
Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, computer programming, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret biological data. The process of analyzing and interpreting data can sometimes be referred to as computational biology, however this distinction between the two terms is often disputed. To some, the term computational biology refers to building and using models of biological systems.

Computational biology refers to the use of techniques in computer science, data analysis, mathematical modeling and computational simulations to understand biological systems and relationships. An intersection of computer science, biology, and data science, the field also has foundations in applied mathematics, molecular biology, cell biology, chemistry, and genetics.
In bioinformatics, sequence clustering algorithms attempt to group biological sequences that are somehow related. The sequences can be either of genomic, "transcriptomic" (ESTs) or protein origin. For proteins, homologous sequences are typically grouped into families. For EST data, clustering is important to group sequences originating from the same gene before the ESTs are assembled to reconstruct the original mRNA.

A protein family is a group of evolutionarily related proteins. In many cases, a protein family has a corresponding gene family, in which each gene encodes a corresponding protein with a 1:1 relationship. The term "protein family" should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy.
In computational biology, gene prediction or gene finding refers to the process of identifying the regions of genomic DNA that encode genes. This includes protein-coding genes as well as RNA genes, but may also include prediction of other functional elements such as regulatory regions. Gene finding is one of the first and most important steps in understanding the genome of a species once it has been sequenced.
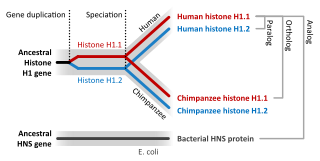
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal gene transfer event (xenologs).

Biological network inference is the process of making inferences and predictions about biological networks. By using these networks to analyze patterns in biological systems, such as food-webs, we can visualize the nature and strength of these interactions between species, DNA, proteins, and more.
Inparanoid is an algorithm that finds orthologous genes and paralogous genes that arose—most likely by duplication—after some speciation event. Such protein-coding genes are called in-paralogs, as opposed to out-paralogs.
The Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center (VBRC) is an online resource providing access to a database of curated viral genomes and a variety of tools for bioinformatic genome analysis. This resource was one of eight BRCs funded by NIAID with the goal of promoting research against emerging and re-emerging pathogens, particularly those seen as potential bioterrorism threats. The VBRC is now supported by Dr. Chris Upton at the University of Victoria.

OrthoDB presents a catalog of orthologous protein-coding genes across vertebrates, arthropods, fungi, plants, and bacteria. Orthology refers to the last common ancestor of the species under consideration, and thus OrthoDB explicitly delineates orthologs at each major radiation along the species phylogeny. The database of orthologs presents available protein descriptors, together with Gene Ontology and InterPro attributes, which serve to provide general descriptive annotations of the orthologous groups, and facilitate comprehensive orthology database querying. OrthoDB also provides computed evolutionary traits of orthologs, such as gene duplicability and loss profiles, divergence rates, sibling groups, and gene intron-exon architectures.
OMA is a database of orthologs extracted from available complete genomes. The orthology predictions of OMA are available in several forms:
In metagenomics, binning is the process of grouping reads or contigs and assigning them to individual genome. Binning methods can be based on either compositional features or alignment (similarity), or both.

Infologs are independently designed synthetic genes derived from one or a few genes where substitutions are systematically incorporated to maximize information. Infologs are designed for perfect diversity distribution to maximize search efficiency.
Horizontal or lateral gene transfer is the transmission of portions of genomic DNA between organisms through a process decoupled from vertical inheritance. In the presence of HGT events, different fragments of the genome are the result of different evolutionary histories. This can therefore complicate investigations of the evolutionary relatedness of lineages and species. Also, as HGT can bring into genomes radically different genotypes from distant lineages, or even new genes bearing new functions, it is a major source of phenotypic innovation and a mechanism of niche adaptation. For example, of particular relevance to human health is the lateral transfer of antibiotic resistance and pathogenicity determinants, leading to the emergence of pathogenic lineages.
In molecular phylogenetics, relationships among individuals are determined using character traits, such as DNA, RNA or protein, which may be obtained using a variety of sequencing technologies. High-throughput next-generation sequencing has become a popular technique in transcriptomics, which represent a snapshot of gene expression. In eukaryotes, making phylogenetic inferences using RNA is complicated by alternative splicing, which produces multiple transcripts from a single gene. As such, a variety of approaches may be used to improve phylogenetic inference using transcriptomic data obtained from RNA-Seq and processed using computational phylogenetics.
Machine learning in bioinformatics is the application of machine learning algorithms to bioinformatics, including genomics, proteomics, microarrays, systems biology, evolution, and text mining.
Non-coding RNAs have been discovered using both experimental and bioinformatic approaches. Bioinformatic approaches can be divided into three main categories. The first involves homology search, although these techniques are by definition unable to find new classes of ncRNAs. The second category includes algorithms designed to discover specific types of ncRNAs that have similar properties. Finally, some discovery methods are based on very general properties of RNA, and are thus able to discover entirely new kinds of ncRNAs.

Christophe Dessimoz is a Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) Professor at the University of Lausanne, Associate Professor at University College London and a group leader at the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics. He was awarded the Overton Prize in 2019 for his contributions to computational biology. Starting in April 2022, he will be joint executive director of the SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics, along with Ron Appel.

OrthoFinder is a command-line software tool for comparative genomics. OrthoFinder determines the correspondence between genes in different organisms. This correspondence provides a framework for understanding the evolution of life on Earth, and enables the extrapolation and transfer of biological knowledge between organisms.

In phylogenetics, reconciliation is an approach to connect the history of two or more coevolving biological entities. The general idea of reconciliation is that a phylogenetic tree representing the evolution of an entity can be drawn within another phylogenetic tree representing an encompassing entity to reveal their interdependence and the evolutionary events that have marked their shared history. The development of reconciliation approaches started in the 1980s, mainly to depict the coevolution of a gene and a genome, and of a host and a symbiont, which can be mutualist, commensalist or parasitic. It has also been used for example to detect horizontal gene transfer, or understand the dynamics of genome evolution.









