Related Research Articles
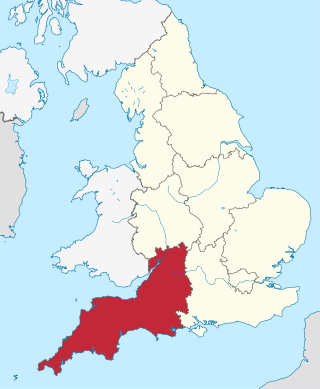
South West England, or the South West of England, is one of nine official regions of England. It consists of the counties of Bristol, Cornwall, Dorset, Devon, Gloucestershire, Somerset and Wiltshire. Cities and large towns in the region include Bath, Bristol, Bournemouth, Cheltenham, Exeter, Gloucester, Plymouth and Swindon. It is geographically the largest of the nine regions of England covering 9,200 square miles (23,800 km2), but the third-least populous, with approximately five million residents.

Avon was a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in the west of England that existed between 1974 and 1996. The county was named after the River Avon, which flows through the area. It was formed from the county boroughs of Bristol and Bath, together with parts of the administrative counties of Gloucestershire and Somerset.
A public health observatory is an organization or program that monitors and reports on the public health of a particular region or topic in order to inform health policy. Depending on the geographical area or focus of work, it may also be called a "regional health observatory", "urban health observatory", or "national health observatory".

The regional chambers of England were a group of indirectly elected regional bodies that were created by the provisions of the Regional Development Agencies Act 1998. There were eight regional chambers, one for each of the regions of England except Greater London, which had opted for an elected mayor and assembly in 1998. All eight regional chambers had adopted the title "regional assembly" or "assembly" as part of their name, though this was not an official status in law. The chambers were abolished over a two-year period between 31 March 2008 and 31 March 2010 and some of their functions were assumed by newly established local authority leaders' boards.
Strategic health authorities (SHA) were part of the structure of the National Health Service in England between 2002 and 2013. Each SHA was responsible for managing performance, enacting directives and implementing health policy as required by the Department of Health at a regional level.

In the United Kingdom, regional development agencies (RDAs) were nine non-departmental public bodies established for the purpose of development, primarily economic, of England's Government Office regions between 1998 and 2010. There was one RDA for each of the NUTS level 1 regions of England. Similar activities were carried out in Wales by the Welsh Government Department of Economy and Transport, in Northern Ireland by the Department of Enterprise, Trade and Investment and in Scotland by Scottish Enterprise and Highlands and Islands Enterprise.

Bus deregulation in Great Britain was the abolition of Road Service Licensing outside of Greater London for bus services. This began in 1980 with long-distance bus services and was extended to local bus services in 1986. The abolition of Road Service Licensing removed the public sector's role in fare-setting, routes and bus frequencies and returned these powers to bus operators under the Transport Act 1985.

Government Offices for the English Regions (GOs) were established in 1994 by the John Major government. Until 2011, they were the primary means by which a wide range of policies and programmes of the Government of the United Kingdom were delivered in the regions of England.
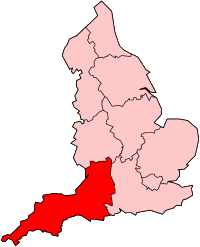
The South West of England Regional Development Agency (SWRDA) was one of the nine Regional Development Agencies set up by the United Kingdom government in 1999. Its purpose was to lead the development of a sustainable economy in South West England, investing to unlock the region's business potential. It was abolished along with all the other RDAs on 31 March 2012, with some of its functions being replaced by local enterprise partnerships.
The "Y" service was a network of British signals intelligence collection sites, the Y-stations. The service was established during the First World War and used again during the Second World War. The sites were operated by a range of agencies including the Army, Navy and RAF plus the Foreign Office, General Post Office and Marconi Company receiving stations ashore and afloat. There were more than 600 receiving sets in use at Y-stations during the Second World War.
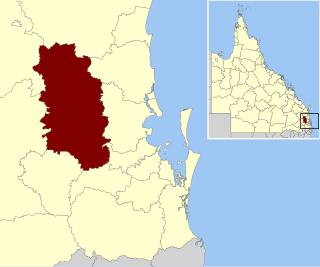
The Somerset Region is a local government area located in the West Moreton region of South East Queensland, Australia, about 100 kilometres (62 mi) northwest of Brisbane and centred on the town of Esk. It was created in 2008 from a merger of the Shire of Esk and the Shire of Kilcoy. It is commonly known as the Brisbane Valley, due to the Brisbane River which courses through the region, although significant parts of the region lie outside the hydrological Brisbane Valley itself.
The counter-terrorism page primarily deals with special police or military organizations that carry out arrest or direct combat with terrorists. This page deals with the other aspects of counter-terrorism:

The regions, formerly known as the government office regions, are the highest tier of sub-national division in England. They were established in 1994 and follow the 1974–96 county borders. They are a continuation of the former 1940s standard regions which followed the 1889–1974 administrative county borders. Between 1994 and 2011, nine regions had partly devolved functions; they no longer fulfil this role, continuing to be used for limited statistical purposes.

The Leeds City Region, or informally Greater Leeds, is a local enterprise partnership city region located in West Yorkshire, England. Prior to the West Yorkshire devolution deal, the partnership covered parts of South and North Yorkshire. According to the Office for National Statistics, as of 2017 the city region ranked 2nd behind Greater London for both population and GVA in the United Kingdom. It has a population of 2,320,214 million and a GVA of £69.62 billion.

A combined authority is a type of local government institution introduced in England outside Greater London by the Local Democracy, Economic Development and Construction Act 2009. Combined authorities are created voluntarily and allow a group of local authorities to pool appropriate responsibility and receive certain delegated functions from central government in order to deliver transport and economic policy more effectively over a wider area.
The Marchmont Observatory conducts academic research in support of local government policy formation concerning skills, employment and education for adults through networking, the development of learning programmes and research.

In the United Kingdom, devolution is the Parliament of the United Kingdom's statutory granting of a greater level of self-government to the Scottish Parliament, the Senedd, the Northern Ireland Assembly and the London Assembly and to their associated executive bodies the Scottish Government, the Welsh Government, the Northern Ireland Executive and in England, the Greater London Authority and combined authorities.
The Community Futures Network of Canada is an extensive network of 269 community futures development corporations. The national Community Futures Program is administered by four regional development agencies, the Atlantic Canada Opportunities Agency (ACOA), Canadian Economic Development for Québec Regions (CED-Q), Western Economic Diversification Canada (WD), and the Federal Economic Development Initiative for Northern Ontario (FedNor) under Industry Canada (IC). In Western Canada the Community Futures Program is delivered through a network of 90 non-profit organizations that are supported by four associations and one Pan-West Community Futures Network.

Counter Terrorism Policing is the national collaboration of police forces working to prevent, deter, and investigate terrorism in the United Kingdom.
References
- ↑ "About Us". South West Observatory (SWO). Archived from the original on 1 August 2013. Retrieved 9 June 2012.
- ↑ "Maintenance & Cleaning Services In London - Home & Office | RDA".
- ↑ "Government Offices | South West | Home". Archived from the original on 26 June 2009. Retrieved 24 June 2009.
- ↑ South West Councils Retrieved 5 May 2018.
- ↑ Yorkshire Futures: Regional Observatories Yorkshire Futures/Regional Observatories Archived 8 May 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Hansard: Questions to the Deputy Prime Minister Parliament of the United Kingdom 14 September 2004. Retrieved 5 May 2018.
- ↑ South West Observatory: Local Intelligence Networks Retrieved 5 May 2018.
- ↑ "Changing State of the South West 2012". South West Observatory (SWO). Archived from the original on 6 May 2018. Retrieved 5 May 2018.