Related Research Articles

Basava (1131–1196), also called Basavēśvara and Basavaṇṇa, was an Indian philosopher, poet, Lingayat social reformer in the Shiva-focused bhakti movement, and a Hindu Shaivite social reformer during the reign of the Kalyani Chalukya/Kalachuri dynasty. Basava was active during the rule of both dynasties but reached the peak of his influence during the rule of King Bijjala II in Karnataka, India.

The Chandelas of Jejakabhukti was an Indian dynasty in Central India. The Chandelas ruled much of the Bundelkhand region between the 9th and the 13th centuries. They belonged to the Chandel clan of the Rajputs.

Lakkundi, also referred to as Lokkugundi, was a major city before the 14th century, and is now a village in Gadag District of Karnataka, India. By 10th century, it was already a major economic and commerce center with mint operations for South India, one mentioned in Kannada and Sanskrit inscriptions and texts. By 12th century, many Hindu and Jain temples had been consecrated here, along with public infrastructure such as stepwells and water reservoirs. Among the major temples are the Brahma Jinalaya (oldest), Mallikarjuna, Lakshminarayana, Manikeshwara, Naganatha, Kumbheshvara, Nanneshwara, Someshwara, Narayana, Nilakanteshwara, Kasivisesvara, Virabhadhara, Virupaksha, and others. As its importance and wealth grew, Lakkundi became one of the capitals of the Hoysala Empire.

Bargarh District is an administrative district of Odisha state in eastern India. The city of Bargarh is its district headquarters. The district was carved out of the erstwhile district of Sambalpur on 1 April 1993.
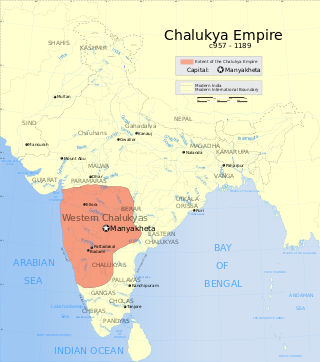
The Western Chalukya Empire ruled most of the western Deccan, South India, between the 10th and 12th centuries. This Kannada-speaking dynasty is sometimes called the Kalyani Chalukya after its regal capital at Kalyani, today's Basavakalyan in the modern Bidar district of Karnataka state, and alternatively the Later Chalukya from its theoretical relationship to the 6th-century Chalukya dynasty of Badami. The dynasty is called Western Chalukyas to differentiate from the contemporaneous Eastern Chalukyas of Vengi, a separate dynasty. Before the rise of these Chalukyas, the Rashtrakuta Empire of Manyakheta controlled most of the Deccan Plateau and Central India for over two centuries. In 973, seeing confusion in the Rashtrakuta empire after a successful invasion of their capital by the ruler of the Paramara dynasty of Malwa, Tailapa II, a feudatory of the Rashtrakuta dynasty ruling from Bijapur region defeated his overlords and made Manyakheta his capital. The dynasty quickly rose to power and grew into an empire under Someshvara I who moved the capital to Kalyani.

The Kalachuris of Kalyani, also Southern Kalachuris, were a 12th-century Indian dynasty, who ruled over parts of present-day northern Karnataka and Maharashtra. This dynasty rose to power in the Deccan region between 1156 and 1181 CE.

Bijjala II Kannada: ಇಮ್ಮಡಿ ಬಿಜ್ಜಳ was the Mahamandaleshwara of the Kalyani Chalukyas. He was the most famous of the southern Kalachuri kings who ruled initially as a vassal of Chalukya Vikramaditya VI. He ruled as the Mahamandalesvara over Karhada-4000 and Tardavadi-1000 provinces, designations given to territories within the larger Western Chalukya kingdom.

Basavakalyana is a historical city and municipal council in the Bidar District of the Indian state of Karnataka. It was the capital of two dynasties—Kalyani Chalukya and Kalachuris of Kalyani. It is famous for the world's tallest Basavanna statue, which stands 108 feet high. It is one of the major cities and industrial hubs of Bidar district.

Veera Ballala II was the most notable monarch of the Hoysala Empire. His successes against the Yadavas of Devagiri, the Southern Kalachuris, the Pandyas of Madurai and the waning Western Chalukya Empire, and his domination over the diminishing Cholas of Tanjore took the Hoysalas to their peak of power. The historian Chaurasia claims by the end of the 12th century, Ballala II's conquests had made the Hoysalas the most powerful dynasty of the Deccan. According to historian Derrett, Ballala II was "the most outstanding among Hoysala kings", and historian William Coelho in comparing Ballala II to King Vishnuvardhana writes, "he vied in glory with his grandfather".
Tailapa III succeeded Jagadhekamalla II to the Western Chalukya throne. His rule saw the beginning of the end of the Chalukya empire. Kakatiya dynasty's Prola II warred with him, defeated and took the Chalukya king captive. This resulted in other feudatories rising against the Chalukyas. The Seuna and the Hoysala started to take away territory. Kalachuri Bijjala II captured the regal capital Kalyani in 1157 when Tailapa III had to flee to Annigeri. Finally Tailapa III was killed by Hoysala Vira Narasimha in 1162.
Jagadhekamalla III succeeded Tailapa III to the highly diminished Western Chalukya empire. His rule was completely overshowded by the emergence of the Southern Kalachuris under Bijjala II who took control of Basavakalyana and ruled from there. He found refuge in the Banavasi region of the Western ghats, while Bijjala his former vassal became suzerain at Kalyana in 1162. The king in exile was a contemporary of Basavanna and other noted Veerashaiva preceptors.
Channabasavanna also known as " Guru Channabasaveshwara " was Basava's nephew and one of the foremost Sharanas of the 12th century. He, along with Basava, Allama Prabhu and Akka Mahadevi, played a pivotal role in the propagation of the Lingayat faith. He was the youngest among the sharana leaders and grew up in the household of Basavanna as he was the son of Nagalambike, Basava's own sister. He also wrote the Karana Hasuge which is one of the most sacred texts of the Lingayats, among many vachanas. He propounded the "shatasthala" philosophy associated with the six holy places of Veerashaiva Lingayat creed. He succeeded to the Shunya Simhasana at Anubhava Mantapa, Kalyana after the departure of Allama Prabhu, circa 1162ad. His young shoulders carried on the legacy of Basava after the latter's departure to Kudalasangama in 1162ad. He is credited to have systematised the entire manual of simple rituals for the followers. He was a strong advocate of the Ishtalinga wearing and expounded the material as well as the esoteric meaning of that divine symbol. He held together the nascent group of Shivasharanas and Jangmas in tumultuous times of clashes with the orthodox Brahmins and heretic Jains. Following the assassination of Kalachuri King Bijjala II in 1167 A.D, Channabasava along with his followers migrated to Ulavi safeguarding the Vachana literature. He attained Samadhi state there at the age of 25 passing on the leadership of the movement to Siddarama.
A large body of Western Chalukya literature in the Kannada language was produced during the reign of the Western Chalukya Empire in what is now southern India. This dynasty, which ruled most of the western Deccan in South India, is sometimes called the Kalyani Chalukya dynasty after its royal capital at Kalyani, and sometimes called the Later Chalukya dynasty for its theoretical relationship to the 6th-century Chalukya dynasty of Badami. For a brief period (1162–1183), the Kalachuris of Kalyani, a dynasty of kings who had earlier migrated to the Karnataka region from central India and served as vassals for several generations, exploited the growing weakness of their overlords and annexed the Kalyani. Around 1183, the last Chalukya scion, Someshvara IV, overthrew the Kalachuris to regain control of the royal city. But his efforts were in vain, as other prominent Chalukya vassals in the Deccan, the Hoysalas, the Kakatiyas and the Seunas destroyed the remnants of the Chalukya power.
Basavakalyana fort, earlier known as Kalyana fort, is located in Bidar district in the Indian state of Karnataka. Its historic importance is dated to the 10th century. The capital of Chalukyas was also shifted from Manyakheta to Kalyana in the 10th century. The fort, integral to the Basavakalyana town, is also famous as Karmabhoomi of Basavanna and hundreds of other Sharanas.
Bidar is a historic place located in the north-eastern part of the South Indian state of Karnataka. Bidar enjoys a picturesque situation, having been situated and built on the brink of a plateau, and thus commanding lovely views of the lowlands (talghat) towards the north and the east. Its latitude is 17°55'N., its longitude 77°32' E., and the height above the sea-level 2,330 feet (710 m). The climate is bracing and the temperature in the hottest season does not usually rise above 105 °F (41 °C). The Bidar plateau is an irregular oblong, 22 miles (35 km) in length and 12 miles (19 km) in extreme breadth.

The Kalachuris of Tripuri, also known the Kalachuris of Chedi, ruled parts of central India during 7th to 13th centuries. They are also known as the Later Kalachuris to distinguish them from their earlier namesakes, especially the Kalachuris of Mahishmati. Their core territory included the historical Chedi region, and their capital was located at Tripuri.

The Kalachuris of Ratnapura were a central Indian dynasty during 11th and 12th centuries. They ruled parts of present-day Chhattisgarh from their capital at Ratnapura. They were an offshoot of the Kalachuris of Tripuri, and ruled as vassals of the parent dynasty for many years.
Malidevaraju was a monarch of Macherla in the Palnadu kingdom, in present-day Andhra Pradesh, India. He fought for the complete control of Palnadu in the Battle of Karempudi but was killed during the conflict.
Rudra-deva was a Kakatiya king, who ruled parts of the present-day Telangana and Andhra Pradesh in southern India. He was the first sovereign ruler of his dynasty.
Mahadeva was a ruler of the Kakatiya dynasty which ruled in the present-day Telangana and Andhra Pradesh regions of India. He died in battle during an invasion of the neighbouring Seuna (Yadava) kingdom. The Yadavas captured his son Ganapati, but later reinstated him on the Kakatiya throne.
References
- 1 2 "43. Rayamurari Sovideva". Great History Of Mudiraja Caste.
- 1 2 3 Hosamani, Dr Ratnakar D. A Study of Historical Monuments in Bidar District (1st Century-17th Century CE). Lulu.com. ISBN 978-0-359-77997-0.
- 1 2 3 Rickmers, Christian Mabel (1899). The Chronology of India, from the Earliest Times to the Beginning Os the Sixteenth Century. A. Constable & Company.
- ↑ Sen, Sailendra Nath (15 March 2013). A Textbook of Medieval Indian History. Midpoint Trade Books Incorporated. p. 52-53. ISBN 978-93-80607-34-4.
- ↑ Bommareddi, Aruna (29 October 2019). Narrative Traditions of a Telugu Epic: Paln?tiv?rula Katha. Notion Press. ISBN 978-1-64678-733-3.