
Wyangala Dam is a major gated rock fill with clay core embankment and gravity dam with eight radial gates and a concrete chute spillway across the Lachlan River, located in the south-western slopes region of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's purpose includes flood mitigation, hydro-power, irrigation, water supply and conservation. The impounded reservoir is called Lake Wyangala.

Burrinjuck Dam is a major gated concrete-walled gravity dam with three spillways across the Murrumbidgee River located in the South West Slopes region of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's purpose includes flood mitigation, hydro-power, irrigation, water supply and conservation. The impounded reservoir is called Lake Burrinjuck.

The Xiaowan Dam is an arch dam on the Lancang (Mekong) River in Nanjian County, Yunnan Province, southwest China. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation and it supports a 4,200 MW power station. Constructed between 2002 and 2010 by Huaneng Power International at a cost of ¥32 billion, it is the world's second highest arch dam at 292 m (958 ft). It is also third highest among dams of all types behind Jinping-I and Nurek and the third largest hydroelectric power station in China.

Taki Dam (滝ダム) is a gravity dam on the Tadami River, 7.3 km (5 mi) east of Tadami in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. Surveys for the dam were carried out in 1958, construction began in 1959 and the dam was complete in 1961. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation and it supports a 92 MW power station consisting of 2 x 46 MW Kaplan turbines. The dam is 46 m (151 ft) tall and 264 m (866 ft) long. It creates a reservoir with a 27,000,000 m3 (21,889 acre⋅ft) capacity, of which 10,300,000 m3 (8,350 acre⋅ft) is active for power generation. The dam's spillway is controlled by four sluice gates and has a 200 m3/s (7,063 cu ft/s) discharge capacity.

The Ingula Pumped Storage Scheme is a pumped-storage power station in the escarpment of the Little Drakensberg range straddling the border of the KwaZulu-Natal and Free State provinces, South Africa. It is about 22 km (14 mi) North-East of Van Reenen. The pumped-storage hydroelectric scheme consists of an upper and a lower dam 4.6 kilometres (2.9 mi) apart and connected to a power station by tunnels. It was constructed by an Eskom and CMC Impregilo Mavundla Joint Venture The scheme was built at a cost of US$3.5 billion. Construction began in 2005 and the power station was scheduled to begin operations in late 2015, but the first two generators were not commissioned until March 2016, the third was brought into commercial operation in August 2016, and the fourth and final one in January 2017.

Victoria Dam is an arch dam located 130 mi (209 km) upstream of the Mahaweli River's mouth and 4 mi (6 km) from Teldeniya. Its main purposes are irrigation and hydroelectric power production. It is the tallest dam in Sri Lanka, and supports a 210 MW power station, the largest hydroelectric power station in the country. Construction of the dam commenced in 1978, and was ceremonially completed by then-President Jayewardene in April 1985.

The Shuibuya Dam is a concrete-face rock-fill embankment dam on the Qingjiang River in Badong County, Enshi, Hubei Province, China. The purpose of the dam is mainly hydroelectricity but it also promotes flood control, navigation, tourism and fishery. At 233 m (764 ft) tall and containing 15,640,000 m3 (20,460,000 cu yd) of material, it is the tallest concrete face rock-fill dam in the world.

The Dachaoshan Dam is a gravity dam on the Lancang (Mekong) River in Yunnan Province, China. The sole purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power production as it supplies water to a power station containing six 225 MW generators for a total installed capacity of 1,350 MW.

The Yantan Dam is a gravity dam on the Hongshui River near Dahua County, Guangxi China. The main purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power production and it has an associated 1,210 MW power station consisting of 4 x 302.5 MW Francis turbine-generators.

The Wanjiazhai Dam is a gravity dam on the Yellow River on the border of Pianguan County, Shaanxi Province and Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. The main purpose of the dam is water supply for the Wanjiazhai Water Control Project along with peak hydroelectric power generation. Construction on the dam began in 1994, the first generator went online in 1998 and the last in 2000.

The Wujiangdu Dam is an arch-gravity dam on the Wu River south of Zunyi, Guizhou Province, China. The purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation, flood control and navigation. The dam's power stations contain five generators for a total installed capacity of 1,130 MW.
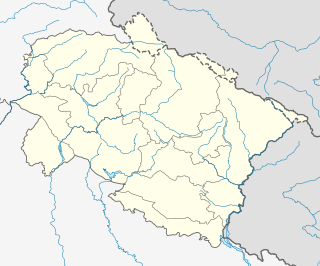
The Ichari Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Tons River 13 km (8 mi) north of Dakpathar in Uttarakhand, India. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power production and it is a run-of-the-river-type. It was completed in 1972. The dam diverts water to the Chibro Power Station which is then returned to the Tons River before being fed to the Khodri Power Station.

The Imha Dam is an embankment dam on the Banbyeoncheon River, a tributary of the Nakdong River, 14 km (9 mi) east of Andong in Gyeongsangbuk-do province, South Korea. The purpose of the dam is flood control, water supply and hydroelectric power generation. Construction on the dam began in 1987 and it was complete in 1991. The 73 m (240 ft) tall rock-fill, central earth-core dam creates a reservoir with a capacity of 595,000,000 m3 (482,374 acre⋅ft) and supplies a 50 MW power station with water. It supplies water for both municipal and industrial uses to Gumi, Dagu, Masan, Changwon, Jinhae, Woolsan, and Busan.

The Andong Dam is an embankment dam on the Nakdong River, 4 km (2 mi) east of Andong in Gyeongsangbuk-do province, South Korea. The purpose of the dam is flood control, water supply and hydroelectric power generation. Construction on the dam began in 1971 and was complete in 1976. The 83 m (272 ft) tall rock-fill, central clay core dam withholds a reservoir of 1,248,000,000 m3 (1,011,770 acre⋅ft) and provides water to an 80 MW pumped-storage power station. The lower reservoir (afterbay) for the power station is created by a 20 m (66 ft) high and 238 m (781 ft) long weir.

The Daecheong Dam is a combination concrete gravity and embankment dam on the Geum River, 16 km (10 mi) north of Daejeon in South Korea. The multi-purpose dam provides benefits of flood control, water supply and hydroelectric power generation. Construction on the dam began in 1975 and was formally commissioned on 1 December 1980. The 72 m (236 ft) high rock-fill dam has a central clay core and has created a reservoir with storage of 1,490,000,000 m3 (1,207,963 acre⋅ft).

The Chungju Dam is a gravity dam on the Namhan River, 6 km (4 mi) northeast of Chungju in Chungcheongbuk-do Province, South Korea. The purpose of the dam is flood control, water supply and hydroelectric power generation. Construction on the dam began in 1978 and was complete in 1985. The 98 m (322 ft) tall dam withholds a reservoir of 2,750,000,000 m3 (2,229,461 acre⋅ft) and supplies water to a 400 MW power station.
The Yangyang Pumped Storage Power Station uses the water of the Namdae-Chun River to operate a 1,000-megawatt (1,300,000 hp) pumped storage hydroelectric power scheme, about 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) west of Yangyang in Gangwon Province, South Korea. The lower reservoir is created by the Yangyang Dam on the Namdae and the upper reservoir by the Inje Dam is located 937 metres (3,074 ft) above the power plant. Construction on the power plant began in 1996 and it was completed and dedicated on September 13, 2006. It is operated by Korean Midland Power Co., a subsidiary of Korea Electric Power Company and was completed at a cost of ₩1.1 trillion won. The first generator was operational on February 23, 2006 and the last August 10, 2006.

The Okutadami Dam (奥只見ダム) is a concrete gravity dam on the Tadami River, 26 km (16 mi) east of Uonuma on the border of Niigata and Fukushima Prefectures, Japan. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation and it supports a 560 MW power station which is the largest conventional hydroelectric power station in Japan. The dam also forms the second largest reservoir in Japan, next to that of the Tokuyama Dam.

The Unbong Dam, or Yunfeng Dam, is a concrete gravity dam on the Yalu River which borders China and North Korea. It is located 33 km (21 mi) northeast of Ji'an in Jilin Province, China and Chasŏng in Chagang Province, North Korea. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation and it supports a 400 MW power station. Construction of the dam had initially began in August 1942 but was halted in 1945 after the surrender of Japan ending World War II. In October 1959, construction on the dam recommenced and in September 1965, the first of the four 100 MW Francis turbine-generators was operational. The last generator was operational on 4 April 1967. The 113.75 m (373 ft) tall dam creates a reservoir with a storage capacity of 3,895,000,000 m3 (3,157,728 acre⋅ft). The dam's spillway is an overflow type with 21 floodgates and has a maximum discharge of 21,900 m3/s (773,391 cu ft/s). The dam is located before a bend in the river and its power station is located on the other side of a ridge that meets the dam’s right abutment. Water is delivered to the power station via two tunnels, 775 m (2,543 ft) and 759 m (2,490 ft) long. Generators 1 and 3 deliver power to China while 2 and 4 deliver to North Korea.

The Deduru Oya Dam is an embankment dam built across the Deduru River in Kurunegala District of Sri Lanka. Built in 2014, the primary purpose of the dam is to retain approximately a billion cubic metres of water for irrigation purposes, which would otherwise flow out to sea. Construction of the dam began in 2006 and was ceremonially completed in 2014, with the presence of former President Mahinda Rajapaksa.


















