
An actuary is a business professional who deals with the measurement and management of risk and uncertainty. The name of the corresponding field is actuarial science. These risks can affect both sides of the balance sheet and require asset management, liability management, and valuation skills. Actuaries provide assessments of financial security systems, with a focus on their complexity, their mathematics, and their mechanisms.
Actuarial science is the discipline that applies mathematical and statistical methods to assess risk in insurance, finance and other industries and professions. More generally, actuaries apply rigorous mathematics to model matters of uncertainty.
A life settlement is the "legal" sale of an existing life insurance policy for more than its cash surrender value, but less than its net death benefit ). There are a number of reasons that a policy owner may choose to sell his or her life insurance policy. The policy owner may no longer need or want his or her policy, he or she may wish to purchase a different kind of life insurance policy, or premium payments may no longer be affordable.
Term life insurance or term assurance is life insurance that provides coverage at a fixed rate of payments for a limited period of time, the relevant term. After that period expires, coverage at the previous rate of premiums is no longer guaranteed and the client must either forgo coverage or potentially obtain further coverage with different payments or conditions. If the life insured dies during the term, the death benefit will be paid to the beneficiary. Term insurance is typically the least expensive way to purchase a substantial death benefit on a coverage amount per premium dollar basis over a specific period of time.

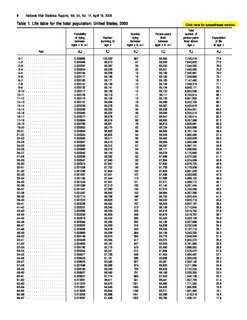
In actuarial science and demography, a life table is a table which shows, for each age, what the probability is that a person of that age will die before his or her next birthday. In other words, it represents the survivorship of people from a certain population. They can also be explained as a long-term mathematical way to measure a population's longevity. Tables have been created by demographers including Graunt, Reed and Merrell, Keyfitz, and Greville.
In the United States, a minimum municipal obligation (MMO) is the state-mandated smallest amount a municipality must contribute to any pension plan established for its employees.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to actuarial science:

The American Academy of Actuaries, also known as the Academy, is the body that represents and unites United States actuaries in all practice areas. Established in 1965, the Academy serves as the profession’s voice on public policy and professionalism issues.
Under European Union law, an annuity is a financial contract which provides an income stream in return for an initial payment with specific parameters. It is the opposite of a settlement funding. A Swiss annuity is not considered a European annuity for tax reasons.
A net premium valuation is an actuarial calculation, used to place a value on the liabilities of a life insurer.
An actuarial reserve is a liability equal to the actuarial present value of the future cash flows of a contingent event. In the insurance context an actuarial reserve is the present value of the future cash flows of an insurance policy and the total liability of the insurer is the sum of the actuarial reserves for every individual policy. Regulated insurers are required to keep offsetting assets to pay off this future liability.
The statutory accounting principles are a set of accounting rules for insurance companies set forth by the National Association of Insurance Commissioners. They are used to prepare the statutory financial statements of insurance companies. Statutory Accounting Principles are designed to assist state insurance departments in the regulation of the solvency of insurance companies. Although there are minor state-by-state variations, they are the basis for state regulation throughout the United States.
Loss reserving refers to the calculation of the required reserves for a tranche of general insurance business. It includes outstanding claims reserves.

Anders Lindstedt was a Swedish mathematician, astronomer, and actuarial scientist, known for the Lindstedt-Poincaré method.

Joshua Milne (1776–1851), was an English actuary.

The Institute and Faculty of Actuaries is the professional body which represents and regulates actuaries in the United Kingdom.
Sir George Francis Hardy was a British actuary, Egyptologist and amateur astronomer. He became a Fellow of the Royal Astronomical Society in 1877 and was President of the Institute of Actuaries from 1908 to 1910.







