
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord, the retina and optic nerve, and the olfactory nerve and epithelia. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral to caudal axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets.

A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers in the peripheral nervous system.

The enteric nervous system (ENS) or intrinsic nervous system is one of the three main divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), the other being the sympathetic (SNS) and parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS), and consists of a mesh-like system of neurons that governs the function of the gastrointestinal tract. It is capable of acting independently of the SNS and PSNS, although it may be influenced by them. The ENS is nicknamed the "second brain". It is derived from neural crest cells.
Myelitis is inflammation of the spinal cord which can disrupt the normal responses from the brain to the rest of the body, and from the rest of the body to the brain. Inflammation in the spinal cord can cause the myelin and axon to be damaged resulting in symptoms such as paralysis and sensory loss. Myelitis is classified to several categories depending on the area or the cause of the lesion; however, any inflammatory attack on the spinal cord is often referred to as transverse myelitis.
Nervous tissue, also called neural tissue, is the main tissue component of the nervous system. The nervous system regulates and controls body functions and activity. It consists of two parts: the central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) comprising the branching peripheral nerves. It is composed of neurons, also known as nerve cells, which receive and transmit impulses, and neuroglia, also known as glial cells or glia, which assist the propagation of the nerve impulse as well as provide nutrients to the neurons.
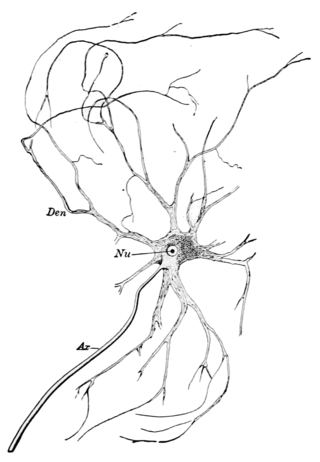
A motor nerve, or efferent nerve, is a nerve that contains exclusively efferent nerve fibers and transmits motor signals from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles of the body. This is different from the motor neuron, which includes a cell body and branching of dendrites, while the nerve is made up of a bundle of axons. Motor nerves act as efferent nerves which carry information out from the CNS to muscles, as opposed to afferent nerves, which transfer signals from sensory receptors in the periphery to the CNS. Efferent nerves can also connect to glands or other organs/issues instead of muscles. The vast majority of nerves contain both sensory and motor fibers and are therefore called mixed nerves.

Oligodendrocytes, also known as oligodendroglia, are a type of neuroglia whose main functions are to provide support and insulation to axons within the central nervous system (CNS) of jawed vertebrates. Their function is similar to that of Schwann cells, which perform the same task in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Oligodendrocytes accomplish this by forming the myelin sheath around axons. Unlike Schwann cells, a single oligodendrocyte can extend its processes to cover around 50 axons, with each axon being wrapped in approximately 1 μm of myelin sheath. Furthermore, an oligodendrocyte can provide myelin segments for multiple adjacent axons.
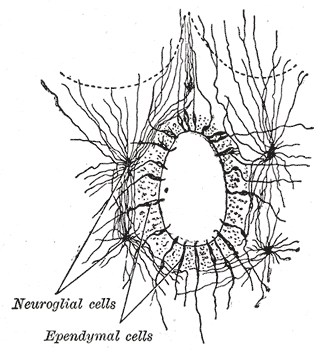
The ependyma is the thin neuroepithelial lining of the ventricular system of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. The ependyma is one of the four types of neuroglia in the central nervous system (CNS). It is involved in the production of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and is shown to serve as a reservoir for neuroregeneration.

Leonard M. Miller School of Medicine (UMMSM) is the University of Miami's graduate medical school in Miami, Florida. Founded in 1952, it is the oldest medical school in the state of Florida.

The neuroimmune system is a system of structures and processes involving the biochemical and electrophysiological interactions between the nervous system and immune system which protect neurons from pathogens. It serves to protect neurons against disease by maintaining selectively permeable barriers, mediating neuroinflammation and wound healing in damaged neurons, and mobilizing host defenses against pathogens.
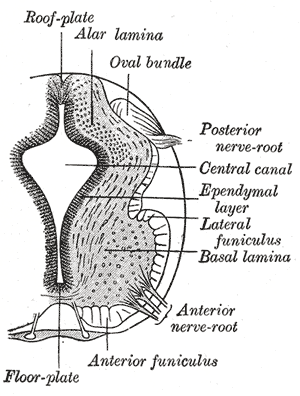
The floor plate is a structure integral to the developing nervous system of vertebrate organisms. Located on the ventral midline of the embryonic neural tube, the floor plate is a specialized glial structure that spans the anteroposterior axis from the midbrain to the tail regions. It has been shown that the floor plate is conserved among vertebrates, such as zebrafish and mice, with homologous structures in invertebrates such as the fruit fly Drosophila and the nematode C. elegans. Functionally, the structure serves as an organizer to ventralize tissues in the embryo as well as to guide neuronal positioning and differentiation along the dorsoventral axis of the neural tube.
Neural tissue engineering is a specific sub-field of tissue engineering. Neural tissue engineering is primarily a search for strategies to eliminate inflammation and fibrosis upon implantation of foreign substances. Often foreign substances in the form of grafts and scaffolds are implanted to promote nerve regeneration and to repair damage caused to nerves of both the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS) by an injury.

A glial scar formation (gliosis) is a reactive cellular process involving astrogliosis that occurs after injury to the central nervous system. As with scarring in other organs and tissues, the glial scar is the body's mechanism to protect and begin the healing process in the nervous system.

Central nervous system diseases or central nervous system disorders are a group of neurological disorders that affect the structure or function of the brain or spinal cord, which collectively form the central nervous system (CNS). These disorders may be caused by such things as infection, injury, blood clots, age related degeneration, cancer, autoimmune disfunction, and birth defects. The symptoms vary widely, as do the treatments.

The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.
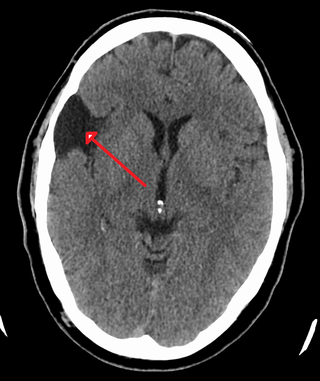
A central nervous system cyst is a type of cyst that presents and affects part of the central nervous system (CNS). They are usually benign and filled with either cerebrospinal fluid, blood, or tumor cells. CNS cysts are classified into two categories: cysts that originate from non-central nervous system tissue, migrate to, and form on a portion of the CNS, and cysts that originate within central nervous system tissue itself. Within these two categories, there are many types of CNS cysts that have been identified from previous studies.
Sally Temple is an American developmental neuroscientist in Albany, New York. She is a co-founder and scientific director for The Neural Stem Cell Institute and is a professor of Neuroscience and Neuropharmacology at Albany Medical College Temple is also the principal investigator in her laboratory that focuses on neural stem cells and therapies for neurological-related disorders

The Journal of Neurotrauma is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering research on neurotraumas. It is an official journal of the National Neurotrauma Society and the International Neurotrauma Society. The journal was established in 1984 and is published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. The editor-in-chief is David L. Brody, MD, PhD.
Neuralstem Inc. is a biotechnology company headquartered in Rockville, Maryland that specializes in developing commercial-scale production of multiple types of central nervous system stem cells. In October 2019 Neuralstem announces that the company has changed its name to Seneca Biopharma, Inc. In April 2021 Seneca Biopharma merged with Leading BioSciences to form the combined company Palisade Bio, Inc.
Jeffrey D. Macklis is an American neuroscientist. He is the Max and Anne Wien Professor of Life Sciences in the Department of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology and Center for Brain Science at Harvard University, Professor of Neurology [Neuroscience] at Harvard Medical School, and on the Executive Committee and a Member of the Principal Faculty of the Neuroscience / Nervous System Diseases Program at the Harvard Stem Cell Institute.













