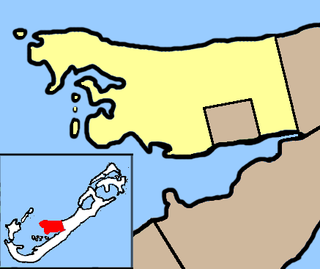
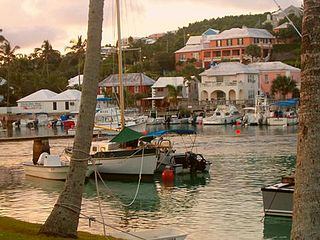Warwick Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named after Robert Rich, 2nd Earl of Warwick (1587-1658).
Pembroke Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named after English aristocrat William Herbert, 3rd Earl of Pembroke (1580–1630).
St. George's Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named after the founder of the Bermuda colony, Admiral Sir George Somers.

Ireland Island is the north-westernmost island in the chain which comprises Bermuda. It forms a long finger of land pointing northeastwards from the main island, the last link in a chain which also includes Boaz Island and Somerset Island. It lies within Sandys Parish, and forms the northwestern coast of the Great Sound. It is regarded as one of the six principal islands of Bermuda, and part of the West End of the archipelago.
Spanish Point is a prominent headland in Bermuda, located in Pembroke Parish five kilometres to the northwest of the capital Hamilton. It forms the eastern coast at the entrance to the Great Sound.
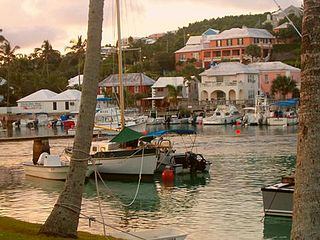
Flatts Village is a small settlement in Bermuda, lying on the southern bank of Flatt's Inlet in Hamilton Parish, almost exactly between the territory's two incorporated municipalities, Hamilton and St. George's.

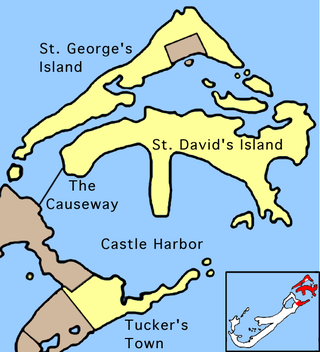
The Causeway is a narrow strip of reclaimed land and bridges in the north of Bermuda linking Hamilton Parish on the mainland in the southwest and Bermuda International Airport on St. David's Island in St. George's Parish in the northeast, which are otherwise divided by Castle Harbour.

Castle Harbour is a large natural harbour in Bermuda. It is located between the northeastern end of the main island and St. David's Island. Originally called Southampton Port, it was renamed as a result of its heavy fortification in the early decades of the Seventeenth century.

Coney Island is part of the chain which makes up Bermuda. It is located in St. George's Parish, in the northeast of the territory.
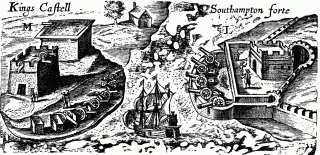
Castle Island is part of the chain which makes up Bermuda. It is located in St. George's Parish, in the northeast of the territory.

Cooper's Island is part of the chain which makes up Bermuda. It is located in St. George's Parish, in the northeast of the territory.

St. George's Harbour is a natural harbour in the north of Bermuda. It serves as the port for the town of St. George's, located on St. George's Island, to its north. To its south is St. David's Island. The harbour and both islands lie within St. George's Parish. It was for two centuries the primary harbour of the British Overseas Territory.

Ferry Reach is a three mile long channel in the north-east of Bermuda, which lies between St. George's Island in the north and St. David's Island in the south south-west of the town of St. George's.

St. David's Island is one of the main islands of the British Overseas Territory of Bermuda. It is located in the far north of the territory, one of the two similarly sized islands that make up the majority of St. George's Parish.

The New England Seamounts is a chain of over twenty underwater extinct volcanic mountains known as seamounts. This chain is located off the coast of Massachusetts in the Atlantic Ocean and extends over 1,000 km from the edge of Georges Bank. Many of the peaks of these mountains rise over 4,000 m from the seabed. The New England Seamounts chain is the longest such chain in the North Atlantic and is home to a diverse range of deep sea fauna. Scientists have visited the chain on various occasions to survey the geologic makeup and biota of the region. The chain is part of the Great Meteor hotspot track and was formed by the movement of the North American Plate over the New England hotspot. The oldest volcanoes that were formed by the same hotspot are northwest of Hudson Bay, Canada. Part of the seamount chain is protected by Northeast Canyons and Seamounts Marine National Monument.

Several of the islands strung across the South entrance of Castle Harbour, Bermuda were fortified in the early days of the territory, hence the harbour's name. When official settlement of the archipelago by England began in 1612 the first permanent town, St. George's was placed on the North side of St. George's Harbour. St. George's Harbour could be accessed directly by channels from the East. Those channels, however, were shallow, suitable, originally, only for small ships. As a consequence, and despite any major settlement on its shores, Castle Harbour was an important anchorage in the early years of the colony, with its main entrance, Castle Roads being an important route in from the open Atlantic for shipping. It was also a weakpoint, as it was remote from the defences of St. George's Harbour, and difficult to reach. It was quickly fortified and garrisoned by a standing militia.
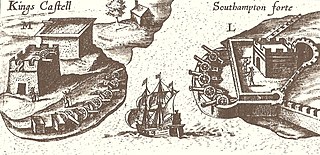
Castle Roads is the primary channel by which vessels enter Castle Harbour, Bermuda, from the Atlantic Ocean. Although little used, today, except by pleasure boats, Castle Harbour was once an important anchorage, and an access route used by ships to reach the still important St. George's Harbour. The infilling of waterways between St. David's Island and Long Bird Island in the 1940s, as well as the Causeway joining the contiguous landmass so created means only small boats can pass between the two Harbours, today. It was once common to use the term roads in reference to a waterway. Other examples include Hampton Roads, in Virginia, and Lahaina Roads, in Hawaii.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Bermuda:

The Cathedral of the Most Holy Trinity is an Anglican cathedral located on Church Street in the City of Hamilton, in Pembroke Parish, in the British Overseas Territory of Bermuda.

The Cathedral of Saint Theresa of Lisieux, or the Cathedral of Saint Theresa of the Little Flower, normally referred to as St. Theresa's Cathedral, is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Hamilton, in the British Overseas Territory of Bermuda. It is one of two cathedrals in Hamilton, the other being that of the state church, the Anglican church of Bermuda, the Cathedral of the Most Holy Trinity. St. Theresa's is the seat of the Catholic Bishop of Bermuda.