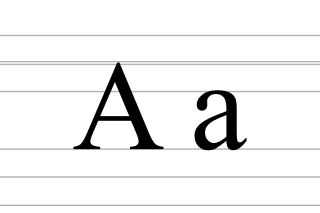
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is a, plural aes.

Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea to the west, the Turkish Straits to the northwest, and the Black Sea to the north. The eastern and southeastern limits have been expanded either to the entirety of Asiatic Turkey or to an imprecise line from the Black Sea to the Gulf of Alexandretta. Topographically, the Sea of Marmara connects the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea through the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, and separates Anatolia from Thrace in Southeast Europe.

Athens is the capital and largest city of Greece. A major coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica region and is the southernmost capital on the European mainland. With its urban area's population numbering over three and a quarter million, it is the eighth largest urban area in the European Union. The Municipality of Athens, which constitutes a small administrative unit of the entire urban area, had a population of 643,452 (2021) within its official limits, and a land area of 38.96 km2 (15.04 sq mi).

Greek is an Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy, southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems.

Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the east. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring thousands of islands. The country comprises nine traditional geographic regions, and has a population of over 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras.

The economy of Greece is the 52nd largest in the world, with a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of $252.732 billion per annum. In terms of purchasing power parity, Greece is the world's 54th largest economy, at $436.757 billion per annum. As of 2023, Greece is the sixteenth largest economy in the European Union and eleventh largest in the eurozone. According to the International Monetary Fund's figures for 2024, Greece's GDP per capita is $24,342 at nominal value and $42,066 at purchasing power parity. Among OECD nations, Greece has a highly efficient and strong social security system; social expenditure stood at roughly 24.1% of GDP.

The Odyssey is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. Like the Iliad, the Odyssey is divided into 24 books. It follows the Greek hero Odysseus, king of Ithaca, and his journey home after the Trojan War. After the war, which lasted ten years, his journey from Troy to Ithaca, via Africa and southern Europe, lasted for ten additional years during which time he encountered many perils and all of his crewmates were killed. In his absence, Odysseus was assumed dead, and his wife Penelope and son Telemachus had to contend with a group of unruly suitors who were competing for Penelope's hand in marriage.

P, or p, is the sixteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is pee, plural pees.

Thessaloniki, also known as Thessalonica, Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica, is the second-largest city in Greece, with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of Macedonia, the administrative region of Central Macedonia and the Decentralized Administration of Macedonia and Thrace. It is also known in Greek as "η Συμπρωτεύουσα", literally "the co-capital", a reference to its historical status as the Συμβασιλεύουσα or "co-reigning" city of the Byzantine Empire alongside Constantinople.

Cleopatra VII Thea Philopator was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler. A member of the Ptolemaic dynasty, she was a descendant of its founder Ptolemy I Soter, a Macedonian Greek general and companion of Alexander the Great. Her first language was Koine Greek, and she is the only Ptolemaic ruler known to have learned the Egyptian language. After her death, Egypt became a province of the Roman Empire, marking the end of the last Hellenistic-period state in the Mediterranean, a period which had lasted since the reign of Alexander.

Tzatziki, also known as cacık or tarator, is a class of dip, soup, or sauce found in the cuisines of Southeastern Europe and West Asia. It is made of salted strained yogurt or diluted yogurt mixed with cucumbers, garlic, salt, olive oil, red wine vinegar, sometimes with lemon juice, and herbs such as dill, mint, parsley and thyme. It is served as a cold appetiser (meze), a side dish, and as a sauce for souvlaki and gyros sandwiches and other foods.

Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek, Dark Ages, the Archaic or Epic period, and the Classical period.

The Greece national football team represents Greece in men's international football matches, and is controlled by the Hellenic Football Federation, the governing body for football in Greece. Greece is one of only ten national teams to have been crowned UEFA European Champions.

PAOK FC, short for "Pan-Thessalonian Athletic Club of Constantinopolitans", and commonly known as PAOK Thessaloniki, PAOK Salonika or simply PAOK, is a Greek professional football club based in Thessaloniki, Macedonia, Greece. PAOK are one of the top domestic clubs, the most widely supported in Northern Greece and the current Greek Super League champions.

A.E.K. Football Club, known simply as A.E.K in Greece and AEK Athens internationally, is a Greek professional football club based in Nea Filadelfeia, Attica, Greece.

Olympiacos F.C., known simply as Olympiacos or Olympiacos Piraeus, is a Greek professional football club based in Piraeus. Part of the major multi-sport club Olympiacos CFP, their name was inspired from the ancient Olympic Games and along with the club's emblem, the laurel-crowned Olympic athlete, symbolize the Olympic ideals of ancient Greece. Their home ground is the Karaiskakis Stadium, a 33,334-capacity stadium in Piraeus.

OFI Football Club, commonly referred to as OFI, is a Greek professional football club based in Heraklion, on the island of Crete. It is part of the OFI multi-sports club. The team competes in the Super League Greece, the top division of the Greek football league system, and hosts home games at the Theodoros Vardinogiannis Stadium in Heraklion, Crete.

Levadiakos Football Club is a Greek professional football club that plays in the Super League Greece. Based in Livadeia, Greece, the club was promoted to the Alpha Ethniki, forerunner of the Super League, after ten seasons in minor divisions in the 2005–06 season, as runner-up of the Football League in 2004–05. It was then relegated to the Beta Ethniki again in 2006–07 and returned to the top tier in 2007–08. The club finished one level above relegation that year but was relegated back to the second division by finishing 14th in 2009–10. The club most recently won promotion back into the Super League Greece after winning the Super League Greece 2 in 2023–24.

Panetolikos Football Club, or with its full name officially romanized as Panaitolikós Gymnastikós Filekpaideftikós Sýllogos, is a Greek professional football club. It is based in Agrinio, Greece. Panetolikos was founded in 1926 and is considered one of the historical clubs in Greece, currently participating in the Greek First Division. Some of the most well known players that started their career in the club are Stratos Apostolakis, former Greek recordman in international caps (96), and Petros Michos.

North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the north. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical region of Macedonia. Skopje, the capital and largest city, is home to a quarter of the country's population of 1.83 million. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians, a South Slavic people. Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks, Roma, Serbs, Bosniaks, Aromanians and a few other minorities.




















