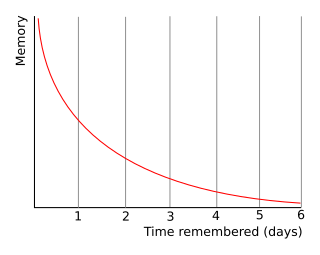
The forgetting curve hypothesizes the decline of memory retention in time. This curve shows how information is lost over time when there is no attempt to retain it. A related concept is the strength of memory that refers to the durability that memory traces in the brain. The stronger the memory, the longer period of time that a person is able to recall it. A typical graph of the forgetting curve purports to show that humans tend to halve their memory of newly learned knowledge in a matter of days or weeks unless they consciously review the learned material.
Language education – the process and practice of teaching a second or foreign language – is primarily a branch of applied linguistics, but can be an interdisciplinary field. There are four main learning categories for language education: communicative competencies, proficiencies, cross-cultural experiences, and multiple literacies.
A vocabulary is a set of words, typically the set in a language or the set known to an individual. The word vocabulary originated from the Latin vocabulum, meaning "a word, name". It forms an essential component of language and communication, helping convey thoughts, ideas, emotions, and information. Vocabulary can be oral, written, or signed and can be categorized into two main types: active vocabulary and passive vocabulary. An individual's vocabulary continually evolves through various methods, including direct instruction, independent reading, and natural language exposure, but it can also shrink due to forgetting, trauma, or disease. Furthermore, vocabulary is a significant focus of study across various disciplines, like linguistics, education, psychology, and artificial intelligence. Vocabulary is not limited to single words; it also encompasses multi-word units known as collocations, idioms, and other types of phraseology. Acquiring an adequate vocabulary is one of the largest challenges in learning a second language.
Organizational learning is the process of creating, retaining, and transferring knowledge within an organization. An organization improves over time as it gains experience. From this experience, it is able to create knowledge. This knowledge is broad, covering any topic that could better an organization. Examples may include ways to increase production efficiency or to develop beneficial investor relations. Knowledge is created at four different units: individual, group, organizational, and inter organizational.

Speed reading is any of many techniques claiming to improve one's ability to read quickly. Speed-reading methods include chunking and minimizing subvocalization. The many available speed-reading training programs may utilize books, videos, software, and seminars. There is little scientific evidence regarding speed reading, and as a result its value seems uncertain. Cognitive neuroscientist Stanislas Dehaene says that claims of reading up to 1,000 words per minute "must be viewed with skepticism".
Communicative language teaching (CLT), or the communicative approach (CA), is an approach to language teaching that emphasizes interaction as both the means and the ultimate goal of study.
Reading for special needs has become an area of interest as the understanding of reading has improved. Teaching children with special needs how to read was not historically pursued due to perspectives of a Reading Readiness model. This model assumes that a reader must learn to read in a hierarchical manner such that one skill must be mastered before learning the next skill. This approach often led to teaching sub-skills of reading in a decontextualized manner. This style of teaching made it difficult for children to master these early skills, and as a result, did not advance to more advanced literacy instruction and often continued to receive age-inappropriate instruction.
Reading comprehension is the ability to process written text, understand its meaning, and to integrate with what the reader already knows. Reading comprehension relies on two abilities that are connected to each other: word reading and language comprehension. Comprehension specifically is a "creative, multifaceted process" that is dependent upon four language skills: phonology, syntax, semantics, and pragmatics.
Competence is the set of demonstrable characteristics and skills that enable and improve the efficiency or performance of a job. Competency is a series of knowledge, abilities, skills, experiences and behaviors, which leads to effective performance in an individual's activities. Competency is measurable and can be developed through training.
The audio-lingual method or Army Method is a method used in teaching foreign languages. It is based on behaviorist theory, which postulates that certain traits of living things, and in this case humans, could be trained through a system of reinforcement. The correct use of a trait would receive positive feedback while incorrect use of that trait would receive negative feedback.
Team-based learning (TBL) is a collaborative learning and teaching strategy that enables people to follow a structured process to enhance student engagement and the quality of student or trainee learning. The term and concept was first popularized by Larry Michaelsen, the central figure in the development of the TBL method while at University of Oklahoma in the 1970s, as an educational strategy that he developed for use in academic settings, as in medical education. Team-based learning methodology can be used in any classroom or training sessions at school or in the workplace.
Language teaching, like other educational activities, may employ specialized vocabulary and word use. This list is a glossary for English language learning and teaching using the communicative approach.

Learning disability, learning disorder, or learning difficulty is a condition in the brain that causes difficulties comprehending or processing information and can be caused by several different factors. Given the "difficulty learning in a typical manner", this does not exclude the ability to learn in a different manner. Therefore, some people can be more accurately described as having a "learning difference", thus avoiding any misconception of being disabled with a possible lack of an ability to learn and possible negative stereotyping. In the United Kingdom, the term "learning disability" generally refers to an intellectual disability, while conditions such as dyslexia and dyspraxia are usually referred to as "learning difficulties".
Reciprocal teaching is an instructional activity that takes the form of a dialogue between teachers and students regarding segments of text for the purpose of constructing the meaning of text. Reciprocal teaching is a reading technique which is thought to promote students' reading comprehension. A reciprocal approach provides students with four specific reading strategies that are actively and consciously used to support comprehension: Questioning, Clarifying, Summarizing, and Predicting. Annemarie Palincsar states that the purpose of reciprocal teaching is to facilitate a group effort between teacher and students as well as among students in the task of bringing meaning to the text.
Reciprocal teaching is best represented as a dialogue between teachers and students in which participants take turns assuming the role of teacher. -Annemarie Sullivan Palincsar
In the field of second language acquisition, there are many theories about the most effective way for language learners to acquire new language forms. One theory of language acquisition is the comprehensible output hypothesis.
The input hypothesis, also known as the monitor model, is a group of five hypotheses of second-language acquisition developed by the linguist Stephen Krashen in the 1970s and 1980s. Krashen originally formulated the input hypothesis as just one of the five hypotheses, but over time the term has come to refer to the five hypotheses as a group. The hypotheses are the input hypothesis, the acquisition–learning hypothesis, the monitor hypothesis, the natural order hypothesis and the affective filter hypothesis. The input hypothesis was first published in 1977.

Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of letters, symbols, etc., especially by sight or touch.
Patricia A. Carpenter is a psychologist who, as of 1997, held the Lee and Marge Gregg Professorship of Psychology at Carnegie Mellon University. Carpenter has studied individual variability in working memory, comprehension rates in speed reading, and how brain function during complex cognitive tasks appears in functional magnetic resonance imaging. With Marcel Just, she coauthored The Psychology of Reading and Language Comprehension (1987).

Extensive reading (ER) is the process of reading longer, easier texts for an extended period of time without a breakdown of comprehension, feeling overwhelmed, or the need to take breaks. It stands in contrast to intensive or academic reading, which is focused on a close reading of dense, shorter texts, typically not read for pleasure. Though used as a teaching strategy to promote second-language development, ER also applies to free voluntary reading and recreational reading both in and out of the classroom. ER is based on the assumption that we learn to read by reading.
Second-language attrition is the decline of second-language skills, which occurs whenever the learner uses the second language to an insufficient degree or due to environmental changes the language use is limited and another language is becoming the dominant one.



