Privacy is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves, and thereby express themselves selectively.
Vance Oakley Packard was an American journalist and social critic. He was the author of several books, including The Hidden Persuaders and The Naked Society. He was a critic of consumerism.
Information privacy is the relationship between the collection and dissemination of data, technology, the public expectation of privacy, and the legal and political issues surrounding them. It is also known as data privacy or data protection.
The right to privacy is an element of various legal traditions that intends to restrain governmental and private actions that threaten the privacy of individuals. Over 150 national constitutions mention the right to privacy.
Center for Democracy & Technology (CDT) is a Washington, D.C.-based 501(c)(3) nonprofit The Organization which focuses on topics such as the rights of individual users in relation to technology policy, with the potential to affect the architecture of the Internet. The CDT has established a set of five key objectives which the organization is centered around. As described on the organization’s website, their first objective is to focus on promoting any legislation that may enable individuals to use technology for purposes of well-intent, while at the same time preventing its usage for harmful purposes. CDT’s second objective is to advocate for transparency, accountability, and a regard for human rights in the context of online platforms; this objective places a particular emphasis on setting a precedent for limiting the collection of the personal information of the average user. CDT’s third objective is to mitigate issues of online media censorship by governments, along with enabling individuals to access information freely without retaliation or punishment. Their fourth objective is to limit the ability of governments to perform surveillance activities on citizens. Lastly, their fifth objective is to highlight the importance of maintaining and supporting the globalized nature of the internet. These objectives are further defined within in the CDT’s six areas of focus including, Cybersecurity and standards, Equity in civic technology, free expression, government surveillance, Open internet, and Privacy and data.
Internet privacy involves the right or mandate of personal privacy concerning the storing, repurposing, provision to third parties, and displaying of information pertaining to oneself via Internet. Internet privacy is a subset of data privacy. Privacy concerns have been articulated from the beginnings of large-scale computer sharing.
Computer ethics is a part of practical philosophy concerned with how computing professionals should make decisions regarding professional and social conduct.
Online advertising, also known as online marketing, Internet advertising, digital advertising or web advertising, is a form of marketing and advertising which uses the Internet to promote products and services to audiences and platform users. Online advertising includes email marketing, search engine marketing (SEM), social media marketing, many types of display advertising, and mobile advertising. Advertisements are increasingly being delivered via automated software systems operating across multiple websites, media services and platforms, known as programmatic advertising.
Personal data, also known as personal information or personally identifiable information (PII), is any information related to an identifiable person.

HTTP cookies are small blocks of data created by a web server while a user is browsing a website and placed on the user's computer or other device by the user's web browser. Cookies are placed on the device used to access a website, and more than one cookie may be placed on a user's device during a session.
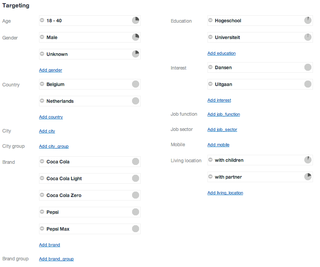
Targeted advertising is a form of advertising, including online advertising, that is directed towards an audience with certain traits, based on the product or person the advertiser is promoting. These traits can either be demographic with a focus on race, economic status, sex, age, generation, level of education, income level, and employment, or psychographic focused on the consumer values, personality, attitude, opinion, lifestyle and interest. This focus can also entail behavioral variables, such as browser history, purchase history, and other recent online activities. Targeted advertising is concentrated in certain traits and consumers who are likely to have a strong preference. These individuals will receive messages instead of those who have no interest and whose preferences do not match a particular product's attributes. This eliminates waste.
Web tracking is the practice by which operators of websites and third parties collect, store and share information about visitors’ activities on the World Wide Web. Analysis of a user's behaviour may be used to provide content that enables the operator to infer their preferences and may be of interest to various parties, such as advertisers. Web tracking can be part of visitor management.
The social data revolution is the shift in human communication patterns towards increased personal information sharing and its related implications, made possible by the rise of social networks in the early 2000s. This phenomenon has resulted in the accumulation of unprecedented amounts of public data.

Web browsing history refers to the list of web pages a user has visited, as well as associated metadata such as page title and time of visit. It is usually stored locally by web browsers in order to provide the user with a history list to go back to previously visited pages. It can reflect the user's interests, needs, and browsing habits.

Digital privacy is often used in contexts that promote advocacy on behalf of individual and consumer privacy rights in e-services and is typically used in opposition to the business practices of many e-marketers, businesses, and companies to collect and use such information and data. Digital privacy can be defined under three sub-related categories: information privacy, communication privacy, and individual privacy.
Since the arrival of early social networking sites in the early 2000s, online social networking platforms have expanded exponentially, with the biggest names in social media in the mid-2010s being Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and Snapchat. The massive influx of personal information that has become available online and stored in the cloud has put user privacy at the forefront of discussion regarding the database's ability to safely store such personal information. The extent to which users and social media platform administrators can access user profiles has become a new topic of ethical consideration, and the legality, awareness, and boundaries of subsequent privacy violations are critical concerns in advance of the technological age.

A user profile is a collection of settings and information associated with a user. It contains critical information that is used to identify an individual, such as their name, age, portrait photograph and individual characteristics such as knowledge or expertise. User profiles are most commonly present on social media websites such as Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn; and serve as voluntary digital identity of an individual, highlighting their key features and traits. In personal computing and operating systems, user profiles serve to categorise files, settings, and documents by individual user environments, known as ‘accounts’, allowing the operating system to be more friendly and catered to the user. Physical user profiles serve as identity documents such as passports, driving licenses and legal documents that are used to identify an individual under the legal system.
Datalogix is a consumer data collection company based in Denver, Colorado. Datalogix provides online, direct mail, and mobile services to their clients. The company's primary objective is to obtain and track offline and online data purchasing behavioral patterns, with the use of information obtained from retailers' loyalty card programs.

The Naked Society is a 1964 book on privacy by Vance Packard. The book argues that changes in technology are encroaching on privacy and could eventually create a society with radically different privacy standards.
Cross-device tracking refers to technology which enables the tracking of users across multiple devices such as smartphones, television sets, smart TVs, and personal computers.





