
MIDI is a technical standard that describes a communication protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and related audio devices for playing, editing, and recording music.

Digital music technology encompasses the use of digital instruments to produce, perform or record music. These instruments vary, including computers, electronic effects units, software, and digital audio equipment. Digital music technology is used in performance, playback, recording, composition, mixing, analysis and editing of music, by professions in all parts of the music industry.

Sound Blaster is a family of sound cards and audio peripherals designed by Creative Technology/Creative Labs of Singapore. The first Sound Blaster card was introduced in 1989.
Video game music (VGM) is the soundtrack that accompanies video games. Early video game music was once limited to sounds of early sound chips, such as programmable sound generators (PSG) or FM synthesis chips. These limitations have led to the style of music known as chiptune, which became the sound of the first video games.
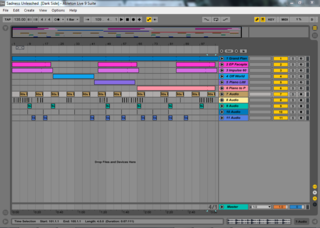
Ableton Live, also known as Live or sometimes colloquially as "Ableton", is a digital audio workstation for macOS and Windows developed by the German company Ableton.

Kurzweil Music Systems is an American company that produces electronic musical instruments. It was founded in 1982 by Stevie Wonder (musician), Ray Kurzweil (innovator) and Bruce Cichowlas.

A MIDI controller is any hardware or software that generates and transmits Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) data to MIDI-enabled devices, typically to trigger sounds and control parameters of an electronic music performance. They most often use a musical keyboard to send data about the pitch of notes to play, although a MIDI controller may trigger lighting and other effects. A wind controller has a sensor that converts breath pressure to volume information and lip pressure to control pitch. Controllers for percussion and stringed instruments exist, as well as specialized and experimental devices. Some MIDI controllers are used in association with specific digital audio workstation software. The original MIDI specification has been extended to include a greater range of control features.
Doepfer Musikelektronik GmbH is a German manufacturer of audio hardware, mostly synthesizer modules, based in Gräfelfing, Upper Bavaria and founded by Dieter Döpfer. The product range covers analog modular systems, MIDI controllers, MIDI hardware sequencers, MIDI-to-CV/Gate/Sync Interfaces, MIDI master keyboards and special MIDI equipment.

David Nicholas George Jackson, nicknamed Jaxon, is an English progressive rock saxophonist, flautist, and composer. He is best known for his work with the band Van der Graaf Generator and his work in Music and Disability. He has also worked with Peter Gabriel, Keith Tippett, Osanna, Judge Smith, David Cross and others.

A MIDI keyboard or controller keyboard is typically a piano-style electronic musical keyboard, often with other buttons, wheels and sliders, used as a MIDI controller for sending Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) commands over a USB or MIDI 5-pin cable to other musical devices or computers. MIDI keyboards lacking an onboard sound module cannot produce sounds themselves, however some models of MIDI keyboards contain both a MIDI controller and sound module.
STEIM was a center for research and development of new musical instruments in the electronic performing arts, located in Amsterdam, Netherlands. Beginning in the 1970's, STEIM became known as a pioneering center for electronic music, where the specific context of electronic music was always strongly related to the physical and direct actions of a musician. In this tradition, STEIM supported artists in residence such as composers and performers, but also multimedia and video artists, helping them to develop setups which allowed for bespoke improvisation and performance with individually designed technology.

A wind controller, sometimes referred to as a wind synthesizer, is an electronic wind instrument. It is usually a MIDI controller associated with one or more music synthesizers. Wind controllers are most commonly played and fingered like a woodwind instrument, usually the saxophone, with the next most common being brass fingering, particularly the trumpet. Models have been produced that play and finger like other acoustic instruments such as the recorder or the tin whistle. The most common form of wind controller uses electronic sensors to convert fingering, breath pressure, bite pressure, finger pressure, and other gesture or action information into control signals that affect musical sounds. The control signals or MIDI messages generated by the wind controller are used to control internal or external devices such as analog synthesizers or MIDI-compatible synthesizers, synth modules, softsynths, sequencers, or even non-instruments such as lighting systems.

The Korg Wavestation is a vector synthesis synthesizer first produced in the early 1990s and later re-released as a software synthesizer in 2004. Its primary innovation was Wave Sequencing, a method of multi-timbral sound generation in which different PCM waveform data are played successively, resulting in continuously evolving sounds. The Wavestation's "Advanced Vector Synthesis" sound architecture resembled early vector synths such as the Sequential Circuits Prophet VS.

Deckadance is a DJ console and mixing tool developed by Image-Line software and acquired in 2015 by Gibson. Initially released in May 2007, it operates on Windows and Mac OS X, and comes in a House Edition and Club Edition. The latter has support for timecoded vinyl.

A synthesizer is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis and frequency modulation synthesis. These sounds may be altered by components such as filters, which cut or boost frequencies; envelopes, which control articulation, or how notes begin and end; and low-frequency oscillators, which modulate parameters such as pitch, volume, or filter characteristics affecting timbre. Synthesizers are typically played with keyboards or controlled by sequencers, software or other instruments, and may be synchronized to other equipment via MIDI.

MainStage is a music application developed by Apple Inc. designed for use in live performance.

Disklavier is a brand of reproducing pianos manufactured by Yamaha Corporation. The first Disklavier was introduced in the United States in 1987.

Controllerism is the art and practice of using musical software controllers, e.g. MIDI, Open Sound Control (OSC), joystick, etc., to build upon, mix, scratch, remix, effect, modify, or otherwise create music, usually by a Digital DJ or Live PA performer, often called a controllerist. Controllerism is also a nod to traditional musicianship and instrumentalism paired with modern computer sequencing software such as Ableton Live and Native Instruments Traktor. However, a working knowledge of scales and chords is not necessarily required as the performers typically focus their efforts more on sequencing events, software effects and instrument manipulations using buttons, knobs, faders, keys, foot switches and pedals than on instrumental notes played in real time.

Laetitia Sonami, is a sound artist, performer, and composer of interactive electronic music who has been based in the San Francisco Bay area since 1978. She is known for her electronic compositions and performances with the ‘’Lady’s Glove’’, an instrument she developed for triggering and manipulating sound in live performance. Many of her compositions include live or sampled text. Sonami also creates sound installation work incorporating household objects embedded with mechanical and electronic components. Although some recordings of her works exist, Sonami generally eschews releasing recorded work.
Maschine is a hardware/software digital audio workstation developed by Native Instruments. Maschine consists of a controller that connects to the included sequencing software, which can be installed on any compatible computer or laptop.















