and carvings. Hungarian music ranges from the rhapsodies of Franz Liszt and folk music to modern songs influenced by folk music and Roma music. Hungary has a rich and colorful literature with many poets and writers although not many are known abroad due to the limited prevalence of the Hungarian language. Some noted authors include Sándor Márai and Imre Kertész, who have been gaining acclaim in recent decades. János Kodolányi was well known in Italy and Finland in the mid-20th century. Imre Kertész won the Nobel Prize in Literature in 2002. Péter Esterházy is popular in Austria and Germany, and Magda Szabó has recently become well known in Europe as well.
Hungarian wine has a history dating back to the Kingdom of Hungary. Outside Hungary, the best-known wines are the white dessert wine Tokaji aszú and the red wine Bull's Blood of Eger.

Tokaj wine region or Tokaj-Hegyalja wine region is a historical wine region located in northeastern Hungary and southeastern Slovakia. It is also one of the seven larger wine regions of Hungary. Hegyalja means "foothills" in Hungarian, and this was the original name of the region.

Alsace wine or Alsatian wine is produced in the Alsace region in France and is primarily white wine. Because of its Germanic influence, it is the only Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée region in France to produce mostly varietal wines, typically from similar grape varieties to those used in German wine. Along with Austria and Germany, it produces some of the most noted dry Rieslings in the world as well as highly aromatic Gewürztraminer wines. Wines are produced under three different AOCs: Alsace AOC for white, rosé and red wines, Alsace Grand Cru AOC for white wines from certain classified vineyards and Crémant d'Alsace AOC for sparkling wines. Both dry and sweet white wines are produced.

White Carniola is a traditional region in southeastern Slovenia on the border with Croatia. Due to its smallness, it is often considered a subunit of the broader Lower Carniola region, although with distinctive cultural, linguistic, and historical features.

Sauternes is a French sweet wine from the Sauternais region of the Graves section in Bordeaux. Sauternes is made from Sémillon, Sauvignon blanc, and Muscadelle grapes that have been affected by Botrytis cinerea, also known as noble rot. This causes the grapes to become partially raisined, resulting in concentrated and distinctively flavored wines. Due to its climate, Sauternes is one of the few wine regions where infection with noble rot is a frequent occurrence. Even so, production is a hit-or-miss proposition, with widely varying harvests from vintage to vintage. Wines from Sauternes, especially the Premier Cru Supérieur estate Château d'Yquem, can be very expensive, due largely to the very high cost of production. Barsac lies within Sauternes, and is entitled to use either name. Somewhat similar but less expensive and typically less-distinguished wines are produced in the neighboring regions of Monbazillac, Cérons, Loupiac and Cadillac. In the United States, there is a semi-generic label for sweet white dessert wines known as sauterne without the "s" at the end and uncapitalized.
Nyírbátor is a town in Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg county, in the Northern Great Plain region of eastern Hungary. With its historic atmosphere, this city is known for its 15th- and 16th-century ecclesiastic and secular architectural heritage and for the Báthory family, former landowners.

Kőröshegy is a village directly south of Balatonföldvár in Siófok District, Somogy County, Hungary.

Penedès is a Spanish Denominación de Origen, DO, for wines in Catalonia (Spain). Penedès DO includes all Penedès region and municipalities of four other counties: Anoia, Alt Camp, Baix Llobregat and Tarragonès. The area is framed by the coastal hills of the Garraf Massif and the higher inland mountains which skirt the Central Depression.

The national symbols of Hungary are flags, icons or cultural expressions that are emblematic, representative or otherwise characteristic of Hungary or Hungarian culture. The highly valued special Hungarian products and symbols are called Hungaricum.

Balaton wine region is one of the seven larger wine regions of Hungary. It consists of six wine regions: Badacsony, Balatonboglár, Balaton-felvidék, Balatonfüred-Csopak, Nagy-Somló and Zala. Its wine regions are spread around Lake Balaton; with these areas having constituted one single wine region back to the 19th century. Wine production was started at the beginning of the 1st century by the Romans. The region is known for its specific white wines showing local particularities; its most widely grown variety is olaszrizling.

























