
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
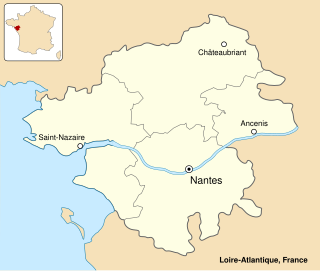
The St Nazaire Raid or Operation Chariot was a British amphibious attack on the heavily defended Normandie dry dock at St Nazaire in German-occupied France during the Second World War. The operation was undertaken by the Royal Navy (RN) and British Commandos under the auspices of Combined Operations Headquarters on 28 March 1942. St Nazaire was targeted because the loss of its dry dock would force any large German warship in need of repairs, such as Tirpitz, sister ship of Bismarck, to return to home waters by running the gauntlet of the Home Fleet of the Royal Navy and other British forces, via the English Channel or the North Sea.

A prisoner-of-war camp is a site for the containment of enemy fighters captured by a belligerent power in time of war.
Marlag und Milag Nord was a Second World War German prisoner-of-war camp complex for men of the British and Canadian Merchant Navy and Royal Navy. It was located around the village of Westertimke, about 30 km (19 mi) north-east of Bremen, though in some sources the camp's location is given as Tarmstedt, a larger village about 4 km (2.5 mi) to the west. There were also American merchant seamen detained here as well as some U.S. Navy personnel.

Captain Stephen Halden Beattie VC was a Welsh recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces.

Sergeant Thomas Frank Durrant VC was a soldier in the British Army during the Second World War and a posthumous English recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces. His award of the Victoria Cross was unique in that it is the only award given to a soldier in a naval action. It was also unusual, though not unique, in having been suggested by a German officer.

HMS Campbeltown was a Town-class destroyer of the Royal Navy during the Second World War. She was originally US destroyer USS Buchanan, and was one of 50 obsolescent U.S. Navy destroyers transferred to the Royal Navy in 1940 as part of the Destroyers for Bases Agreement. Campbeltown became one of the most famous of these ships when she was used in the St Nazaire Raid in 1942.
Stalag III-C was a German Army World War II prisoner-of-war camp for Allied soldiers. It was located on a plain near the village of Alt Drewitz bei Küstrin then located in the Neumark of the province of Brandenburg, about 50 mi (80 km) east of Berlin.

Task Force Baum, also known as the Hammelberg raid was a secret and controversial World War II task force set up by U.S. Army General George S. Patton and commanded by Capt. Abraham Baum in late March 1945. Baum was given the task of penetrating 50 miles (80 km) behind German lines and liberating the POWs in camp Oflag XIII-B, near Hammelburg. Controversy surrounds the true reasons behind the mission, which most likely was to liberate Patton's son-in-law, John K. Waters, taken captive in Tunisia in 1943. The result of the mission was a complete failure; of the roughly 300 men of the task force, 32 were killed in action during the raid and only 35 made it back to Allied-controlled territory, with the remainder being taken prisoner. All of the 57 tanks, jeeps, and other vehicles were lost.
Oflag VII-B was a World War II German prisoner-of-war camp for officers (Offizierlager), located in Eichstätt, Bavaria, about 100 km (62 mi) north of Munich.
Stalag XIII-D Nürnberg Langwasser was a German Army World War II prisoner-of-war camp built on what had been the Nazi party rally grounds in Nuremberg, northern Bavaria.
Stalag XIII-C was a German Army World War II prisoner-of-war camp (Stammlager) built on what had been the training camp at Hammelburg, Lower Franconia, Bavaria, Germany.
The Raid at Ožbalt was the most successful known prison break of the Second World War. It was an operation on 31 August 1944 in which 105 Allied prisoners of war (POWs) were rescued by Slovene Partisans, Special Operations Executive (SOE), and MI9. The majority were liberated from a work site at the village of Ožbalt about 25 kilometres (16 mi) west of Maribor on the railway line to Dravograd in the German Reichsgau Steiermark (Styria), now part of modern-day northern Slovenia. Six of the liberated POWs were separated from the group during an engagement with the Germans a few days after their liberation. One later reunited with the escape group. Following a 14-day trek across 250 kilometres (160 mi) they were flown out of a Partisan airfield at Semič to Bari, Italy. The successful escapees consisted of twenty Frenchmen, nine New Zealanders, twelve Australians, and fifty-nine British POWs.
Robert Charles Michael Vaughan Wynn, 7th Baron Newborough, DSC was a British peer and Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve officer who played a decisive role during the St. Nazaire Raid in 1942 where he commanded a Motor Torpedo Boat. Captured after his boat had to be abandoned, he was sent to Colditz after an escape attempt. He was repatriated after feigning illness.

Approximately three million German prisoners of war were captured by the Soviet Union during World War II, most of them during the great advances of the Red Army in the last year of the war. The POWs were employed as forced labor in the Soviet wartime economy and post-war reconstruction. By 1950 almost all surviving POWs had been released, with the last prisoner returning from the USSR in 1956. According to Soviet records 381,067 German Wehrmacht POWs died in NKVD camps. A commission set up by the West German government found that 3,060,000 German military personnel were taken prisoner by the USSR and that 1,094,250 died in captivity. According to German historian Rüdiger Overmans ca. 3,000,000 POWs were taken by the USSR; he put the "maximum" number of German POW deaths in Soviet hands at 1.0 million. Based on his research, Overmans believes that the deaths of 363,000 POWs in Soviet captivity can be confirmed by the files of Deutsche Dienststelle (WASt), and additionally maintains that "It seems entirely plausible, while not provable, that 700,000 German military personnel listed as missing actually died in Soviet custody."

Oflag IX-A was a World War II German prisoner-of-war camp located in Spangenberg Castle in the small town of Spangenberg in northeastern Hesse, Germany.
Heinz Schnabel and Harry Wappler were two Second World War German prisoners of war who escaped from a British prison camp and attempted to fly to the continent in a stolen aircraft on 24 November 1941.
Donald Roy DSO was a British Commando officer during the Second World War. As a captain in No.2 Commando, Roy led an assault troop in the St. Nazaire Raid in March 1942.

Stalag Luft II was a Luftwaffe-run prisoner-of-war (POW) camp during World War II, in Łódź, in the occupied territory of Poland.









