Sierra National Forest is a U.S. national forest located on the western slope of central Sierra Nevada in Central California and bounded on the northwest by Yosemite National Park and the south by Kings Canyon National Park. The forest is known for its mountain scenery and beautiful lakes. Forest headquarters are located in Clovis, California. There are local ranger district offices in North Fork and Prather.
The 3,848 acres (6.013 sq mi) Landels-Hill Big Creek Reserve located in the southern region of Big Sur, California is owned by the University of California Natural Reserve System. It is located off State Route 1 in 50 miles (80 km) south of Monterey and adjacent to the Big Creek State Marine Reserve and Big Creek State Marine Conservation Area. It is open to the general public one day a year.
An experimental forest, or experimental range, as defined by the United States Forest Service, is "an area administered ... 'to provide for the research necessary for the management of the land.'"

The San Joaquin Experimental Range is an ecosystem research experimental area in the foothills of the Sierra Nevada. The range is located in O'Neals, California, outside of the Sierra National Forest about 32 kilometres (20 mi) north of Fresno, California. The range includes a portion of California grassland and California woodlands with blue oak, interior live oak, and bull pine.

The Frontenac Arch Biosphere Reserve is a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve located in southeastern Ontario, Canada. The biosphere reserve was designated in 2002, and is one of 16 biosphere reserves in Canada. The Frontenac Arch Biosphere operates primarily within a 2,700 km2. region from Brockville to Kingston, extending north to Verona and Perth.
Mantaritza Biosphere Reserve is situated to the north of Golyama Syutka Peak in the Rhodope Mountains in Bulgaria, and covers an area of 1319,9 hectares. The reserve was established in 1968 to protect the old coniferous forests and the biotopes of the Western capercaillie. The area was declared as biosphere reserve in 1977. It represents century-old forests of pure and mixed stands of Norway spruce (Picea abies), European birch (Fagus sylvatica) and European silver fir (Abies alba). The reserve is situated in the Bulgarian Floristic sub-region of West Rhodope within the Central European mountain biotic province. The varied fauna includes brown bear (Ursus arctos), red deer (Cervus elaphus), roe deer (Capreolus capreolus), wild boar, pine marten (Martes martes), European badger (Meles meles), hazel grouse (Bonasa bonasia), black woodpecker (Dryocopus martius) and crested tit (Parus cristatus).
Fontainebleau et du Gâtinais is a biosphere reserve located in the Ile de France region, some 70 km south-east of Paris, first designated in 1998 and extended in 2010. The biosphere reserve is composed of temperate deciduous forest, heathlands, open rock areas and several wetlands. In total, the reserve protects 150,544 hectares. The center of the biosphere, is located at 48°22′N2°33′E.

Loch Druidibeag is a freshwater loch situated on the island of South Uist, in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. The loch is near the northern end of the island, to the north-east of Howmore and to the east of the A865 road and south of the B890.
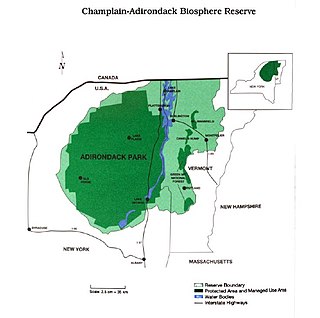
The Champlain-Adirondack Biosphere Network is a UNESCO-designated biosphere reserve. The Champlain-Adirondack Biosphere Network is part of a global network of 727 biosphere reserves in 131 countries and it is one of 28 internationally recognized biosphere regions in the United States.

The California Coast Ranges Biosphere Reserve was a UNESCO Biosphere reserve located along the California Coast Ranges of northern California and the San Francisco Bay area until June 2017. This biosphere reserve includes a highly diverse complex of evergreen sclerophyllous woodland, coastal, estuary and marine ecosystems.

The San Dimas Biosphere Reserve and Experimental Forest is an experimental forest located in the front range of the San Gabriel Mountains of southern California. San Dimas constitutes a protected field laboratory jointly managed by the Angeles National Forest and the Pacific Southwest Research Station of the United States Forest Service under the designation San Dimas Experimental Forest. It was designated as a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve in 1976 and withdrawn from the programme in July 2018.
Niwot Ridge is an alpine ecology research station located 65 km north-west of Denver in north-central Colorado. It is on the Front Range of the southern Rocky Mountains and lies within the Roosevelt National Forest. Niwot Ridge is 2,900 metres (9,500 ft) high.

The Central Plains Biosphere Reserve was a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve located in the western central Great Plains in north-central Colorado in the shortgrass prairie. The 6,210 hectares (24.0 sq mi) reserve encompasses the Central Plains Experimental Range (CPER) administered by the United States Department of Agriculture's Agricultural Research Service.

The Fraser Experimental Forest is an outdoor research laboratory to study timber, water, wildlife management, and their integration in the high elevation subalpine coniferous forests. The experimental forest was established in 1937, and encompasses 9,328 hectares (36.02 sq mi). It is situated on the west side of the Continental Divide in north-central Colorado and includes the entire watershed of main Saint Louis Creek, a tributary of the Fraser River.

Waterton Biosphere Reserve is a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve encompassing Waterton Lakes National Park in the extreme south-west of the Province of Alberta, Canada. The reserve includes a section of the east slopes of the Rocky Mountains extending from the Continental Divide to the edge of the Canadian Great Plains to the east. The Glacier Biosphere Reserve and National Park in Montana, USA is located to the south of the area. The reserve is administered by Waterton Lakes National Park and the Waterton Biosphere Association.

The Jornada Biosphere Reserve is a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve in southern New Mexico. It is one of three biosphere reserves representing the Chihuahuan Desert. The area extends from the crest of the San Andres Mountains, which are dominated by shrub woodlands, to the Jornada Plains characterized by semi-desert grasslands.

The Ciénaga de Zapata Biosphere Reserve is a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve situated on the southern coast of Cuba at Matanzas province. The 628,171 hectares (2,425.38 sq mi) reserve encompasses the Zapata Swamp and is one of the largest and most important wetlands in the Caribbean region with a marine southern borderline. Ciénaga de Zapata was designated a Ramsar site in 2001. This area is a cluster biosphere reserve with several core areas, highly valuable for conservation located in the Ciénaga de Zapata National Park.
La Encrucijada Biosphere Reserve is a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve situated in the Pacific Coastal Lowlands physiographic region of Mexico. It covers 144,848 hectares (559.26 sq mi) stretching over six municipalities in the Costa de Chiapas. It is composed of two large coastal lagoon systems that correspond to two core areas, and a wide variety of natural ecosystems including mangroves, zapotonales, tule swamps and marshes, as well as patches of tropical seasonal forest, coastal dunes and palm trees.

The Volcán Tacaná Biosphere Reserve is a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve at the Tacaná Volcano in Chiapas, Mexico, on the border with Guatemala. The volcano is part of the Central America Volcanic Arc. The 6,378 hectares (24.63 sq mi) reserve contains fragile ecosystems very rich in wild flora and fauna species of cultural, scientific, economic and biological relevance. Its rich biodiversity and high endemism are found particularly in the high mountain ecosystem and landscapes and in the volcanic edifice which presents geophysical features of great scientific and aesthetic value. Average annual rainfall can amount to 2,000–5,000 millimetres (79–197 in), as in the case of Soconusco.

The Luquillo Experimental Forest is a protected area of tropical rainforest in northeastern Puerto Rico. The experimental forest is located in the Sierra de Luquillo some 50 km (30 mi) east of San Juan, the capital of the island. It is a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve and is used for research into silviculture, forest regeneration, and other purposes.