Related Research Articles

Alexander I of Epirus, also known as Alexander Molossus, was a king of Epirus (343/2–331 BC) of the Aeacid dynasty. As the son of Neoptolemus I and brother of Olympias, Alexander I was an uncle, and a brother-in-law, of Alexander the Great. He was also an uncle to Pyrrhus of Epirus.
During the 290s BC, Hellenistic civilization begins its emergence throughout the successor states of the former Argead Macedonian Empire of Alexander the Great, resulting in the diffusion of Greek culture throughout the Levant and advances in science, mathematics, philosophy, etc. Meanwhile, the Roman Republic is embroiled in war against the Samnites, the Mauryan Empire continues to thrive in Ancient India, and the Kingdom of Qin in Ancient China, the one which in the future will conquer its adversaries and unite China, begins to emerge as a significant power during the Warring States period.

The year 305 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Megellus and Augurinus. The denomination 305 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 296 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Violens and Caecus. The denomination 296 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 295 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. It was known in the Roman Republic as the Year of the Consulship of Rullianus and Mus. The denomination 295 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
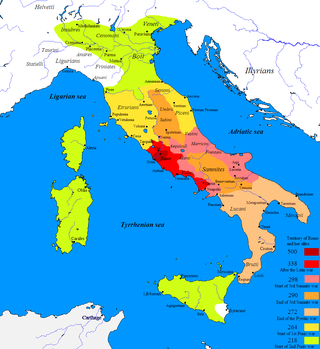
The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanian tribe.
The gens Gavia, or occasionally Gabia, was a Roman family of plebeian descent. It first appears in history during the first century BC, but none of its members obtained any of the curule magistracies until imperial times. The Gavi Arch at Verona was built in honor of one of the Gavii.

Samnium is a Latin exonym for a region of Southern Italy anciently inhabited by the Samnites. Their own endonyms were Safinim for the country and Safineis for the people. The language of these endonyms and of the population was the Oscan language. However, not all the Samnites spoke Oscan, and not all the Oscan-speakers lived in Samnium.

Lucius Cornelius Scipio Barbatus was one of the two elected Roman consuls in 298 BC. He led the Roman army to victory against the Etruscans near Volterra. A member of the noble Roman family of Scipiones, he was the father of Lucius Cornelius Scipio and Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Asina and great-grandfather of Scipio Africanus.

The Samnites were an ancient Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy.
The Battle of Sentinum was the decisive battle of the Third Samnite War, fought in 295 BC near Sentinum, in which the Romans overcame a formidable coalition of Samnites, Etruscans, and Umbrians and Senone Gauls. The Romans won a decisive victory that broke up the tribal coalition and paved the way for the Romans' complete victory over the Samnites. The Romans involved in the battle of Sentinum were commanded by consuls Publius Decius Mus and Quintus Fabius Maximus Rullianus.

The Battle of Bovianum was fought in 305 BC between the Romans and the Samnites.
Gellius Egnatius was the leader of the Varriani, a leading clan of the Samnites during the Third Samnite War, which broke out in 298 BC. By the end of the second campaign the Samnites appeared completely defeated, however in the following year Gellius Egnatius marched into Etruria, and roused the Etruscans to a close co-operation against Rome. This had the effect of withdrawing Roman troops from Samnium for a period of time; but the forces of the confederates were defeated by the combined armies of consuls Lucius Volumnius Flamma Violens and Appius Claudius Caecus.
Lucius Volumnius Flamma Violens was a consul of the Roman Republic twice, in 307 BC and 296 BC, a novus homo, the first of his plebeian gens to attain the consulship. Volumnius served in both his consulships with the patrician Appius Claudius Caecus. He took an active role in leading Roman forces during the Third Samnite War.
The gens Carvilia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome, which first distinguished itself during the Samnite Wars. The first member of this gens to achieve the consulship was Spurius Carvilius Maximus, in 293 BC.
The gens Atinia was a minor plebeian family at ancient Rome, which came to prominence during the late Republic. No members of this gens ever attained the consulship, although several were praetors in the early second century BC, beginning with Gaius Atinius Labeo 195.

Gnaeus Gellius was a Roman historian. Very little is known about his life and work, which has only survived in scattered fragments. He continued the historical tradition set by Fabius Pictor of writing a year-by-year history of Rome from mythological times to his day. However, with about a hundred books, Gellius' Annales were massively more developed than the other Roman annalists, and was only surpassed by Livy's gigantic History of Rome.
Publius Cornelius Rufinus was a Roman politician and general of the third century BC.
The gens Gellia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome, where they settled after the Second Punic War or earlier. The first of the Gellii to obtain the consulship was Lucius Gellius Poplicola, in 72 BC, but the most famous member of this gens is probably the grammarian Aulus Gellius, who flourished during the second century AD.
References
- ↑ Livy, ix. 44. 13.