
In mathematics and physics, Laplace's equation is a second-order partial differential equation named after Pierre-Simon Laplace, who first studied its properties. This is often written as
In particle physics, the Dirac equation is a relativistic wave equation derived by British physicist Paul Dirac in 1928. In its free form, or including electromagnetic interactions, it describes all spin-1⁄2 massive particles, called "Dirac particles", such as electrons and quarks for which parity is a symmetry. It is consistent with both the principles of quantum mechanics and the theory of special relativity, and was the first theory to account fully for special relativity in the context of quantum mechanics. It was validated by accounting for the fine structure of the hydrogen spectrum in a completely rigorous way.
Linear elasticity is a mathematical model of how solid objects deform and become internally stressed due to prescribed loading conditions. It is a simplification of the more general nonlinear theory of elasticity and a branch of continuum mechanics.

In quantum field theory, the mass gap is the difference in energy between the lowest energy state, the vacuum, and the next lowest energy state. The energy of the vacuum is zero by definition, and assuming that all energy states can be thought of as particles in plane-waves, the mass gap is the mass of the lightest particle.
The Schwarzschild solution describes spacetime under the influence of a massive, non-rotating, spherically symmetric object. It is considered by some to be one of the simplest and most useful solutions to the Einstein field equations.
In mathematics, a volume element provides a means for integrating a function with respect to volume in various coordinate systems such as spherical coordinates and cylindrical coordinates. Thus a volume element is an expression of the form
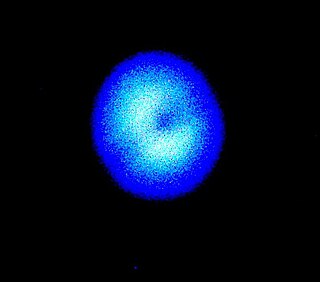
In optics, the Fresnel diffraction equation for near-field diffraction is an approximation of the Kirchhoff–Fresnel diffraction that can be applied to the propagation of waves in the near field. It is used to calculate the diffraction pattern created by waves passing through an aperture or around an object, when viewed from relatively close to the object. In contrast the diffraction pattern in the far field region is given by the Fraunhofer diffraction equation.
Cylindrical multipole moments are the coefficients in a series expansion of a potential that varies logarithmically with the distance to a source, i.e., as . Such potentials arise in the electric potential of long line charges, and the analogous sources for the magnetic potential and gravitational potential.

The Newman–Penrose (NP) formalism is a set of notation developed by Ezra T. Newman and Roger Penrose for general relativity (GR). Their notation is an effort to treat general relativity in terms of spinor notation, which introduces complex forms of the usual variables used in GR. The NP formalism is itself a special case of the tetrad formalism, where the tensors of the theory are projected onto a complete vector basis at each point in spacetime. Usually this vector basis is chosen to reflect some symmetry of the spacetime, leading to simplified expressions for physical observables. In the case of the NP formalism, the vector basis chosen is a null tetrad: a set of four null vectors—two real, and a complex-conjugate pair. The two real members often asymptotically point radially inward and radially outward, and the formalism is well adapted to treatment of the propagation of radiation in curved spacetime. The Weyl scalars, derived from the Weyl tensor, are often used. In particular, it can be shown that one of these scalars— in the appropriate frame—encodes the outgoing gravitational radiation of an asymptotically flat system.
The Frank–Tamm formula yields the amount of Cherenkov radiation emitted on a given frequency as a charged particle moves through a medium at superluminal velocity. It is named for Russian physicists Ilya Frank and Igor Tamm who developed the theory of the Cherenkov effect in 1937, for which they were awarded a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1958.
A ratio distribution is a probability distribution constructed as the distribution of the ratio of random variables having two other known distributions. Given two random variables X and Y, the distribution of the random variable Z that is formed as the ratio Z = X/Y is a ratio distribution.
In mathematics, the cylindrical harmonics are a set of linearly independent functions that are solutions to Laplace's differential equation, , expressed in cylindrical coordinates, ρ (radial coordinate), φ (polar angle), and z (height). Each function Vn(k) is the product of three terms, each depending on one coordinate alone. The ρ-dependent term is given by Bessel functions (which occasionally are also called cylindrical harmonics).
In mathematics, the spectral theory of ordinary differential equations is the part of spectral theory concerned with the determination of the spectrum and eigenfunction expansion associated with a linear ordinary differential equation. In his dissertation, Hermann Weyl generalized the classical Sturm–Liouville theory on a finite closed interval to second order differential operators with singularities at the endpoints of the interval, possibly semi-infinite or infinite. Unlike the classical case, the spectrum may no longer consist of just a countable set of eigenvalues, but may also contain a continuous part. In this case the eigenfunction expansion involves an integral over the continuous part with respect to a spectral measure, given by the Titchmarsh–Kodaira formula. The theory was put in its final simplified form for singular differential equations of even degree by Kodaira and others, using von Neumann's spectral theorem. It has had important applications in quantum mechanics, operator theory and harmonic analysis on semisimple Lie groups.
In mathematics, the Plancherel theorem for spherical functions is an important result in the representation theory of semisimple Lie groups, due in its final form to Harish-Chandra. It is a natural generalisation in non-commutative harmonic analysis of the Plancherel formula and Fourier inversion formula in the representation theory of the group of real numbers in classical harmonic analysis and has a similarly close interconnection with the theory of differential equations. It is the special case for zonal spherical functions of the general Plancherel theorem for semisimple Lie groups, also proved by Harish-Chandra. The Plancherel theorem gives the eigenfunction expansion of radial functions for the Laplacian operator on the associated symmetric space X; it also gives the direct integral decomposition into irreducible representations of the regular representation on L2(X). In the case of hyperbolic space, these expansions were known from prior results of Mehler, Weyl and Fock.
An LC circuit can be quantized using the same methods as for the quantum harmonic oscillator. An LC circuit is a variety of resonant circuit, and consists of an inductor, represented by the letter L, and a capacitor, represented by the letter C. When connected together, an electric current can alternate between them at the circuit's resonant frequency:
In fluid dynamics, a flow with periodic variations is known as pulsatile flow, or as Womersley flow. The flow profiles was first derived by John R. Womersley (1907–1958) in his work with blood flow in arteries. The cardiovascular system of chordate animals is a very good example where pulsatile flow is found, but pulsatile flow is also observed in engines and hydraulic systems, as a result of rotating mechanisms pumping the fluid.
In optics, the Fraunhofer diffraction equation is used to model the diffraction of waves when the diffraction pattern is viewed at a long distance from the diffracting object, and also when it is viewed at the focal plane of an imaging lens.
Multipole radiation is a theoretical framework for the description of electromagnetic or gravitational radiation from time-dependent distributions of distant sources. These tools are applied to physical phenomena which occur at a variety of length scales - from gravitational waves due to galaxy collisions to gamma radiation resulting from nuclear decay. Multipole radiation is analyzed using similar multipole expansion techniques that describe fields from static sources, however there are important differences in the details of the analysis because multipole radiation fields behave quite differently from static fields. This article is primarily concerned with electromagnetic multipole radiation, although the treatment of gravitational waves is similar.
Lagrangian field theory is a formalism in classical field theory. It is the field-theoretic analogue of Lagrangian mechanics. Lagrangian mechanics is used to analyze the motion of a system of discrete particles each with a finite number of degrees of freedom. Lagrangian field theory applies to continua and fields, which have an infinite number of degrees of freedom.

Batch normalization is a method used to make training of artificial neural networks faster and more stable through normalization of the layers' inputs by re-centering and re-scaling. It was proposed by Sergey Ioffe and Christian Szegedy in 2015.






















