
Rosaceae, the rose family, is a medium-sized family of flowering plants that includes 4,828 known species in 91 genera.

The Rubiaceae are a family of flowering plants, commonly known as the coffee, madder, or bedstraw family. It consists of terrestrial trees, shrubs, lianas, or herbs that are recognizable by simple, opposite leaves with interpetiolar stipules and sympetalous actinomorphic flowers. The family contains about 13,500 species in about 620 genera, which makes it the fourth-largest angiosperm family. Rubiaceae has a cosmopolitan distribution; however, the largest species diversity is concentrated in the tropics and subtropics. Economically important genera include Coffea, the source of coffee, Cinchona, the source of the antimalarial alkaloid quinine, ornamental cultivars, and historically some dye plants.

The MaloideaeC.Weber was the apple subfamily, a grouping used by some taxonomists within the rose family, Rosaceae. Recent molecular phylogenetic evidence has shown that the traditional Spiraeoideae and Amygdaloideae form part of the same clade as the traditional Maloideae, and the correct name for this group is Amygdaloideae. Earlier circumscriptions of Maloideae are more-or-less equivalent to subtribe Malinae or to tribe Maleae. The group includes a number of plants bearing commercially important fruits, such as apples and pears, while others are cultivated as ornamentals.

Amygdaloideae is a subfamily within the flowering plant family Rosaceae. It was formerly considered by some authors to be separate from Rosaceae, and the family names Prunaceae and Amygdalaceae have been used. Reanalysis from 2007 has shown that the previous definition of subfamily Spiraeoideae was paraphyletic. To solve this problem, a larger subfamily was defined that includes the former Amygdaloideae, Spiraeoideae, and Maloideae. This subfamily, however, is to be called Amygdaloideae rather than Spiraeoideae under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants as updated in 2011.

Prunus is a genus of trees and shrubs, which includes the fruits plums, cherries, peaches, nectarines, apricots, and almonds.

The Rutaceae is a family, commonly known as the rue or citrus family, of flowering plants, usually placed in the order Sapindales.

The quince is the sole member of the genus Cydonia in the Malinae subtribe of the Rosaceae family. It is a deciduous tree that bears hard, aromatic bright golden-yellow pome fruit, similar in appearance to a pear. Ripe quince fruits are hard, tart, and astringent. They are seldom eaten raw, but are processed into marmalade, jam, paste or alcoholic beverages.

Apocynaceae is a family of flowering plants that includes trees, shrubs, herbs, stem succulents, and vines, commonly known as the dogbane family, because some taxa were used as dog poison. Members of the family are native to the European, Asian, African, Australian, and American tropics or subtropics, with some temperate members. The former family Asclepiadaceae is considered a subfamily of Apocynaceae and contains 348 genera. A list of Apocynaceae genera may be found here.

Aronia is a genus of deciduous shrubs, the chokeberries, in the family Rosaceae native to eastern North America and most commonly found in wet woods and swamps. The genus Aronia is considered to have 3 species. The most common and widely used is Aronia melanocarpa which emerged from Eastern North America. The lesser known Aronia arbutifolia and the hybrid form of the abovementioned species called Aronia prunifolia were first cultivated in Central and Eastern North America. In the eighteenth century, the first shrubs of the best-known species Aronia melanocarpa reached Europe where they were first cultivated in Scandinavia and Russia.

Spiraea, sometimes spelled spirea in common names, and commonly known as meadowsweets or steeplebushes, is a genus of about 80 to 100 species of shrubs in the family Rosaceae. They are native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere, with the greatest diversity in eastern Asia.

Photinia is a genus of about 30 species of small trees and large shrubs, but the taxonomy has recently varied greatly, with the genera Heteromeles, Stranvaesia and Aronia sometimes included in Photinia.

Aruncus is a genus of clump-forming herbaceous perennial plants in the family Rosaceae. Botanical opinion of the number of species differs, with from one to four species accepted. They are closely related to the genera Filipendula and Spiraea, and are native to mountainous damp woodland in temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Creamy white plumes of flowers are produced above veined and toothed leaflets.

Holodiscus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rosaceae, native to the Americas, from southwestern British Columbia, Canada and the western United States south to Bolivia.

Neillia is a genus of the botanical family Rosaceae. They are deciduous shrubs or subshrubs. They produce clusters of terminal or axillary flowers, and have dry dehiscent fruits. They are native to eastern and central Asia.

Gillenia is a genus of two species of perennial herbs in the family Rosaceae, Gillenia stipulata and Gillenia trifoliata. Common names for plants in this genus include: Bowman's root, Indian-physic, American ipecac. This genus is endemic to dry open woods with acidic soils in eastern North America. Both plants are subshrubs with exposed semi-woody branches and serrated leaves; the larger lower leaves are divided into palmately arranged leaflets. Plants bloom in May, June, or July; blooms are composed of five slender white petals which are loosely arranged and typically appear slightly twisted and limp as if they were wilted. The flowers mature into small capsules. G. stipulata and G. trifoliata are often planted as ornamentals and used in herbal medicine.
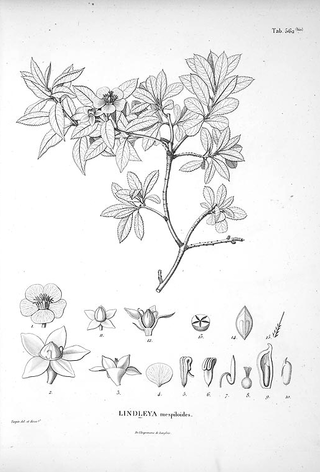
Lindleya is a genus of Mexican evergreen trees of the family Rosaceae. The sole species, L. mespiloides, grows to a height of 6 metres (20 ft) and bears solitary white fragrant flowers in summer. The fruit are dry dehiscent capsules.

Sorbaria sorbifolia, the false spiraea, is a species of flowering plant in the family Rosaceae. The common name is also spelled false spirea. Other common names include false goat's beard, sorb-leaved schizonotus, Ural false spirea, and in Chinese: 珍珠梅; pinyin: zhen zhu mei; lit. 'pearl plum'.

Neillieae is a tribe of flowering plants in rose family and the Amygdaloideae subfamily. It includes the genera Physocarpus and Neillia.

The subfamily Dryadoideae consists of four genera in the family Rosaceae, all of which contain representative species with root nodules that host the nitrogen-fixing bacterium Frankia. They are subshrubs, shrubs, or small trees with a base chromosome number of 9, whose fruits are either an achene or an aggregate of achenes.

The Maleae are the apple tribe in the rose family, Rosaceae. The group includes a number of plants bearing commercially important fruits, such as apples and pears, while others are cultivated as ornamentals. Older taxonomies separated some of this group as tribe Crataegeae, as the Cydonia group, or some genera were placed in family Quillajaceae.




















