
Ink is a gel, sol, or solution that contains at least one colorant, such as a dye or pigment, and is used to color a surface to produce an image, text, or design. Ink is used for drawing or writing with a pen, brush, reed pen, or quill. Thicker inks, in paste form, are used extensively in letterpress and lithographic printing.

Lithography is a planographic method of printing originally based on the immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German author and actor Alois Senefelder and was initially used mostly for musical scores and maps. Lithography can be used to print text or images onto paper or other suitable material. A lithograph is something printed by lithography, but this term is only used for fine art prints and some other, mostly older, types of printed matter, not for those made by modern commercial lithography.

Etching is traditionally the process of using strong acid or mordant to cut into the unprotected parts of a metal surface to create a design in intaglio (incised) in the metal. In modern manufacturing, other chemicals may be used on other types of material. As a method of printmaking, it is, along with engraving, the most important technique for old master prints, and remains in wide use today. In a number of modern variants such as microfabrication etching and photochemical milling, it is a crucial technique in modern technology, including circuit boards.

Printmaking is the process of creating artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand processed technique, rather than a photographic reproduction of a visual artwork which would be printed using an electronic machine ; however, there is some cross-over between traditional and digital printmaking, including risograph.

The CMYK color model is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation CMYK refers to the four ink plates used: cyan, magenta, yellow, and key.

Halftone is the reprographic technique that simulates continuous-tone imagery through the use of dots, varying either in size or in spacing, thus generating a gradient-like effect. "Halftone" can also be used to refer specifically to the image that is produced by this process.
Dye-sublimation printing is a term that covers several distinct digital computer printing techniques that involve using heat to transfer dye onto a substrate.

A T-shirt is a style of fabric shirt named after the T shape of its body and sleeves. Traditionally, it has short sleeves and a round neckline, known as a crew neck, which lacks a collar. T-shirts are generally made of stretchy, light, and inexpensive fabric and are easy to clean. The T-shirt evolved from undergarments used in the 19th century and, in the mid-20th century, transitioned from undergarments to general-use casual clothing.

The Ben Day process is a printing and photoengraving technique for producing areas of gray or various colors by using fine patterns of ink on the paper. It was developed in 1879 by illustrator and printer Benjamin Henry Day Jr.. The process is commonly described in terms of Ben Day dots, but other shapes can be used, such as parallel lines or textures.

In color reproduction and colorimetry, a gamut, or color gamut, is a convex set containing the colors that can be accurately represented, i.e. reproduced by an output device or measured by an input device. Devices with a larger gamut can represent more colors. Similarly, gamut may also refer to the colors within a defined color space, which is not linked to a specific device. A trichromatic gamut is often visualized as a color triangle. A less common usage defines gamut as the subset of colors contained within an image, scene or video.
Color theory, or more specifically traditional color theory, is the historical body of knowledge describing the behavior of colors, namely in color mixing, color contrast effects, color harmony, color schemes and color symbolism. Modern color theory is generally referred to as Color science. While there is no clear distinction in scope, traditional color theory tends to be more subjective and have artistic applications, while color science tends to be more objective and have functional applications, such as in chemistry, astronomy or color reproduction. Color theory dates back at least as far as Aristotle's treatise On Colors. A formalization of "color theory" began in the 18th century, initially within a partisan controversy over Isaac Newton's theory of color and the nature of primary colors. By the end of the 19th century, a schism had formed between traditional color theory and color science.
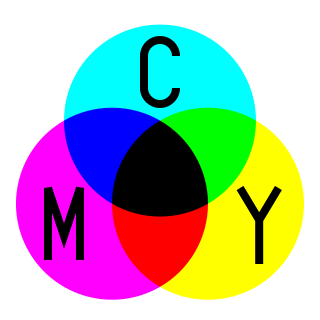
Subtractive color or subtractive color mixing predicts the spectral power distribution of light after it passes through successive layers of partially absorbing media. This idealized model is the essential principle of how dyes and pigments are used in color printing and photography, where the perception of color is elicited after white light passes through microscopic "stacks" of partially absorbing media allowing some wavelengths of light to reach the eye and not others, and also in painting, whether the colors are mixed or applied in successive layers.

Rotogravure is a type of intaglio printing process, which involves engraving the image onto an image carrier. In gravure printing, the image is engraved onto a cylinder because, like offset printing and flexography, it uses a rotary printing press.

Lenticular printing is a technology in which lenticular lenses are used to produce printed images with an illusion of depth, or the ability to change or move as they are viewed from different angles.
The colors of postage stamps are at once obvious, and among the most difficult areas of philately. Different denominations of stamps have been printed in different colors since the very beginning; as with their successors, postal clerks could distinguish the Penny Black and Two pence blue more quickly by color than by reading the value, and the practice generally continues today. In practice, the actual color of a stamp may vary, and while collectors will pay high prices for rare shades, it may not be easy to tell those apart from variations caused by age, light, chemicals, and other factors. Stamp colors are routinely described by color name rather with any sort of a numerical system like CMYK; several color guides showing a selection of colors have been produced, but are not especially popular with collectors.
Color printing or colour printing is the reproduction of an image or text in color.
In four-color printing, under color addition (UCA) is a technique for darkening areas of the printed image by adding colored inks. It is meant to achieve the same results as under color removal, but from a different starting position.
Viscosity printing is a multi-color printmaking technique that incorporates principles of relief printing and intaglio printing. It was pioneered by Stanley William Hayter.

Bokashi is a technique used in Japanese woodblock printmaking. It achieves a variation in lightness and darkness (value) of a single color or multiple colors by hand applying a gradation of ink to a moistened wooden printing block, rather than inking the block uniformly. This hand-application had to be repeated for each sheet of paper that was printed.
Micael Priest was an American artist and raconteur. Due to Priest's color-blindness, his primary medium was pen and ink, which he put to great use in inexpensively printed, highly graphic, rock posters. Often printed in single color or split-fountain reliefs, the posters were done mostly for Armadillo World Headquarters, a music hall in Austin, Texas that operated from August 7, 1970 to December 31, 1980.













