Related Research Articles

The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) found in many animals.
In academia, computational immunology is a field of science that encompasses high-throughput genomic and bioinformatics approaches to immunology. The field's main aim is to convert immunological data into computational problems, solve these problems using mathematical and computational approaches and then convert these results into immunologically meaningful interpretations.
HLA-DP is a protein/peptide-antigen receptor and graft-versus-host disease antigen that is composed of 2 subunits, DPα and DPβ. DPα and DPβ are encoded by two loci, HLA-DPA1 and HLA-DPB1, that are found in the MHC Class II region in the Human Leukocyte Antigen complex on human chromosome 6 . Less is known about HLA-DP relative to HLA-DQ and HLA-DR but the sequencing of DP types and determination of more frequent haplotypes has progressed greatly within the last few years.
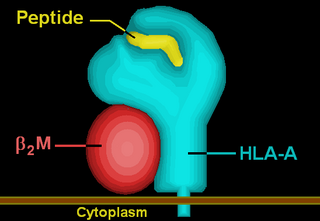
HLA-A is a group of human leukocyte antigens (HLA) that are encoded by the HLA-A locus, which is located at human chromosome 6p21.3. HLA is a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigen specific to humans. HLA-A is one of three major types of human MHC class I transmembrane proteins. The others are HLA-B and HLA-C. The protein is a heterodimer, and is composed of a heavy α chain and smaller β chain. The α chain is encoded by a variant HLA-A gene, and the β chain (β2-microglobulin) is an invariant β2 microglobulin molecule. The β2 microglobulin protein is encoded by the B2M gene, which is located at chromosome 15q21.1 in humans.
Immunogenetics or immungenetics is the branch of Medical Immunology and Medical Genetics that explores the relationship between the immune system and genetics.

HLA-A*02 (A*02) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within the HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of the α2 domain of the HLA-A α-chain. For A*02, the α chain is encoded by the HLA-A*02 gene and the β chain is encoded by the B2M locus. In 2010 the World Health Organization Naming Committee for Factors of the HLA System revised the nomenclature for HLAs. Before this revision, HLA-A*02 was also referred to as HLA-A2, HLA-A02, and HLA-A*2.
HLA-Cw*16 (Cw*16) is an HLA-C allele-group. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-Cw*16 gene products. This allele group is most commonly found in West Africa, but A single Haplotype of Cw16 is found in Western Europe at unusually high frequencies. There is no useful serology for Cw*16.

Transporter associated with antigen processing 1 (TAP1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAP1 gene. A member of the ATP-binding cassette transporter family, it is also known as ABCB2.
Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ alpha 1, also known as HLA-DQA1, is a human gene present on short arm of chromosome 6 (6p21.3) and also denotes the genetic locus which contains this gene. The protein encoded by this gene is one of two proteins that are required to form the DQ heterodimer, a cell surface receptor essential to the function of the immune system.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DP(W2) beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DPB1 gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DQ(6) alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DQA2 gene. Also known as HLA-DXA or DAAP-381D23.2, it is part of the human leucocyte antigen system.
HLA-B60 (B60) is an HLA - B serotype. B60 is a split antigen serotype that recognizes certain B40 serotypes.
HLA-B61 (B61) is an HLA - B serotype. B61 is a split antigen serotype that recognizes certain B40 serotypes.

Paul Ichiro Terasaki was an American scientist in the field of human organ transplant technology, and professor emeritus of surgery at UCLA School of Medicine.
The European Federation for Immunogenetics (EFI) is the European association of people with interests in the field of immunogenetics.
The HLA Informatics Group (HIG) is a research group led by Professor Steven Marsh at the Anthony Nolan Research Institute that develops, runs and maintains the IMGT (immunogenetics)/HLA Database and the IPD. The IMGT/HLA database originated as part of IMGT and was merged with IPD in 2003. The IMGT/HLA Database is a central repository for sequences of the human major histocompatibility complex and currently contains over 5,000 allele sequences, including over 1,800 HLA-B sequences.
Human Immunology is a peer-reviewed academic journal published by Elsevier. This journal features original research articles, review articles and brief communications on the subjects of immunogenetics, cellular immunology and immune regulation, and clinical immunology, and is the journal of the American Society for Histocompatibility and Immunogenetics (ASHI).

Lady Julia Gwynaeth Bodmer was a British geneticist and trained economist. Involved in the discovery and definition of the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system of genetic markers, Bodmer became one of the world's leading experts in HLA serology and the genetic definition of the HLA system. A prominent figure in the field of immunogenetics, her discoveries helped the understanding and development of knowledge about HLA associations with diseases including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and cancer. As well as being a distinguished scientist in her own right, she collaborated throughout her career with her husband, the human and cancer geneticist Sir Walter Bodmer. The couple had three children.

Narinder Kumar Mehra is an Indian immunologist, head of the department of transplant immunology and immunogenetics of the SRL Limited, Gurgaon. He is a former dean of research and holds the ICMR Dr. C.G. Pandit National Chair at AIIMS. An elected fellow of the International Medical Sciences Academy, The World Academy of Sciences, Indian National Science Academy and National Academy of Sciences, India, Mehra is known for his research on histocompatibility and immunogenetics. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Medical Sciences in 1992. He received the Chevalier of the National Order of Merit from François Mitterrand in 2003.
IMGT or the international ImMunoGeneTics information system is a collection of databases and resources for immunoinformatics, particularly the V, D, J, and C gene sequences, as well as a providing other tools and data related to the adaptive immune system. IMGT/LIGM-DB, the first and still largest database hosted as part of IMGT contains reference nucleotide sequences for 360 species' T-cell receptor and immunoglobulin molecules, as of 2023. These genes encode the proteins which are the foundation of adaptive immunity, which allows highly specific recognition and memory of pathogens.
References
- ↑ "UCL IRIS".
- ↑ "Nucleic Acids Research". Archived from the original on 2012-07-12.
- ↑ "BioNews - Race and genetics in stem cell transplantation".
- ↑ "Histocompatibility and immunogenetics". Anthony Nolan.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-04-25. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "IMGT Index". Archived from the original on 2012-04-25.
- ↑ [Immunoinformatics: predicting immunogenicity in silico - Page 44]
- ↑ [Immunoinformatics: bioinformatic strategies for better ...: Volume 254 - Page 170]