Related Research Articles
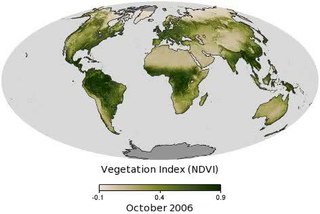
Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic characteristics. It is broader than the term flora which refers to species composition. Perhaps the closest synonym is plant community, but vegetation can, and often does, refer to a wider range of spatial scales than that term does, including scales as large as the global. Primeval redwood forests, coastal mangrove stands, sphagnum bogs, desert soil crusts, roadside weed patches, wheat fields, cultivated gardens and lawns; all are encompassed by the term vegetation.

Landscape ecology is the science of studying and improving relationships between ecological processes in the environment and particular ecosystems. This is done within a variety of landscape scales, development spatial patterns, and organizational levels of research and policy. Concisely, landscape ecology can be described as the science of landscape diversity as the synergetic result of biodiversity and geodiversity.

Urban ecology is the scientific study of the relation of living organisms with each other and their surroundings in the context of an urban environment. The urban environment refers to environments dominated by high-density residential and commercial buildings, paved surfaces, and other urban-related factors that create a unique landscape dissimilar to most previously studied environments in the field of ecology. The goal of urban ecology is to achieve a balance between human culture and the natural environment.

Habitat fragmentation describes the emergence of discontinuities (fragmentation) in an organism's preferred environment (habitat), causing population fragmentation and ecosystem decay. Causes of habitat fragmentation include geological processes that slowly alter the layout of the physical environment, and human activity such as land conversion, which can alter the environment much faster and causes the extinction of many species. More specifically, habitat fragmentation is a process by which large and contiguous habitats get divided into smaller, isolated patches of habitats.

A metapopulation consists of a group of spatially separated populations of the same species which interact at some level. The term metapopulation was coined by Richard Levins in 1969 to describe a model of population dynamics of insect pests in agricultural fields, but the idea has been most broadly applied to species in naturally or artificially fragmented habitats. In Levins' own words, it consists of "a population of populations".
Ecotopes are the smallest ecologically distinct landscape features in a landscape mapping and classification system. As such, they represent relatively homogeneous, spatially explicit landscape functional units that are useful for stratifying landscapes into ecologically distinct features for the measurement and mapping of landscape structure, function and change.
Spatial ecology studies the ultimate distributional or spatial unit occupied by a species. In a particular habitat shared by several species, each of the species is usually confined to its own microhabitat or spatial niche because two species in the same general territory cannot usually occupy the same ecological niche for any significant length of time.
Landscape connectivity in ecology is, broadly, "the degree to which the landscape facilitates or impedes movement among resource patches". Alternatively, connectivity may be a continuous property of the landscape and independent of patches and paths. Connectivity includes both structural connectivity and functional connectivity. The degree to which a landscape is connected determines the amount of dispersal there is among patches, which influences gene flow, local adaptation, extinction risk, colonization probability, and the potential for organisms to move as they cope with climate change.
Landscape epidemiology draws some of its roots from the field of landscape ecology. Just as the discipline of landscape ecology is concerned with analyzing both pattern and process in ecosystems across time and space, landscape epidemiology can be used to analyze both risk patterns and environmental risk factors. This field emerges from the theory that most vectors, hosts and pathogens are commonly tied to the landscape as environmental determinants control their distribution and abundance. In 1966, Evgeniy Pavlovsky introduced the concept of natural nidality or focality, defined by the idea that microscale disease foci are determined by the entire ecosystem. With the recent availability of new computing technologies such as geographic information systems, remote sensing, statistical methods including spatial statistics and theories of landscape ecology, the concept of landscape epidemiology has been applied analytically to a variety of disease systems, including malaria, hantavirus, Lyme disease and Chagas' disease.

Revegetation is the process of replanting and rebuilding the soil of disturbed land. This may be a natural process produced by plant colonization and succession, manmade rewilding projects, accelerated process designed to repair damage to a landscape due to wildfire, mining, flood, or other cause. Originally the process was simply one of applying seed and fertilizer to disturbed lands, usually grasses or clover. The fibrous root network of grasses is useful for short-term erosion control, particularly on sloping ground. Establishing long-term plant communities requires forethought as to appropriate species for the climate, size of stock required, and impact of replanted vegetation on local fauna. The motivations behind revegetation are diverse, answering needs that are both technical and aesthetic, but it is usually erosion prevention that is the primary reason. Revegetation helps prevent soil erosion, enhances the ability of the soil to absorb more water in significant rain events, and in conjunction reduces turbidity dramatically in adjoining bodies of water. Revegetation also aids protection of engineered grades and other earthworks.

In ecology, urban ecosystems are considered a ecosystem functional group within the intensive land-use biome. They are structurally complex ecosystems with highly heterogeneous and dynamic spatial structure that is created and maintained by humans. They include cities, smaller settlements and industrial areas, that are made up of diverse patch types. Urban ecosystems rely on large subsidies of imported water, nutrients, food and other resources. Compared to other natural and artificial ecosystems human population density is high, and their interaction with the different patch types produces emergent properties and complex feedbacks among ecosystem components.
Source–sink dynamics is a theoretical model used by ecologists to describe how variation in habitat quality may affect the population growth or decline of organisms.

Cross-boundary subsidies are caused by organisms or materials that cross or traverse habitat patch boundaries, subsidizing the resident populations. The transferred organisms and materials may provide additional predators, prey, or nutrients to resident species, which can affect community and food web structure. Cross-boundary subsidies of materials and organisms occur in landscapes composed of different habitat patch types, and so depend on characteristics of those patches and on the boundaries in between them. Human alteration of the landscape, primarily through fragmentation, has the potential to alter important cross-boundary subsidies to increasingly isolated habitat patches. Understanding how processes that occur outside of habitat patches can affect populations within them may be important to habitat management.
Patch dynamics is an ecological perspective that the structure, function, and dynamics of ecological systems can be understood through studying their interactive patches. Patch dynamics, as a term, may also refer to the spatiotemporal changes within and among patches that make up a landscape. Patch dynamics is ubiquitous in terrestrial and aquatic systems across organizational levels and spatial scales. From a patch dynamics perspective, populations, communities, ecosystems, and landscapes may all be studied effectively as mosaics of patches that differ in size, shape, composition, history, and boundary characteristics.
An ecological metacommunity is a set of interacting communities which are linked by the dispersal of multiple, potentially interacting species. The term is derived from the field of community ecology, which is primarily concerned with patterns of species distribution, abundance and interactions. Metacommunity ecology combines the importance of local factors and regional factors to explain patterns of species distributions that happen in different spatial scales.
Landscape limnology is the spatially explicit study of lakes, streams, and wetlands as they interact with freshwater, terrestrial, and human landscapes to determine the effects of pattern on ecosystem processes across temporal and spatial scales. Limnology is the study of inland water bodies inclusive of rivers, lakes, and wetlands; landscape limnology seeks to integrate all of these ecosystem types.

Ecosystem Functional Type (EFT) (Fig.1) is a new ecological concept to characterize ecosystem functioning. Ecosystem Functional Types are defined as groups of ecosystems or patches of the land surface that share similar dynamics of matter and energy exchanges between the biota and the physical environment. The EFT concept is analogous to the Plant Functional Types (PFTs) concept, but defined at a higher level of the biological organization. As plant species can be grouped according to common functional characteristics, ecosystems can be grouped according to their common functional behavior.
In landscape ecology, spatial configuration describes the spatial pattern of patches in a landscape. Most traditional spatial configuration measurements take into account aspects of patches within the landscape, including patches' size, shape, density, connectivity and fractal dimension. Other measurements are pixel-based, such as contagion and lacunarity. Together with spatial composition, spatial configuration is a basic component of landscape heterogeneity indices.
Seascape ecology is a scientific discipline that deals with the causes and ecological consequences of spatial pattern in the marine environment, drawing heavily on conceptual and analytical frameworks developed in terrestrial landscape ecology..

Landscape genetics is the scientific discipline that combines population genetics and landscape ecology. It broadly encompasses any study that analyses plant or animal population genetic data in conjunction with data on the landscape features and matrix quality where the sampled population lives. This allows for the analysis of microevolutionary processes affecting the species in light of landscape spatial patterns, providing a more realistic view of how populations interact with their environments. Landscape genetics attempts to determine which landscape features are barriers to dispersal and gene flow, how human-induced landscape changes affect the evolution of populations, the source-sink dynamics of a given population, and how diseases or invasive species spread across landscapes.
References
- ↑ Gustafson, E.J. (1998). "Quantifying landscape spatial pattern: what is the state of the art?". Ecosystems. 1 (2): 143–156. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.499.6965 . doi:10.1007/s100219900011.
| This ecology-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |