Related Research Articles
Human cloning is the creation of a genetically identical copy of a human. The term is generally used to refer to artificial human cloning, which is the reproduction of human cells and tissue. It does not refer to the natural conception and delivery of identical twins. The possibilities of human cloning have raised controversies. These ethical concerns have prompted several nations to pass laws regarding human cloning.

A genetic chimerism or chimera is a single organism composed of cells with more than one distinct genotype. Animal chimeras can be produced by the merger of two embryos. In plants and some animal chimeras, mosaicism involves distinct types of tissue that originated from the same zygote but differ due to mutation during ordinary cell division.

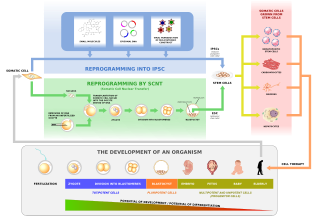
In genetics and developmental biology, somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is a laboratory strategy for creating a viable embryo from a body cell and an egg cell. The technique consists of taking a denucleated oocyte and implanting a donor nucleus from a somatic (body) cell. It is used in both therapeutic and reproductive cloning. In 1996, Dolly the sheep became famous for being the first successful case of the reproductive cloning of a mammal. In January 2018, a team of scientists in Shanghai announced the successful cloning of two female crab-eating macaques from foetal nuclei.
In philosophy and neuroscience, neuroethics is the study of both the ethics of neuroscience and the neuroscience of ethics. The ethics of neuroscience concerns the ethical, legal, and social impact of neuroscience, including the ways in which neurotechnology can be used to predict or alter human behavior and "the implications of our mechanistic understanding of brain function for society... integrating neuroscientific knowledge with ethical and social thought".

Leon Richard Kass is an American physician, scientist, educator, and public intellectual. Kass is best known as a proponent of liberal arts education via the "Great Books," as a critic of human cloning, life extension, euthanasia and embryo research, and for his tenure as chairman of the President's Council on Bioethics from 2001 to 2005. Although Kass is often referred to as a bioethicist, he eschews the term and refers to himself as "an old-fashioned humanist. A humanist is concerned broadly with all aspects of human life, not just the ethical."
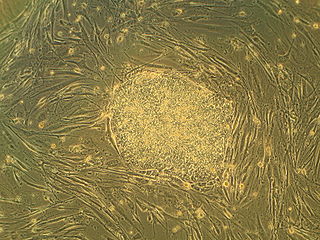
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre-implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells. Isolating the inner cell mass (embryoblast) using immunosurgery results in destruction of the blastocyst, a process which raises ethical issues, including whether or not embryos at the pre-implantation stage have the same moral considerations as embryos in the post-implantation stage of development.
The Dickey–Wicker Amendment is the name of an appropriation bill rider attached to a bill passed by United States Congress in 1995, and signed by former President Bill Clinton, which prohibits the United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) from using appropriated funds for the creation of human embryos for research purposes or for research in which human embryos are destroyed. HHS funding includes the funding for the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is named after Jay Dickey and Roger Wicker, two Republican Representatives. Technically, the Dickey Amendment is a rider to other legislation, which amends the original legislation. The rider receives its name from the name of the Congressman that originally introduced the amendment, Representative Dickey. The Dickey amendment language has been added to each of the Labor, HHS, and Education appropriations acts for fiscal years 1997 through 2009. The original rider can be found in Section 128 of P.L. 104–99.

A designer baby is a baby whose genetic makeup has been selected or altered, often to exclude a particular gene or to remove genes associated with disease. This process usually involves analysing a wide range of human embryos to identify genes associated with particular diseases and characteristics, and selecting embryos that have the desired genetic makeup; a process known as preimplantation genetic diagnosis. Screening for single genes is commonly practiced, and polygenic screening is offered by a few companies. Other methods by which a baby's genetic information can be altered involve directly editing the genome before birth, which is not routinely performed and only one instance of this is known to have occurred as of 2019, where Chinese twins Lulu and Nana were edited as embryos, causing widespread criticism.

Hwang Woo-suk is a South Korean veterinarian and researcher. He was a professor of theriogenology and biotechnology at Seoul National University until he was dismissed on March 20, 2006. He was considered a pioneering expert in stem cell research and even called the "Pride of Korea". However, he became infamous around November 2005 for fabricating a series of stem cell experiments that were published in high-profile journals, the case known as the Hwang affair.

A stem cell line is a group of stem cells that is cultured in vitro and can be propagated indefinitely. Stem cell lines are derived from either animal or human tissues and come from one of three sources: embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, or induced pluripotent stem cells. They are commonly used in research and regenerative medicine.

The stem cell controversy concerns the ethics of research involving the development and use of human embryos. Most commonly, this controversy focuses on embryonic stem cells. Not all stem cell research involves human embryos. For example, adult stem cells, amniotic stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells do not involve creating, using, or destroying human embryos, and thus are minimally, if at all, controversial. Many less controversial sources of acquiring stem cells include using cells from the umbilical cord, breast milk, and bone marrow, which are not pluripotent.
Stem cell research policy varies significantly throughout the world. There are overlapping jurisdictions of international organizations, nations, and states or provinces. Some government policies determine what is allowed versus prohibited, whereas others outline what research can be publicly financed. Of course, all practices not prohibited are implicitly permitted. Some organizations have issued recommended guidelines for how stem cell research is to be conducted.
Stem cell laws are the law rules, and policy governance concerning the sources, research, and uses in treatment of stem cells in humans. These laws have been the source of much controversy and vary significantly by country. In the European Union, stem cell research using the human embryo is permitted in Sweden, Spain, Finland, Belgium, Greece, Britain, Denmark and the Netherlands; however, it is illegal in Germany, Austria, Ireland, Italy, and Portugal. The issue has similarly divided the United States, with several states enforcing a complete ban and others giving support. Elsewhere, Japan, India, Iran, Israel, South Korea, China, and Australia are supportive. However, New Zealand, most of Africa, and most of South America are restrictive.
Stem cell laws and policy in the United States have had a complicated legal and political history.

Françoise Elvina BaylisFISC is a Canadian bioethicist whose work is at the intersection of applied ethics, health policy, and practice. The focus of her research is on issues of women's health and assisted reproductive technologies, but her research and publication record also extend to such topics as research involving humans, gene editing, novel genetic technologies, public health, the role of bioethics consultants, and neuroethics. Baylis' interest in the impact of bioethics on health and public policy as well as her commitment to citizen engagement]and participatory democracy sees her engage with print, radio, television, and other online publications.
Sir Richard Lavenham Gardner, FRSB, FRS is a British embryologist and geneticist. He is currently an Emeritus Professor at the University of York, and was previously a Royal Society Research Professor.
Human germline engineering is the process by which the genome of an individual is edited in such a way that the change is heritable. This is achieved by altering the genes of the germ cells, which then mature into genetically modified eggs and sperm. For safety, ethical, and social reasons, there is broad agreement among the scientific community and the public that germline editing for reproduction is a red line that should not be crossed at this point in time. There are differing public sentiments, however, on whether it may be performed in the future depending on whether the intent would be therapeutic or non-therapeutic.

S. Matthew Liao is a Taiwanese-American philosopher specializing in bioethics and normative ethics. Liao currently holds the Arthur Zitrin Chair of Bioethics, and is the Director of the Center for Bioethics and Affiliated Professor in the Department of Philosophy at New York University. He has previously held appointments at Oxford, Johns Hopkins, Georgetown, and Princeton.

The He Jiankui affair is a scientific and bioethical controversy concerning the use of genome editing following its first use on humans by Chinese scientist He Jiankui, who edited the genomes of human embryos in 2018. He became widely known on 26 November 2018 after he announced that he had created the first human genetically edited babies. He was listed in Time magazine's 100 most influential people of 2019. The affair led to ethical and legal controversies, resulting in the indictment of He and two of his collaborators, Zhang Renli and Qin Jinzhou. He eventually received widespread international condemnation.

The Hwang affair, or Hwang scandal, or Hwanggate, is a case of scientific misconduct and ethical issues surrounding a South Korean biologist, Hwang Woo-suk, who claimed to have created the first human embryonic stem cells by cloning in 2004. Hwang and his research team at the Seoul National University reported in the journal Science that they successfully developed a somatic cell nuclear transfer method with which they made the stem cells. In 2005, they published again in Science the successful cloning of 11 person-specific stem cells using 185 human eggs. The research was hailed as "a ground-breaking paper" in science. Hwang was elevated as "the pride of Korea", "national hero" [of Korea], and a "supreme scientist", to international praise and fame. Recognitions and honours immediately followed, including South Korea's Presidential Award in Science and Technology, and Time magazine listing him among the "People Who Mattered 2004" and the most influential people "The 2004 Time 100".
References
- ↑ Dennis, Carina (2002). "China: Stem cells rise in the East". Nature . 419 (6905): 334–6. Bibcode:2002Natur.419..334D. doi: 10.1038/419334a . PMID 12353004.
- ↑ "Regulations & Laws". Bioethics Network in China. 18 March 2007. Retrieved 24 April 2009.
- 1 2 3 Murray, Fiona; Spar, Debora (21 September 2006). "Bit Player or Powerhouse? China and Stem-Cell Research". The New England Journal of Medicine . 355 (12): 1191–4. doi:10.1056/NEJMp068151. PMID 16990381. Archived from the original on 25 June 2009. Retrieved 21 April 2009.
- ↑ Wang Yanguang (2003). "Chinese Ethical Views on Embryo Stem (ES) Cell Research". In Song, Sang-yong; Koo, Young-Mo; Darryl R.J. Macer (eds.). Asian Bioethics in the 21st Century . Retrieved 24 April 2009.