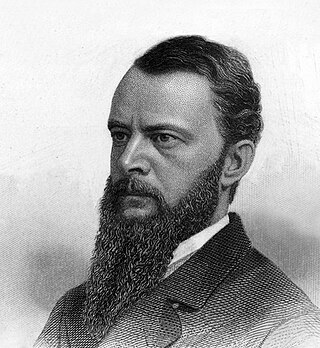The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States (C.S.), the Confederacy, or the South, was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confederacy was composed of eleven U.S. states that declared secession and warred against the United States during the American Civil War. The states were South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina.

Jefferson F. Davis was an American politician who served as the first and only president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as a member of the Democratic Party before the American Civil War. He was the United States Secretary of War from 1853 to 1857.

Judah Philip Benjamin was an American lawyer and politician who served as a United States senator from Louisiana, a Cabinet officer of the Confederate States and, after his escape to Britain at the end of the American Civil War, an English barrister. Benjamin was the first Jew to hold a Cabinet position in North America and the first to be elected to the United States Senate who had not renounced his faith.

Braxton Bragg was an American army officer during the Second Seminole War and Mexican–American War and Confederate general in the Confederate Army during the American Civil War, serving in the Western Theater. His most important role was as commander of the Army of Mississippi, later renamed the Army of Tennessee, from June 1862 until December 1863.

The Beauvoir estate, built in Biloxi, Mississippi, along the Gulf of Mexico, was the post-war home (1876–1889) of the former President of the Confederate States of America Jefferson Davis. The National Park Service designated the house and plantation as a National Historic Landmark.

John Henninger Reagan was an American politician from Texas. A Democrat, Reagan resigned from the U.S. House of Representatives when Texas declared secession from the United States and joined the Confederate States of America. He served in the cabinet of Jefferson Davis as Postmaster General.

The Lost Cause of the Confederacy is an American pseudohistorical and historical negationist myth that claims the cause of the Confederate States during the American Civil War was just, heroic, and not centered on slavery. First enunciated in 1866, it has continued to influence racism, gender roles, and religious attitudes in the Southern United States into the 21st century. Historians have dismantled many parts of the Lost Cause mythos.
Burton Jesse Hendrick, born in New Haven, Connecticut, was an American author. While attending Yale University, Hendrick was editor of both The Yale Courant and The Yale Literary Magazine. He received his BA in 1895 and his master's in 1897 from Yale. After completing his degree work, Hendrick became editor of the New Haven Morning News. In 1905, after writing for The New York Evening Post and The New York Sun, Hendrick left newspapers and became a "muckraker" writing for McClure's Magazine. His "The Story of Life-Insurance" exposé appeared in McClure's in 1906. Following his career at McClure's, Hendrick went to work in 1913 at Walter Hines Page's World's Work magazine as an associate editor. In 1919, Hendrick began writing biographies, when he was the ghostwriter of Ambassador Morgenthau's Story for Henry Morgenthau, Sr.

Virginia City is a 1940 American Western film directed by Michael Curtiz and starring Errol Flynn, Miriam Hopkins, Randolph Scott, and a mustachioed Humphrey Bogart in the role of the real-life outlaw John Murrell. Based on a screenplay by Robert Buckner, the film is about a Union officer who escapes from a Confederate prison and is sent to Virginia City from where his former prison commander is planning to send five million dollars in gold to Virginia to save the Confederacy. The film premiered in its namesake, Virginia City, Nevada. The film was shot in black and white (sepiatone).

The Rise and Fall of the Confederate Government (1881) is a book written by Jefferson Davis, who served as President of the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War. Davis wrote the book as a straightforward history of the Confederate States of America and as an apologia for the causes that he believed led to and justified the American Civil War.
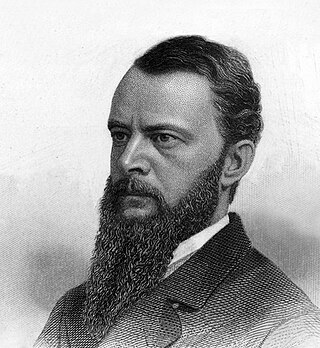
Edward Alfred Pollard was an American author, journalist, and Confederate sympathizer during the American Civil War who wrote several books on the causes and events of the war, notably The Lost Cause: A New Southern History of the War of the Confederates (1866) and The Lost Cause Regained (1868), wherein Pollard originated the long-standing pseudo-historical ideology of the Lost Cause of the Confederacy.

George Davis was a Confederate politician and railroad counsel who served as attorney general of the Confederate States for 480 days in 1864 and 1865.

Charles Gustavus Ulrich Dahlgren was a brigadier general of Mississippi State Troops with allegiance to the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War. He commanded the 3rd Brigade of the Mississippi Militia, before a dispute with the President of the Confederate States of America, Jefferson Davis, over transfer of the state troops to the Confederate States Army cost him his career.
Confederate gold refers to hidden caches of gold lost after the American Civil War. Millions of dollars' worth of gold was lost or unaccounted for after the war, and its possible location has been the source of speculation of many historians and treasure hunters. Allegedly, some of the Confederate treasury was hidden in order to wait for the rising again of the South and at other times simply so that the Union would not gain possession of it.

William Charles "Jack" Davis is an American historian who was a professor of history at Virginia Tech and the former director of programs at that school's Virginia Center for Civil War Studies. Specializing in the American Civil War, Davis has written more than 40 books on that subject and other aspects of early southern U.S. history, such as the Texas Revolution. He is the only three-time winner of the Jefferson Davis Prize for Confederate history and was awarded the Jules and Frances Landry Award for Southern History. His book Lone Star Rising has been called "the best one-volume history of the Texas revolution yet written".

Jefferson Davis Memorial Historic Site is a 12.668-acre (5.127 ha) state historic site located in Irwin County, Georgia that marks the spot where Confederate States President Jefferson Davis was captured by United States Cavalry on Wednesday, May 10, 1865. The historic site features a granite monument with a bronze bust of Davis that is located at the place of capture. The memorial museum, built in 1939 by the Works Progress Administration, features Civil War era weapons, uniforms, artifacts and an exhibit about the president's 1865 flight from Richmond, Virginia to Irwin County, Georgia.

Varina Anne "Winnie" Davis was an American author who is best known as the youngest daughter of President Jefferson Davis of the Confederate States of America and Varina (Howell) Davis. Born near the end of the war, by the late 1880s she became known as the "Daughter of the Confederacy". Images of her were widely circulated when she was young, helping morale. Later in the 1880s, she appeared with her father on behalf of Confederate veterans' groups. After his death, she and her mother moved in 1891 to New York City, where they both worked as writers. She published a biography and two novels, in addition to numerous articles. Davis died from an infectious disease at age 34.

There are several works of art in the United States Capitol honoring former leaders of the Confederate States of America and generals in the Confederate States Army, including six statues in the National Statuary Hall Collection, busts and portraits.
Was Jefferson Davis Right? is a 1998 book by James Ronald Kennedy and Walter Donald Kennedy, published by Pelican Publishing Company. The authors wrote the work to defend the secession of the Confederate States of America, which Jefferson Davis pursued as the secessonist president.
Jefferson Davis and His Cabinet is a 1944 non-fiction book by Rembert Wallace Patrick, published by Louisiana State University Press in 1944. It describes the Cabinet of the Confederate States of America.