
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy.
A computed tomography scan is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists.

Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In clinical practice, the distinction between lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis is rarely made and the words are usually treated as synonymous. Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels is known as lymphangitis. Infectious lymphadenitis affecting lymph nodes in the neck is often called scrofula.
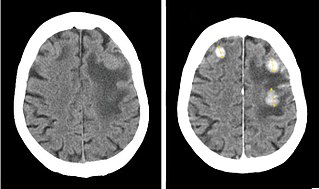
Iodinated contrast is a form of water-soluble, intravenous radiocontrast agent containing iodine, which enhances the visibility of vascular structures and organs during radiographic procedures. Some pathologies, such as cancer, have particularly improved visibility with iodinated contrast.

Gadopentetic acid, sold under the brand name Magnevist, is a gadolinium-based MRI contrast agent.

Dystroglycan is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DAG1 gene.
MRI contrast agents are contrast agents used to improve the visibility of internal body structures in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The most commonly used compounds for contrast enhancement are gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs). Such MRI contrast agents shorten the relaxation times of nuclei within body tissues following oral or intravenous administration.

Cholescintigraphy or hepatobiliary scintigraphy is scintigraphy of the hepatobiliary tract, including the gallbladder and bile ducts. The image produced by this type of medical imaging, called a cholescintigram, is also known by other names depending on which radiotracer is used, such as HIDA scan, PIPIDA scan, DISIDA scan, or BrIDA scan. Cholescintigraphic scanning is a nuclear medicine procedure to evaluate the health and function of the gallbladder and biliary system. A radioactive tracer is injected through any accessible vein and then allowed to circulate to the liver, where it is excreted into the bile ducts and stored by the gallbladder until released into the duodenum.

Angus George Dalgleish FRCP FRCPath FMedSci is a professor of oncology at St George's, University of London, best known for his contributions to HIV/AIDS research. Dalgleish stood in 2015 for Parliament as a UKIP candidate.

d-Deprenyl, also known as or dextro-N-propargyl-N-methylamphetamine, is an MAO-B inhibitor that metabolizes into d-amphetamine and d-methamphetamine and is therefore also a norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent. It is the opposite enantiomer of l-deprenyl (selegiline).

Contrast CT, or contrast enhanced computed tomography (CECT), is X-ray computed tomography (CT) using radiocontrast. Radiocontrasts for X-ray CT are generally iodine-based types. This is useful to highlight structures such as blood vessels that otherwise would be difficult to delineate from their surroundings. Using contrast material can also help to obtain functional information about tissues. Often, images are taken both with and without radiocontrast. CT images are called precontrast or native-phase images before any radiocontrast has been administered, and postcontrast after radiocontrast administration.
A giant virus, sometimes referred to as a girus, is a very large virus, some of which are larger than typical bacteria. All known giant viruses belong to the phylum Nucleocytoviricota.
Harmonic phase (HARP) algorithm is a medical image analysis technique capable of extracting and processing motion information from tagged magnetic resonance image (MRI) sequences. It was initially developed by N. F. Osman and J. L. Prince at the Image Analysis and Communications Laboratory at Johns Hopkins University. The method uses spectral peaks in the Fourier domain of tagged MRI, calculating the phase images of their inverse Fourier transforms, which are called harmonic phase (HARP) images. The motion of material points through time is then tracked, under the assumption that the HARP value of a fixed material point is time-invariant. The method is fast and accurate, and has been accepted as one of the most popular tagged MRI analysis methods in medical image processing.

Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy is a bilateral enlargement of the lymph nodes of pulmonary hila. It is a radiographic term for the enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes and is most commonly identified by a chest x-ray.
In the field of medicine, radiomics is a method that extracts a large number of features from medical images using data-characterisation algorithms. These features, termed radiomic features, have the potential to uncover tumoral patterns and characteristics that fail to be appreciated by the naked eye. The hypothesis of radiomics is that the distinctive imaging features between disease forms may be useful for predicting prognosis and therapeutic response for various cancer types, thus providing valuable information for personalized therapy. Radiomics emerged from the medical fields of radiology and oncology and is the most advanced in applications within these fields. However, the technique can be applied to any medical study where a pathological process can be imaged.

Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) are abnormal differences seen in magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in patients with Alzheimer's disease. ARIA is associated with amyloid-modifying therapies, particularly human monoclonal antibodies such as aducanumab. There are two types of ARIA: ARIA-E and ARIA-H. The phenomenon was first seen in trials of bapineuzumab.

An MRI sequence in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a particular setting of pulse sequences and pulsed field gradients, resulting in a particular image appearance.
Nola M. Hylton is an American oncologist who is Professor of Radiology and Director of the Breast Imaging Research Group at the University of California, San Francisco. She pioneered the usage of magnetic resonance imaging for the detection, diagnosis, and staging of breast cancer by using MRIs to locate tumors and characterize the surrounding tissue.
Spectral imaging is an umbrella term for energy-resolved X-ray imaging in medicine. The technique makes use of the energy dependence of X-ray attenuation to either increase the contrast-to-noise ratio, or to provide quantitative image data and reduce image artefacts by so-called material decomposition. Dual-energy imaging, i.e. imaging at two energy levels, is a special case of spectral imaging and is still the most widely used terminology, but the terms "spectral imaging" and "spectral CT" have been coined to acknowledge the fact that photon-counting detectors have the potential for measurements at a larger number of energy levels.

Gadopiclenol, sold under the brand name Elucirem among others, is a contrast agent used with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect and visualize lesions with abnormal vascularity in the central nervous system and in the body. Gadopiclenol is a paramagnetic macrocyclic non-ionic complex of gadolinium.













