
Evolution is the change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. The process of evolution has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation.
The European Society for Evolutionary Biology (ESEB) was founded on 28 August 1987 in Basel (Switzerland), with ~ 450 evolutionary biologists attending the inaugural congress of the Society; Arthur Cain became the Society’s first president. The founding of the ESEB was closely linked to the launching of the Society’s journal, the Journal of Evolutionary Biology, with Stephen C. Stearns as the first Editor in Chief, and the first issue appearing in January 1988. See the editorial opening of the journal; see also Steve Stearns’ account of the early days of the ESEB.

George Christopher Williams was an American evolutionary biologist.
Evolutionary medicine or Darwinian medicine is the application of modern evolutionary theory to understanding health and disease. Modern biomedical research and practice have focused on the molecular and physiological mechanisms underlying health and disease, while evolutionary medicine focuses on the question of why evolution has shaped these mechanisms in ways that may leave us susceptible to disease. The evolutionary approach has driven important advances in the understanding of cancer, autoimmune disease, and anatomy. Medical schools have been slower to integrate evolutionary approaches because of limitations on what can be added to existing medical curricula. The International Society for Evolution, Medicine and Public Health coordinates efforts to develop the field. It owns the Oxford University Press journal Evolution, Medicine and Public Health and The Evolution and Medicine Review.
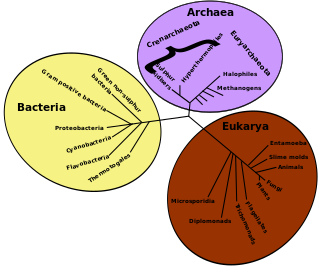
Evolutionary ecology lies at the intersection of ecology and evolutionary biology. It approaches the study of ecology in a way that explicitly considers the evolutionary histories of species and the interactions between them. Conversely, it can be seen as an approach to the study of evolution that incorporates an understanding of the interactions between the species under consideration. The main subfields of evolutionary ecology are life history evolution, sociobiology, the evolution of interspecific interactions and the evolution of biodiversity and of ecological communities.

Douglas Joel Futuyma is an American evolutionary biologist. He is a Distinguished Professor in the Department of Ecology and Evolution at Stony Brook University in Stony Brook, New York and a Research Associate on staff at the American Museum of Natural History in New York City. His research focuses on speciation and population biology. Futuyma is the author of a widely used undergraduate textbook on evolution and is also known for his work in public outreach, particularly in advocating against creationism.

Randolph Martin Nesse is an American physician, scientist and author who is notable for his role as a founder of the field of evolutionary medicine and evolutionary psychiatry.
Paul H. Harvey is a British evolutionary biologist. He is Professor of Zoology and was head of the zoology department at the University of Oxford from 1998 to 2011 and Secretary of the Zoological Society of London from 2000 to 2011, holding these posts in conjunction with a professorial fellowship at Jesus College, Oxford.

The Journal of Evolutionary Biology is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published monthly covering the field of evolutionary biology. It is owned by the European Society for Evolutionary Biology. The founding editor-in-chief was Stephen C. Stearns. He was succeeded by Pierre-Henri Gouyon (1992–1995), Rolf Hoekstra (1996–1999), Peter van Tienderen (2000–2003), Juha Merilä (2004–2007), Allen Moore (2007–2010), Michael G. Ritchie (2011-2017), and Wolf U. Blanckenhorn (2017-2021). The current editor is Max Reuter.
Marcus Thomas Pius Gilbert is an evolutionary biologist. His work is highly cited, and influential in the fields of palaeogenomics, evolutionary genomics and evolutionary hologenomics. He is currently the director of the University of Copenhagen's Center for Evolutionary Hologenomics.
Laurent Keller is a Swiss evolutionary biologist, myrmecologist and author. He was a professor at the University of Lausanne from 1996 to 2023. In March 2023, the journal Science reported that sexual harassment allegations were leveled against Keller. According to the Science article, the University of Lausanne sent an email to staff in February of 2023 to inform them that Laurent Keller no longer works there.

John Charles Avise is an American evolutionary geneticist, conservationist, natural historian, and prolific science author. He is an Emeritus Distinguished Professor of Ecology & Evolution, University of California, Irvine, and was previously a Distinguished Professor of Genetics at the University of Georgia.

Jeffrey Alexander Hutchings FRSC was a Canadian fisheries scientist. He was a professor of biology, and the Izaak Walton Killam Memorial Chair in Fish, Fisheries, and Oceans at Dalhousie University.

Godfrey Matthew Hewitt was a British professor and evolutionary geneticist at the University of East Anglia who was very influential in the development of the fields of molecular ecology, phylogeography, speciation and hybridisation.
Frederic Lawrence Holmes was an American historian of science, specifically of chemistry, medicine and biology. He was Avalon Professor of the History of Medicine at Yale University and was known for his work developing Yale's programs in history of science and medicine. His scholarship included notable studies of Claude Bernard, Antoine Lavoisier, Justus Liebig, Hans Adolf Krebs, Matthew Meselson, Franklin Stahl, and Seymour Benzer. He was awarded a George Sarton Medal for lifetime achievement in the history of science and served as a president of the History of Science Society.
Paul E. Turner is an American evolutionary biologist and virologist, the Rachel Carson Professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at Yale University, and a faculty member in microbiology at the Yale School of Medicine. His research focuses on the evolutionary genetics of viruses, particularly bacteriophages and RNA viruses transmitted by mosquitoes.
Loeske E. B. KruukFRS is an evolutionary ecologist who is a Royal Society Research Professor at the University of Edinburgh. She was awarded the 2018 European Society for Evolutionary Biology President's Award. In 2023, she was elected as a Fellow of the Royal Society.
Jessica Gurevitch is a plant ecologist known for meta-analysis in the fields of ecology and evolution.

C. Brandon Ogbunu(gafor) is an American computational biologist who is an Assistant Professor of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at Yale University, and an External Professor at the Santa Fe Institute. He uses experimental and computational tools to understand the causes of disease, ranging from molecular underpinnings to the social determinants of public health. In addition, he runs a parallel research program at the intersection between science and culture, where he explores the social forces that craft science, and how sciences influences society.

Bruce Smith Lieberman is an American paleontologist.












