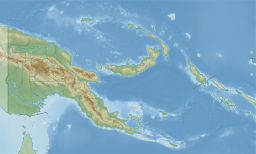
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).

Bougainville Island is the main island of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, which is part of Papua New Guinea. It was previously the main landmass in the German Empire-associated North Solomons. Its land area is 9,300 km2 (3,600 sq mi). The population of the whole province, including nearby islets such as the Carterets, is approximately 300,000. The highest point is Mount Balbi, on the main island, at 2,715 m (8,907 ft). The much-smaller Buka Island, c. 500 km2 (190 sq mi), lies to the north, across the 400–500 m (1,300–1,600 ft) wide Buka Strait. Even though the strait is narrow, there is no bridge across it, but there is a regular ferry service between the key settlements on either side. The main airport in the north is in the town of Buka.

The Torres Strait, also known as Zenadh Kes, is a strait between Australia and the Melanesian island of New Guinea. It is 151 km (94 mi) wide at its narrowest extent. To the south is Cape York Peninsula, the northernmost extremity of the Australian mainland. To the north is the Western Province of Papua New Guinea. It is named after the Spanish navigator Luís Vaz de Torres, who sailed through the strait in 1606.

The Torres Strait Islands are a group of at least 274 small islands in the Torres Strait, a waterway separating far northern continental Australia's Cape York Peninsula and the island of New Guinea. They span an area of 48,000 km2 (19,000 sq mi), but their total land area is 566 km2 (219 sq mi).

The Bismarck Sea lies in the southwestern Pacific Ocean within the nation of Papua New Guinea. It is located northeast of the island of New Guinea and south of the Bismarck Archipelago. It has coastlines in districts of the Islands Region, Momase Region, and Papua Region.

The indigenous peoples of New Guinea in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Melanesians. There is genetic evidence for two major historical lineages in New Guinea and neighboring islands:
- a first wave from the Malay Archipelago perhaps 50,000 years ago when New Guinea and Australia were a single landmass called Sahul ...
- and, much later, a wave of Austronesian people from the north who introduced Austronesian languages and pigs about 3,500 years ago. They also left a small but significant genetic trace in many coastal Papuan peoples.
The North New Guinea languages of Papua New Guinea and Indonesia form a possible linkage of Western Oceanic languages. They have been in heavy contact with Papuan languages.

The Evangelical Lutheran Church of Papua New Guinea is a Protestant church denomination located in Papua New Guinea that professes the Lutheran branch of the Christian faith. The Church is incorporated by a 1991 Act of the Parliament of Papua New Guinea and it has a baptized membership of approximately 900,000 members.

The Territory of New Guinea was an Australian-administered United Nations trust territory on the island of New Guinea from 1914 until 1975. In 1949, the Territory and the Territory of Papua were established in an administrative union by the name of the Territory of Papua and New Guinea. That administrative union was renamed as Papua New Guinea in 1971. Notwithstanding that it was part of an administrative union, the Territory of New Guinea at all times retained a distinct legal status and identity until the advent of the Independent State of Papua New Guinea.

The Eastern Trans-Fly languages are a small independent family of Papuan languages spoken in the Oriomo Plateau to the west of the Fly River in New Guinea.
The Catholic Church in Papua New Guinea is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope in Rome. Papua New Guinea has approximately two million Catholic adherents, approximately 27% of the country's total population.

Talbot Islands are a group of Torres Strait Islands in Queensland, Australia. They lie between the Australian mainland and the island of New Guinea and a few kilometres west of Saibai Island, Torres Strait, only 4 km from the Papua New Guinea mainland at the mouth of the Mai Kussa River.

Umboi is a volcanic island between the mainland of Papua New Guinea and the island of New Britain. It is separated from New Britain by the Dampier Strait and Huon Peninsula, and New Guinea by the Vitiaz Strait. It has an elevation of 1,335 metres.

Daru Island is an island in the Western Province of Papua New Guinea. It is one of the Torres Strait Islands. The eponymous town on the island is the capital of the province, and houses the vast majority of the island's population of 20,524 (2009). Daru Island is elliptical in shape, with dimensions of 5.0 by 3.7 kilometers, an area of 14.7 km², and an elevation of up to 27 m. The island is separated from the mainland in the north, specifically the mouth of Oriomo River, by the 3.5 km wide Daru Roads. The shortest distance to the larger Bristow Island in the south is 1.3 km.
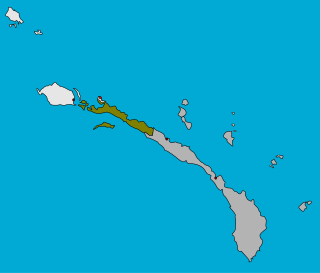
Tikana Rural LLG is a local government area in New Ireland Province, Papua New Guinea. The LLG administers the northern section of the island of New Ireland, as well as Djaul Island and some Tigak islands in the strait between New Ireland and New Hanover.

The Mombum languages, also known as the Komolom or Muli Strait languages, are a pair of Trans–New Guinea languages, Mombum (Komolom) and Koneraw, spoken on Komolom Island just off Yos Sudarso Island, and on the southern coast of Yos Sudarso Island, respectively, on the southern coast of New Guinea. Komolom Island is at the southern end of the Muli Strait.

New Guinea is the world's second-largest island with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi). Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the 150-kilometre wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua, South Papua, and West Papua. The largest cities on the island are Jayapura and Port Moresby.
West Bird's Head languages are a small family of poorly documented Papuan languages spoken on the Bird's Head Peninsula of New Guinea.
Papua New Guinean Australians are the citizens and residents of Australia who were born in Papua New Guinea (PNG) or have Papua New Guinean ancestry.
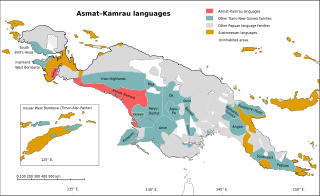
The Asmat–Muli Strait languages are a branch of the Trans–New Guinea languages spoken along the southern coast of Indonesian New Guinea, established by Timothy Usher and Edgar Suter.