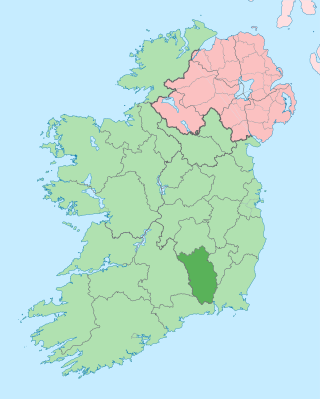
County Kilkenny is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and is part of the Southern Region. It is named after the city of Kilkenny. Kilkenny County Council is the local authority for the county. At the 2022 census the population of the county was 103,685. The county was based on the historic Gaelic kingdom of Ossory (Osraighe), which was coterminous with the Diocese of Ossory.

Kilkenny is a city in County Kilkenny, Ireland. It is located in the South-East Region and in the province of Leinster. It is built on both banks of the River Nore. The 2022 census gave the population of Kilkenny as 27,184, the thirteenth-largest urban center in Ireland.

Gloucester Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of St Peter and the Holy and Indivisible Trinity and formerly St Peter's Abbey, in Gloucester, England, stands in the north of the city near the River Severn. It originated with the establishment of a minster, Gloucester Abbey, dedicated to Saint Peter and founded by Osric, King of the Hwicce, in around 679.

Anglo-Saxon architecture was a period in the history of architecture in England from the mid-5th century until the Norman Conquest of 1066. Anglo-Saxon secular buildings in Britain were generally simple, constructed mainly using timber with thatch for roofing. No universally accepted example survives above ground. Generally preferring not to settle within the old Roman cities, the Anglo-Saxons built small towns near their centres of agriculture, at fords in rivers or sited to serve as ports. In each town, a main hall was in the centre, provided with a central hearth.

Chester Cathedral is a Church of England cathedral and the mother church of the Diocese of Chester. It is located in the city of Chester, Cheshire, England. The cathedral, formerly the abbey church of a Benedictine monastery dedicated to Saint Werburgh, is dedicated to Christ and the Blessed Virgin Mary. Since 1541, it has been the seat of the Bishop of Chester.

William Wilkinson Wardell (1823–1899) was a civil engineer and architect, notable not only for his work in Australia, the country to which he emigrated in 1858, but for a successful career as a surveyor and ecclesiastical architect in England and Scotland before his departure.

St. John's Cathedral is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Limerick, Ireland. Designed by the architect Philip Charles Hardwick, ground was broken in 1857 and the first Mass celebrated on 7 March 1859. It replaced a chapel founded in 1753.

St John's Cathedral is the cathedral of the Anglican Diocese of Brisbane and the metropolitan cathedral of the ecclesiastical province of Queensland, Australia. It is dedicated to St John the Evangelist. The cathedral is situated in Ann Street in the Brisbane central business district, and is the successor to an earlier pro-cathedral, which occupied part of the contemporary Queens Gardens on William Street, from 1854 to 1904. The cathedral is the second-oldest Anglican church in Brisbane, predated only by the extant All Saints church on Wickham Terrace (1862). The cathedral is listed on the Queensland Heritage Register.

Holy Trinity Cathedral is an Anglican cathedral situated in Parnell, a residential suburb of Auckland, New Zealand. It is the 'mother church' of the Anglican Diocese of Auckland and the seat of the Bishop of Auckland. The current main church building was consecrated in 1973.

Cathedral of Christ the King is a Roman Catholic cathedral located in Mullingar, County Westmeath, Ireland. It is situated near the centre of Mullingar next to the Royal Canal. The cathedral is both the cathedral church of the Diocese of Meath and the principal centre of worship in the catholic parish of Mullingar, including parts of counties Meath and Westmeath.

Templemore, Clonmore and Killea is an ecclesiastical parish in the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Cashel and Emly. The parish includes the town of Templemore and the nearby villages of Clonmore and Killea in County Tipperary.

St Canice's Cathedral, also known as Kilkenny Cathedral, is a cathedral of the Church of Ireland in Kilkenny city, Ireland. It is in the ecclesiastical province of Dublin. Previously the cathedral of the Diocese of Ossory, it is now one of six cathedrals in the United Dioceses of Cashel and Ossory.

The history of Kilkenny began with an early sixth-century ecclesiastical foundation, this relates to a church built in honour of St. Canice, now St. Canice's Cathedral and was a major monastic centre from at least the eighth century. The Annals of the Four Masters recorded the first reference Cill Chainnigh in 1085. Prehistoric activity has been recorded suggesting intermittent settlement activity in the area in the Mesolithic and Bronze Age. Information on the history of Kilkenny can be found from newspapers, photographs, letters, drawings, manuscripts and archaeology. Kilkenny is documented in manuscripts from the 13th century onwards and one of the most important of these is Liber Primus Kilkenniensis.

Teruel Cathedral or Catedral de Santa María de Mediavilla de Teruel is a Roman Catholic church in Teruel, Aragon, Spain. Dedicated to St. Mary, it is a notable example of Mudéjar architecture. Together with other churches in the town and in the province of Zaragoza, it has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1986.

The Cathedral of the Assumption is the mother church of the Metropolitan Province of Cashel and the cathedral church of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Cashel and Emly in Thurles, County Tipperary in Ireland. It is the cathedra of the Archbishop of Cashel and Emly and stands on the site of earlier chapels, which were the only Roman Catholic churches in Thurles. Following the English Reformation, many archdiocesan assets, including the cathedral at the Rock of Cashel were appropriated by the established church. James Butler II (1774–91), on being appointed by the Holy See, moved his residence and cathedra from Cashel, favouring Thurles instead, where his successors continue to reign today.

St Fethlimidh's Cathedral, Kilmore is one of two cathedral churches in the Diocese of Kilmore, Elphin and Ardagh in the Church of Ireland. It is situated in the parish of Kilmore, southwest of the county town of Cavan. The name Kilmore - Cill Mhor meaning 'the great church' - reflects an earlier prominence that the Annals of the Four Masters have traced to an early medieval foundation. Of that church there are no physical remains

St. Mary’s Collegiate Church Gowran, also known as the Church of the Blessed Virgin of the Assumption, is a church in the centre of the town of Gowran, County Kilkenny, Ireland. The site is a National Monument in the care of the Gowran Development Association (GDA) and the Office of Public Works (OPW). The church and its family connections have been of huge importance to Gowran and further afield over the centuries. The church is a collegiate church, which means that the priests or chaplains attached to it lived in community together. The present church was not a monastery or an abbey; however experts believe the church was built on the site of an earlier monastery. The presence of an Ogham stone on the site, which is on display in the chancel, suggests there was a place of worship here dating back 2000 years to Celtic times or beyond.

Green's Bridge, or Greensbridge, is an elegant, Palladian-style, limestone arch bridge that crosses the river Nore in Kilkenny, Ireland. The bridge is a series of five elliptical arches of high-quality carved limestone masonry with a two-arch culvert to the east. Its graceful profile, architectural design value, and civil engineering heritage endow it with national significance. Historian Maurice Craig described it as one of the five-finest bridges in Ireland. It was built by William Colles and designed by George Smith, and was completed in 1766. The bridge was 250 years old in 2016.

William Robertson, an Irish architect, was born in Kilkenny, Ireland, some days before 4 December 1770. He attended the Dublin Society where he was awarded with a silver medal for his drawing skills in 1795.

Perpendicular Gothic architecture was the third and final style of English Gothic architecture developed in the Kingdom of England during the Late Middle Ages, typified by large windows, four-centred arches, straight vertical and horizontal lines in the tracery, and regular arch-topped rectangular panelling. Perpendicular was the prevailing style of Late Gothic architecture in England from the 14th century to the 17th century. Perpendicular was unique to the country: no equivalent arose in Continental Europe or elsewhere in the British-Irish Isles. Of all the Gothic architectural styles, Perpendicular was the first to experience a second wave of popularity from the 18th century on in Gothic Revival architecture.





























