This article needs additional citations for verification .(October 2020) |
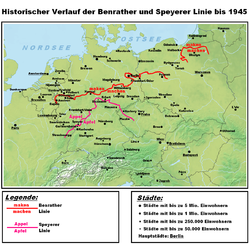
In German dialectology, the Speyer line or Main line (Main River) is an isogloss separating the Central German dialects to the north, which have a stop in words like Appel "apple", from the Upper German dialects to the south, which have an affricate, Apfel. [1]
The Speyer line begins in Alsace near Strasbourg, and runs northeast to Thüringen, crossing the Rhine at Speyer. After passing close to Erfurt, it turns southeast and continues into the formerly German-speaking parts of Bohemia. The line is exemplified by place names containing an uncombined /p/ phoneme, which are located north of the line and include Paderborn, Potsdam, and Wuppertal. Those with an affricate /pf/, including Pfaffenhofen and Pforzheim, lie mostly to the south.