The ecology of California can be understood by dividing the state into a number of ecoregions, which contain distinct ecological communities of plants and animals in a contiguous region. The ecoregions of California can be grouped into four major groups: desert ecoregions, Mediterranean ecoregions, forested mountains, and coastal forests.

The California Central Valley grasslands is a temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in California's Central Valley. It a diverse ecoregion containing areas of desert grassland, prairie, savanna, riparian forest, marsh, several types of seasonal vernal pools, and large lakes such as now-dry Tulare Lake, Buena Vista Lake, and Kern Lake.

The Llanos is a vast tropical grassland plain situated to the east of the Andes in Colombia and Venezuela, in northwestern South America. It is an ecoregion of the tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome.

The Humid Chaco is tropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in South America. It lies in the basin of the Paraná River, covering portions of central Paraguay and northern Argentina, and with a small portion of southwestern Brazil and northwestern Uruguay. The natural vegetation is a mosaic of grasslands, palm savanna, and forest.

The Terai–Duar savanna and grasslands is a narrow lowland ecoregion at the base of the Himalayas, about 25 km (16 mi) wide, and a continuation of the Indo-Gangetic Plain in India, Nepal and Bhutan. It is colloquially called Terai in the Ganges Basin east to Nepal, then Dooars in West Bengal, Bhutan and Assam east to the Brahmaputra River. It harbours the world's tallest grasslands, which are the most threatened and rare worldwide.
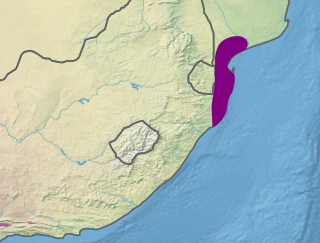
The Maputaland coastal forest mosaic is a subtropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion on the Indian Ocean coast of Southern Africa. It covers an area of 29,961 square kilometres (11,568 sq mi) in southern Mozambique, Eswatini, and the KwaZulu-Natal Province of South Africa. Mozambique's capital Maputo lies within the ecoregion.

The Upper Gangetic Plains moist deciduous forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion of northern India.

The Northern Congolian forest–savanna mosaic is a forest and savanna ecoregion of central Africa. It extends east and west across central Africa, covering parts of Cameroon, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, South Sudan, and Uganda. It is part of the belt of transitional forest-savanna mosaic that lie between Africa's moist equatorial Guineo-Congolian forests and the tropical dry forests, savannas, and grasslands to the north and south.

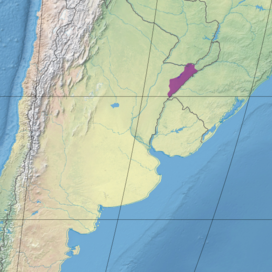
The Uruguayan savanna, also known as the Brazilian-Uruguayan savanna, is a subtropical grassland and savanna ecoregion which includes all of Uruguay and southernmost Brazil, along with portions of Argentina along the Uruguay River. In Brazil, this ecoregion is known as Pampas.

The Hawaiian tropical low shrublands are a tropical savanna ecoregion in the Hawaiian Islands.

The Lake Chad flooded savanna is a flooded grasslands and savannas ecoregion in Africa. It includes the seasonally- and permanently-flooded grasslands and savannas in the basin of Lake Chad in Central Africa, and covers portions of Cameroon, Chad, Niger, and Nigeria.

The Carpentaria tropical savanna is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in northern Australia.

The Trans Fly savanna and grasslands are a lowland ecoregion on the south coast of the island of New Guinea in both the Indonesian and Papua New Guinean sides of the island. With their monsoon and dry season climate these grasslands are quite different from the tropical rainforest that covers most of the island and resemble the landscape of northern Australia which lies to the south.

The Southeast Australia temperate savanna ecoregion is a large area of grassland dotted with eucalyptus trees running north–south across central New South Wales, Australia.

The southern Congolian forest–savanna mosaic is an ecoregion that covers a large area of the southern Democratic Republic of the Congo and northeastern Angola. Its rich blend of habitats provides key insights into the biogeography of central Africa with the extensive climatic variation that it has been experiencing for the last 10 million years. The human population is not high.

The Espinal (NT0801) is an ecoregion of dry, thorny forest, savanna and steppe in Argentina. It has been extensively modified by large scale cattle ranching, but remnants of the original flora remain. It is threatened by the advance of the irrigation-based agricultural frontier.

The Patagonian grasslands (NT0804) is an ecoregion in the south of Argentina. The grasslands are home to diverse fauna, including several rare or endemic species of birds. There are few protected areas. The grasslands are threatened by overgrazing by sheep, which supply high-quality merino wool. Efforts are being made to develop sustainable grazing practices to avoid desertification.

The Southern New Guinea lowland rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in southeastern New Guinea. The ecoregion covers portions of New Guinea's southern lowlands.

The Cuban wetlands is a flooded grasslands and savannas ecoregion on the island of Cuba and nearby smaller islands. The ecoregion covers 5,631 km2 (2,174 sq mi), about 4% of the island's area.