
A buoy is a floating device that can have many purposes. It can be anchored (stationary) or allowed to drift with ocean currents.

A weather station is a facility, either on land or sea, with instruments and equipment for measuring atmospheric conditions to provide information for weather forecasts and to study the weather and climate. The measurements taken include temperature, atmospheric pressure, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, and precipitation amounts. Wind measurements are taken with as few other obstructions as possible, while temperature and humidity measurements are kept free from direct solar radiation, or insolation. Manual observations are taken at least once daily, while automated measurements are taken at least once an hour. Weather conditions out at sea are taken by ships and buoys, which measure slightly different meteorological quantities such as sea surface temperature (SST), wave height, and wave period. Drifting weather buoys outnumber their moored versions by a significant amount.

A diving shot line, shot line, or diving shot, a type of downline or descending line, is an item of diving equipment consisting of a ballast weight, a line and a buoy. The weight is dropped on the dive site. The line connects the weight and the buoy and is used by divers to as a visual and tactile reference to move between the surface and the dive site more safely and more easily, and as a controlled position for in-water staged decompression stops. It may also be used to physically control rate of descent and ascent, particularly by surface-supplied divers.

The surface layer is the layer of a turbulent fluid most affected by interaction with a solid surface or the surface separating a gas and a liquid where the characteristics of the turbulence depend on distance from the interface. Surface layers are characterized by large normal gradients of tangential velocity and large concentration gradients of any substances transported to or from the interface.

In fluid dynamics, a wind wave, or wind-generated water wave, is a surface wave that occurs on the free surface of bodies of water as a result of the wind blowing over the water's surface. The contact distance in the direction of the wind is known as the fetch. Waves in the oceans can travel thousands of kilometers before reaching land. Wind waves on Earth range in size from small ripples to waves over 30 m (100 ft) high, being limited by wind speed, duration, fetch, and water depth.

Wave power is the capture of energy of wind waves to do useful work – for example, electricity generation, water desalination, or pumping water. A machine that exploits wave power is a wave energy converter (WEC).

A weather ship, or ocean station vessel, was a ship stationed in the ocean for surface and upper air meteorological observations for use in weather forecasting. They were primarily located in the north Atlantic and north Pacific oceans, reporting via radio. The vessels aided in search and rescue operations, supported transatlantic flights, acted as research platforms for oceanographers, monitored marine pollution, and aided weather forecasting by weather forecasters and in computerized atmospheric models. Research vessels remain heavily used in oceanography, including physical oceanography and the integration of meteorological and climatological data in Earth system science.
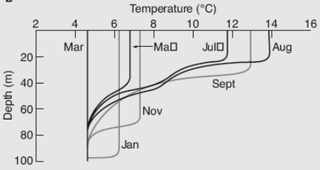
The oceanic or limnological mixed layer is a layer in which active turbulence has homogenized some range of depths. The surface mixed layer is a layer where this turbulence is generated by winds, surface heat fluxes, or processes such as evaporation or sea ice formation which result in an increase in salinity. The atmospheric mixed layer is a zone having nearly constant potential temperature and specific humidity with height. The depth of the atmospheric mixed layer is known as the mixing height. Turbulence typically plays a role in the formation of fluid mixed layers.

GNSS reflectometry involves making measurements from the reflections from the Earth of navigation signals from Global Navigation Satellite Systems such as GPS. The idea of using reflected GNSS signals for earth observation was first proposed in 1993 by Martin-Neira. It was also investigated by researchers at NASA Langley Research Center and is also known as GPS reflectometry.
The World Ocean Circulation Experiment (WOCE) was a component of the international World Climate Research Program, and aimed to establish the role of the World Ocean in the Earth's climate system. WOCE's field phase ran between 1990 and 1998, and was followed by an analysis and modeling phase that ran until 2002. When the WOCE was conceived, there were three main motivations for its creation. The first of these is the inadequate coverage of the World Ocean, specifically in the Southern Hemisphere. Data was also much more sparse during the winter months than the summer months, and there was—and still is to some extent—a critical need for data covering all seasons. Secondly, the data that did exist was not initially collected for studying ocean circulation and was not well suited for model comparison. Lastly, there were concerns involving the accuracy and reliability of some measurements. The WOCE was meant to address these problems by providing new data collected in ways designed to "meet the needs of global circulation models for climate prediction."

Weather buoys are instruments which collect weather and ocean data within the world's oceans, as well as aid during emergency response to chemical spills, legal proceedings, and engineering design. Moored buoys have been in use since 1951, while drifting buoys have been used since 1979. Moored buoys are connected with the ocean bottom using either chains, nylon, or buoyant polypropylene. With the decline of the weather ship, they have taken a more primary role in measuring conditions over the open seas since the 1970s. During the 1980s and 1990s, a network of buoys in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean helped study the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Moored weather buoys range from 1.5–12 metres (5–40 ft) in diameter, while drifting buoys are smaller, with diameters of 30–40 centimetres (12–16 in). Drifting buoys are the dominant form of weather buoy in sheer number, with 1250 located worldwide. Wind data from buoys has smaller error than that from ships. There are differences in the values of sea surface temperature measurements between the two platforms as well, relating to the depth of the measurement and whether or not the water is heated by the ship which measures the quantity.

Wave radar is a type of radar for measuring wind waves. Several instruments based on a variety of different concepts and techniques are available, and these are all often called. This article, gives a brief description of the most common ground-based radar remote sensing techniques.
The following are considered ocean essential climate variables (ECVs) by the Ocean Observations Panel for Climate (OOPC) that are currently feasible with current observational systems.
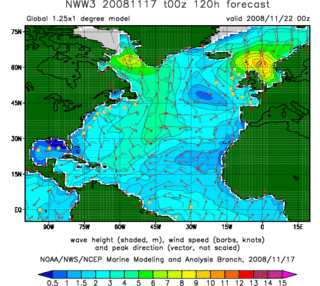
In fluid dynamics, wind wave modeling describes the effort to depict the sea state and predict the evolution of the energy of wind waves using numerical techniques. These simulations consider atmospheric wind forcing, nonlinear wave interactions, and frictional dissipation, and they output statistics describing wave heights, periods, and propagation directions for regional seas or global oceans. Such wave hindcasts and wave forecasts are extremely important for commercial interests on the high seas. For example, the shipping industry requires guidance for operational planning and tactical seakeeping purposes.
The marine optical buoy (MOBY) measures light at and very near the sea surface in a specific location over a long period of time, serving as part of an ocean color observation system. Satellites are another component of the system, providing global coverage through remote sensing; however, satellites measure light above the Earth's atmosphere, becoming subject to interference from the atmosphere itself and other light sources. The Marine Optical Buoy helps alleviate that interference and thus improve the quality of the overall ocean color observation system.
The Lysekil project is an ongoing wave power project which is run by the Centre for Renewable Electric Energy Conversion at Uppsala University in Sweden. It is located to the south of Lysekil, Västra Götaland County, on the west coast approximately 100 km (62 mi) north of Gothenburg. As of February 2024 there were 11 wave energy converters (WECs) located on the site, with a total capacity of 260 kW.

A current meter is an oceanographic device for flow measurement by mechanical, tilt, acoustical or electrical means.
PowerBuoy is a series of low-carbon emission marine power stations manufactured by Ocean Power Technologies (OPT), a renewable energy company located in New Jersey. PowerBuoys are most commonly used to provide power to offshore payloads generated through eco-friendly means. The PowerBuoy is designed to act as an Uninterruptible power supply. It stores energy in onboard batteries so that it can still provide continuous power through low generation periods.
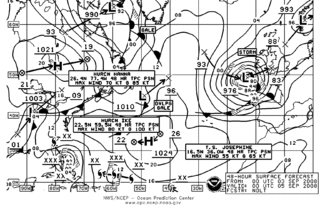
Marine weather forecasting is the process by which mariners and meteorological organizations attempt to forecast future weather conditions over the Earth's oceans. Mariners have had rules of thumb regarding the navigation around tropical cyclones for many years, dividing a storm into halves and sailing through the normally weaker and more navigable half of their circulation. Marine weather forecasts by various weather organizations can be traced back to the sinking of the Royal Charter in 1859 and the RMS Titanic in 1912.














